Abstract
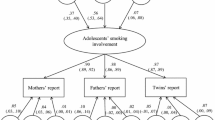
Not much is known about the genetic and environmental determinants of various aspects of substance use in adolescents. This study examined whether the inheritance of initiation of tobacco use in adolescents is independent of the inheritance of the number of cigarettes smoked. Alternative multifactorial threshold models were applied to data on tobacco use in 1676 Dutch adolescent twin pairs. The three models that were considered are (i) the single liability dimension model, (ii) the independent liability dimension model, and (iii) the combined model (CM). The results showed that there is not one underlying continuum of liability to smoking. The CM was the best-fitting model. This model postulates that there are separate initiation and quantity dimensions but allows for the possibility that there are some individuals who are so low on the liability to level of consumption that they are not using tobacco. There were no differences between males and females in the magnitude of the genetic and environmental influences on individual differences in smoking initiation and quantity smoked. Smoking initiation was influenced by genetic factors (39%) and shared environmental influences (54%). Once smoking is initiated genetic factors determine to a large extent (86%) the quantity that is smoked.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abraham, M. D., Cohen, P. D. A., van Til, R., and de Winter, M. A. L. (1999). Licit and Illicit Drug Use in The Netherlands, 1997, CEDRO Centrum Voor Drugsonderzoek, Universiteit van Amsterdam, Amsterdam.
Boomsma, D. I., Koopmans, J. R., van Doornen, L. J. P., and Orlebeke, J. F. (1994). Genetic and social influences on starting to smoke: A study of Dutch adolescent twins and their parents. Addiction 89:219-226.
Collins, A. C., and Marks, M. J. (1991). Progress towards the development of animal related models of smoking-related behaviors. J. Addict. Dis. 10:109-126.
Eaves, L. J. (1977). Inferring the causes of human variation. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. Ser. A 140:324-355.
Falconer, D. S. (1989). Introduction to Quantitative Genetics, 3rd ed., Longman Group, Essex.
Gilbert, D. G. (1995). Smoking: Individual Differences, Psychopathology and Emotion, Taylor and Francis, Washington, DC.
Goldsmith, H. H. (1991). A zygosity questionnaire for young twins: A research note. Benet. Genet. 21:257-270.
Han, C., McGue, M. K., and Iacono, W. G. (1999). Lifetime tobacco, alcohol and other substance use in adolescent Minnesota twins: Univariate and multivariate behavioral genetic analyses. Addiction 94:981-993.
Heath, A. C. (1995). Genetic influences on drinking behavior in humans. In Begleiter, H., and Kissin, B. (eds.), Alcohol and Alcoholism, Vol 1. Genetic Factors and Alcoholism, Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 82-121.
Heath, A. C., and Madden, P. A. F. (1995). Genetic influences on smoking behavior. In Turner, J. R., Cardon, L. R., and Hewitt, J. K. (eds.), Behavior Genetic Approaches in Behavioral Medicine, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 45-65.
Heath, A. C., and Martin, N. G. (1988). Teenage alcohol use in the Australian Twin Register: Genetic and social determinants of starting to drink. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 12:735-741.
Heath, A. C., and Martin, N. G. (1993). Genetic models for the natural history of smoking: Evidence for a genetic influence on smoking persistence. Addict. Behav. 18:19-34.
Heath, A. C., Meyer, J., Eaves, L. J., and Martin, N. G. (1991a). The inheritance of alcohol consumption patterns in a general population twin sample: I. Multidimensional scaling of quantity/frequency data. J. Stud. Alcohol 52:345-351.
Heath, A. C., Meyer, J., Jardine, R., and Martin, N. G. (1991b). The inheritance of alcohol consumption patterns in a general population twin sample: II. Determinants of consumption frequency and quantity consumed. J. Stud. Alcohol 52:425-433.
Hopper, J. L., White, V. M., Macaskill, G. T., and Hill, D. J. (1992). Alcohol use, smoking habits and the Junior Eysenck Personality Questionnaire in adolescent Australian twins. Acta Genet. Med. Gemmellol. Twin Res. 41:311-324.
Johnston, L. D., O'Malley, P. M., and Bachman, J. G. (1998). National Survey Results from the Monitering the Future Study, 1975–1997, Vol. 1. Secondary School Students, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD.
Kendler, K. S., Gardner, C., and Prescott, C. A. (1997). Religion, psychopathology and substance use and abuse: A multi-measure, genetic-epidemiologic study. Am. J. Psychiatry 154: 322-329.
Kendler, K. S., Neale, M. C., Sullivan, P. F., Corey, L. A., Gardner, C. O., and Prescott, C. A. (1999). A population-based twin study in women of smoking initiation and nicotine dependence. Psychol. Med. 29:299-308.
Koopmans, J. R. (1997). The Genetics of Health-Related Behaviors. A Study of Adolescent Twins and Their Parents, Thesis, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam.
Koopmans,. J. R., and Boomsma, D. I. (1996). Familial resemblances in alcohol use: Genetic or cultural transmission? J. Stud. Alcohol 57:19-28.
Koopmans, J. R., Boomsma, D. I., Heath, A. C., and van Doornen, L. J. P. (1995). A Multivariate genetic analysis of sensation seeking. Behav. Genet. 25:349-356.
Koopmans, J. R., van Doornen, L. J. P., and Boomsma, D. I. (1997). The association between alcohol use and smoking in adolescent and young adult twins: A bivariate genetic analysis. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 21(3):537-546.
Maes, H. M., Woodard, C. E., Murrelle, L., Meyer, J. M., Silberg, J. L., Hewitt, J. K., Rutter, M., Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Carbonneau, R., Neale, M. C., and Eaves, L. J. (1999). Tobacco, alcohol and drug use in eight-to sixteen-year-old twins: The Virginia Twin Study of Adolescent Behavioral Development. J. Stud. Alcohol 60:293-305.
Magnus, P., Berg, K., and Nance, W. E. (1983). Predicting zygosity in Norwegian twin pairs born 1915–1960. Clin. Genet. 24:103-112.
McGue, M., Sharma, A., and Benson, P. (1996). Parent and sibling influences on adolescent alcohol use and misuse: Evidence from a U.S. adoption cohort. J. Stud. Alcohol 57(1):8-18.
Neale, M. C. (1995). Mx: Statistical Modeling, 3rd ed., Department of Psychiatry, Box 710 MCV, Richmond, VA23298.
Neale, M. C., and Cardon, L. R. (1992). Methodology for Genetic Studies of Twins and Families, Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht.
Neale, M. C., Eaves, L. J., Kendler, K. S., and Hewitt, J. K. (1989). Bias in correlations from selected samples of relatives: The effects of soft selection. Behav. Genet. 19:163-169.
Office of Applied Studies (1999). National Household Survey on Drug Abuse: Main Findings 1997, Department of Health and Human Services, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
Pianezza, M. L., Sellers, E. M., and Tyndale, R. F. (1998). Nicotine metabolism defect reduces smoking. Nature 393:750.
Pomerleau. (1995). Individual differences in sensitivity to nicotine: Implications for genetic research on nicotine dependence. Behav. Genet. 25(2):161-177.
Rietveld, M. J. H., Koopmans, J. R., Maes, H. H., and Boomsma, D. I. (1996). Genetic and environmental influences on alcohol use and smoking by maternal religious involvement in Dutch adolescent twins. Behav. Genet. 26(6):595 (abstract).
True, W. R., Heath, A. C., Scherrer, J. F., Waterman, B., Goldberg, J., Lin, N., Eisen, S. A., Lyons, M. J., and Tsuang, M. T. (1997). Genetic and environmental contributions to smoking. Addiction 92(10):1277-1287.
Urberg, K. A., Degirmencioglu, S. M., and Pilgrim, C. (1997). Close friend and group influence on adolescent cigarette smoking and alcohol use. Dev. Psychol. 33(5):834-844.
World Health Organization (1997). Tobacco or Health: A Global Status Report, WHO, Geneva.
Zuckerman, M. (1994). Behavioral Expressions and Biosocial Bases of Sensation Seeking, Cambridge University Press, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koopmans, J.R., Slutske, W.S., Heath, A.C. et al. The Genetics of Smoking Initiation and Quantity Smoked in Dutch Adolescent and Young Adult Twins. Behav Genet 29, 383–393 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021618719735
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021618719735