Abstract
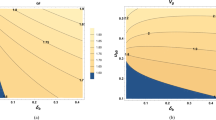
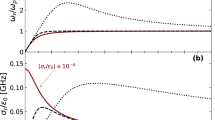
The effect of ion–neutral collisions on the propagation of MHD waves and surface waves at a single magnetic interface is investigated. The dispersion equations for MHD waves in a partially ionized medium are derived. There are three damped propagating modes in a uniform unbounded medium: an Alfvén mode, and fast and slow modes. The damping of waves depends on both the collisional frequency and the ionization fraction. Wave damping increases as ionization fraction decreases. Surface waves are discussed in three cases: (a) the incompressible limit, (b) the low β plasma, and (c) for parallel propagation. The incompressible limit leads to Alfvén surface waves in a partially ionized medium and the dispersion characteristics are similar to those obtained by Uberoi and Datta. In the low β plasma of the Earth's auroral F region there are two damped propagating magnetoacoustic surface waves for θ=π/3. There is only one damped surface mode for θ=π/2, but no surface wave is able to propagate for θ=0°. For the case of parallel propagation (θ=0°) the results obtained in the absence of ion-neutral collisions are consistent with the results of Jain and Roberts. It is found that a three-mode structure of damped propagating waves occurs owing to ion–neutral collisions for a comparatively high ionization fraction. For the case of the solar photosphere, where the ionization fraction is low, two weakly damped surface waves are found, though the damping is almost negligible. The pattern of propagation is similar to that found in the case discussed by Jain and Roberts, but the wave speeds are lower due to ion–neutral collisions. The strong collisions tie the ion–neutral species together and reduce the damping.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfvén, H.: 1954, On the Origin of Solar System, Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Amagishi, Y. and Tanaka, M.: 1993, Phys. Rev Lett.. 71, 360.
Amagishi, Y. and Tsushima, A.: 1984, Plasma Phys. Controlled Fusion 26, 1489.
Balsara, D. S.: 1996, Astrophys. J. 465, 775.
Basu, B. and Coppi, B.: 1989, J.Geophys. Res. 94, 5316.
Bhatia, P.K.: 1974, J.Plasma Phys. 11, 1.
Carvens, T. E.: 1986, in B. Battrick, E. J. Rolfe and R. Reinhard (eds.), Proc. 20th ESLAB Symposium on the Exploration of Halley's Comet Vol. 1, Publ. Div., ESTEC, Noordwijk, p. 241.
Ershkovich, A. I., McKenzie, J. F., and Axford, W. I.: 1989, Astrophys. J. 344, 932.
Hoh, F. C.: 1963, Phys. Fluids 6, 1184.
Ip, W. H. and Axford, W.I.: 1987, Nature 325, 418.
Jain, R. and Roberts, B.: 1991, Solar Phys. 133, 263.
Kulsrud, R. and Pearce, W. P.: 1969, Astrophys. J. 156, 445.
Kumar, N. and Srivastava, K. M.: 1998, J. Plasma Phys. 60, 731.
Lehnert, B.: 1959, Suppl. Nuovo Cimento 13, 59.
Lehnert, B.: 1960, Arkiv Physik 18, 251.
Lehnert, B.: 1968, Nucl. Fusion 8, 173.
Lehnert, B.: 1972a, Electron. and Plasma Phys. Roy. Inst. of Tech., Stockholm, Rep. TRITA-EPP-72-05.
Lehnert, B.: 1972b, Electron. and Plasma Phys. Roy. Inst. of Tech., Stockholm, Rep. TRITA-EPP-72-06.
Lehnert, B.: 1972c, Proc. Fifth European Conf. on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Phys., Grenoble, p. 32.
Maheshwari, S. L. and Bhatia, P. K.: 1978, J. Plasma Phys. 19, 83.
Martin, C. E., Heyvaerts, J., and Priest, E. R.: 1997, Astron. Astrophys. 326, 1176.
Miles, A. J. and Roberts, B.: 1989, Solar Phys. 119, 257.
Muller, G.: 1974, Plasma Phys. 16, 813.
Myers, P. C. and Goodman, A.: 1988, Astrophys. J. 326, L27.
Piddington, J. H.: 1954a, Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 14, 638.
Piddington, J. H. 1954b, Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 14, 651.
Pudritz, R. E.: 1990, Astrophys. J. 350, 195.
Roberts, B.: 1981, Solar Phys. 69, 27.
Roberts, B.: 1991, in E. R. Priest and A. W. Hood (eds.), Advances in Solar System Magnetohydrodynamics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Shukla, P. K., Mirza, A. M., and Faria, R. T., Jr.: 1998, J. Geophys. Res., 103, 9417.
Simon, A.: 1963, Phys. Fluids 6, 382.
Suzuki, M. and Sakai, J.I.: 1996, Astrophys. J. 465, 393.
Swanson, D. G.: 1989, Plasma Waves, Academic Press, New York.
Uberoi, C. and Datta, A.: 1998, Phys. Plasmas 5, 4149.
Wentzel, D. G.: 1979, Astrophys. J. 227, 319.
Zweibel, E. G.: 1989, Astrophys. J. 340, 550.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N., Roberts, B. ION–Neutral Collisions Effect on MHD Surface Waves. Solar Physics 214, 241–266 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024299029918
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024299029918