Abstract
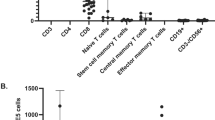
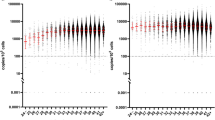
X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome (XHIM) is a severe congenital immunodeficiency caused by mutations in CD154 (CD40 ligand, gp39), the T cell ligand for CD40 on B cells. Chronic or cyclic neutropenia is a frequent complicating feature that heightens susceptibility to severe infections. We describe a patient with a variant of XHIM who produced elevated levels of serum IgA as well as IgM and suffered from chronic severe neutropenia. Eight of ten leukocyte transfusions with cells from a maternal aunt, performed because of mucosal infections, resulted in similar episodes of endogenous granulocyte production. Transfection studies with the mutant CD154 protein indicate that the protein is expressed at the cell surface and forms an aberrant trimer that does not interact with CD40. The data suggest that allogeneic cells from the patient's aunt, probably activated T cells bearing functional CD154, may interact with CD40+ recipient cells to produce maturation of myeloid precursors in the bone marrow.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Allen RC, Armitage RJ, Conley ME, Rosenblatt H, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Bedell MA, Edelhoff S, Disteche CM, Simoneaux DK, Fanslow WC, Belmont J, Spriggs MK: CD40 ligand gene defects responsible for X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome. Science 259:990–993, 1993
Fuleihan R, Ramesh N, Loh R, Jabara H, Rosen FS, Chatila T, Fu SM, Stamenkovic I, Geha RS: Defective expression of the CD40 ligand in X chromosome-linked immunoglobulin deficiency with normal or elevated IgM. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:2170–2173, 1993
Aruffo A, Farrington M, Hollenbaugh D, Milatovich A, Nonoyama S, Bajorath J, Grosmaire LS, Stenkamp R, Neubauer M, Roberts RL, Noelle RJ, Ledbetter JA, Francke U, Ochs HD: The CD40 ligand, gp39, is defective in activated T cells from patients with X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome. Cell 72:291–300, 1993
DiSanto JP, Bonnefoy JY, Gauchat JF, Fischer A, de Saint Basile G: CD40 ligand mutations in x-linked immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM. Nature 361:541–543, 1993
Notarangelo LD, Duse M, Ugazio AG: Immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM (HIM). Immunodef Rev 3:101–122, 1992
Levy J, Espanol-Boren T, Thomas C, Fischer A, Tovo P, Bordigoni P, Resnick I, Fasth A, Baer M, Gomez L, Sanders EAM, Tabone M-D, Plantaz D, Etzioni A, Monafo V, Abinun M, Hammarstrom L, Abrahamsen T, Jones A, Finn A, Klemola T, DeVries E, Sanal O, Peitsch MC, Notarangelo LD: Clinical spectrum of X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome. J Pediatr 131:47–54, 1997
Simon G, Marodi L: Successful treatment of cyclic neutropenia associated with hyperimmunoglobulin M syndrome using recombinant granulocyte-colony stimulating factor. Orvosi Hetilap 136:2169–2172, 1995
Wang WC, Cordoba J, Infante AJ, Conley ME: Successful treatment of neutropenia in the hyper-immunoglobulin M syndrome with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Am J Pediatr Hematol-Oncol 16:160–163, 1994
Levitt D, Haver P, Rich K, Cooper MD: Hyper IgM immunode-ficiency. A primary dysfunction of B lymphocyte isotype switching. J Clin Invest 72:1650–1657, 1983
Kyong CU, Virella G, Fudenberg HH: X-linked immunodeficiency with increased IgM: Clinical, ethnic, and immunologic heterogeneity. Pediatr Res 12:1024–1026, 1978
Liu Y, Phelan J, Go RC, Prchal JF, Prchal JT. Rapid determination of clonality by detection of two closely-linked X chromosome exonic polymorphisms using allele-specific PCR. J Clin Invest 99:1984–1990, 1997
Watson J: Continuous proliferation of murine antigen-specific helper T lymphocytes in culture. J Exp Med 150:1510–1519, 1979
Everson MP, Spalding DM, Koopman WJ: Enhancement of IL-2-induced T cell proliferation by a novel factor(s) present in murine spleen dendritic cell-T cell culture supernatants. J Immunol 142:1183–1194, 1989
Bensinger WI, Price TH, Dale DC, Appelbaum FR, Clift R, Lilleby K, Williams B, Storb R, Thomas ED, Buckner CD: The effects of daily recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administration on normal granulocyte donors undergoing leukapheresis. Blood 81:1883–1888, 1993
Odum N, Kanner SB, Ledbetter JA, Svejgaard A: MHC class II molecules deliver costimulatory signals in human T cells through a functional linkage with IL-2-receptors. J Immunol 150:5289–5298, 1993
Spriggs MK, Armitage RJ, Strockbine L, Clifford KN, Macduff BM, Sato TA, Maliszewski CR, Fanslow WC: Recombinant human CD40 ligand stimulates B cell proliferation and immunoglobulin E secretion. J Exp Med 176:1543–1550, 1992
Hsu YM, Lucci J, Su L, Ehrenfels B, Garber E, Thomas D: Heteromultimeric complexes of CD40 ligand are present on the cell surface of human T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 272:911–915, 1997
Karpusas M, Hsu YM, Wang JH, Thompson J, Lederman S, Chess L, Thomas, D. 2 A crystal structure of an extracellular fragment of human CD40 ligand. Structure 3:1031–1039, 1995
Hess S, Kurrle R, Lauffer L, Riethmuller G, Engelmann H: A cytotoxic CD40/p55 tumor necrosis factor receptor hybrid detects CD40 ligand on herpesvirus saimiri-transformed T cells. Eur J Immunol 25:80–86, 1995
Pietravalle F, Lecoanet-Henchoz S, Blasey H, Aubry JP, Elson G, Edgerton MD, Bonnefoy JY, Gauchat JF: Human native soluble CD40L is a biologically active trimer, processed inside microsomes. J Biol Chem 271:5965–5967, 1996
Renshaw BR, Fanslow WC, 3rd, Armitage RJ, Campbell KA, Liggitt D, Wright B, Davison BL, Maliszewski CR: Humoral immune responses in CD40 ligand-deficient mice. J Exp Med 180:1889–1900, 1994
Fikrig E, Barthold SW, Chen M, Grewal IS, Craft J, Flavell RA. Protective antibodies in murine Lyme disease arise independently of CD40 ligand. J Immunol 157:1–3, 1996
Borrow P, Tishon A, Lee S, Xu J, Grewal IS, Oldstone MB, Flavell RA: CD40L-deficient mice show deficits in antiviral immunity and have an impaired memory CD8+ CTL response. J Exp Med 183:2129–2142, 1996
Bajorath J, Seyama K, Nonoyama S, Ochs HD, Aruffo A: Classification of mutations in the human CD40 ligand, gp39, that are associated with X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome. Protein Sci 5:531–534, 1996
Peitsch MC, Jongeneel CV: A 3-D model for the CD40 ligand predicts that it is a compact trimer similar to the tumor necrosis factors. Int Immunol 5:233–238, 1993
Foy TM, Aruffo A, Bajorath J, Buhlmann JE, Noelle RJ: Immune regulation by CD40 and its ligand GP39. Annu Rev Immunol 14:591–617, 1996
Ostenstad B, Giliani S, Mellbye OJ, Nilsen BR, Abrahamsen T: A boy with X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome and natural killer cell deficiency. Clin Exp Immunol 107:230–234, 1997
Caux C, Massacrier C, Vanbervliet B, Dubois B, van Kooten C, Durand, I, Banchereau J: Activation of human dendritic cells through CD40 cross-linking. J Exp Med 180:1263–1272, 1994
Kozlowski C, Evans DI: Neutropenia associated with X-linked agammaglobulinaemia. J Clin Pathol 44:388–390, 1991
Farrar JE, Rohrer J, Conley ME: Neutropenia in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 81:271–276, 1996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atkinson, T.P., Smith, C.A., Hsu, YM. et al. Leukocyte Transfusion-Associated Granulocyte Responses in a Patient with X-Linked Hyper-IgM Syndrome. J Clin Immunol 18, 430–439 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023286807853
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023286807853