Abstract
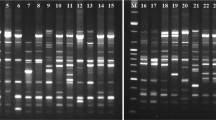
There is an urgent need for the developmentof early identification techniques inolive-trees due to the economic importanceof cultivar identification in periods ofexpansion like now. We have been able toidentify 22 olive-tree cultivars using only10 different, specific, repeatable markers.These markers were designed by the cloningof significant RAPD bands obtained in PCRperformed on bulked DNA to retain thegenetic variability of each cultivar.Clones were partially or totally sequencedand new primers derived from thesesequences were used to obtain SequenceCharacterised Amplified Region (SCAR)fragments. We have demonstrated that theuse of the 10 SCAR markers is enough toprovide a simple, cheap, and reliableprocedure to identify 22 geographicallyrelated olive-tree cultivars.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam-Blondon, A.F., M. Sevignac, H. Bannerot & M. Dron, 1998. SCAR, RAPD and RFLP markers linked to a dominant gene (Are) conferring resistance to anthracnose in common bean. Theor Appl Genet 88: 865-870.
Besnard, G., P. Baradat & A. Berville, 2001. Genetic relationships in the olive (Olea europaea L.) reflect multilocal selection of cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 102: 251-258.
Bewsey, K.E., J.P. Huff & M.E. Johnson, 1991. Rapid isolation and purifiation from agarose gels: the phenol-freeze-fracture method. Biotechniques 10: 724-725.
Bodénès, C., S. Joandet, F. Laigret & A. Kremer, 1997. Detection of genomic regions differentiating two closely related oak species Quercus petraea (Matt.) and Quercus robur L. Heredity 78: 433-444.
Claros, M.G., R. Crespillo, M.L. Aguilar & F.M. Cánovas, 2000. DNA fingerprinting and classification of geographically related genotypes of olive-tree (Olea europaea L.). Euphytica 116: 131-142.
Dulson, J., L.S. Kott & V.L. Ripley, 1998. Efficacy of bulked DNA samples for RAPD DNA fingerprinting of genetically complex Brassica napus cultivars. Euphytica 102: 65-70.
Fabbri, A., J.I. Hormaza & V.S. Polito, 1995. Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis of olive (Olea europaea L.) cultivars. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 120: 538-542.
Gemas, V.J., M.J. Rijo-Johansen, R. Tenreiro & P. Fevereiro, 2000. Inter-varietal and intra-varietal analysis of 3 Olea europaea L. cultivars using the RAPD technique. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 75: 312-319.
Gu, W.K., N.F. Weeden, J. Wu & D.H. Wallace, 1995. Large-scale, cost-effective screening of PCR products in marker assisted selection applications. Theor Appl Genet 91: 465-470.
Jones, C.J., K.J. Edwards, S. Castaglione, M.O. Winfield, F. Sala, C. van de Wiel, G. Bredemeijer, B. Vosman, M. Matthes, A. Daly, R. Brettschneider, P. Bettini, M. Buiatti, E. Maestri, A. Malcevschi, N. Marmiroli, R. Aert, G. Volckaert, J. Rueda, R. Linacero, A. Vázquez & A. Karp, 1997. Reproducibility testing of RAPD, AFLP and SSR markers in plants by a network of European laboratories. Mol Breeding 3: 381-390.
Kasai, K., Y. Morikawa, V.A. Sorri, J.P.T. Valkonen, C. Gebhardt & K.N. Watanabe, 2000. Development of SCAR markers to the PVY resistance gene Ryadg based on a common feature of plant disease resistance genes. Genome 43: 1-8.
Konieczny, A. & F.M. Ausubel, 1993. A procedure for mapping Arabidopsis mutations using codominant ecotype-specific PCRbased markers. Plant J 4: 403-410.
Lawson, W.R., K.C. Goulter, R.J. Henry, G.A. Kong & J.K. Kochman, 1998. Marker-assisted selection for two rust resistance genes in sunflower. Mol Breeding 4: 227-234.
Massei, G. & S.E. Hartley, 2000. Disarmed by domestication? Induced responses to browsing in wild and cultivated olive. Oecologia 122: 225-231.
McGregor, C.E., C.A. Lambert, M.M. Greyling, J.H. Louw & L. Warnich, 2000. A comparative assessment of DNA fingerprinting techniques (RAPD, ISSR, AFLP and SSR) in tetraploid potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) germplasm. Euphytica 113: 135-144.
Mekuria, G.T., G.G. Collins & M. Sedgley, 1999. Genetic variability between different accessions of some common commercial olive cultivars. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 74: 309-314.
Moury, B., S. Pflieger, A. Blattes, V. Lefebvre & A. Palloix, 2000. A CAPS marker to assist selection of tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) resistance in pepper. Genome 43: 137-142.
Murray, M. & W.F. Thompson, 1980. Rapid isolation of high molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8: 4321-4325.
Naqvi, N.I. & B.B. Chatoo, 1996. Development of a sequence characterized amlified region (SCAR) based indirect selection method for a dominant blast-resistance gene in rice. Genome 39: 26-30.
Negi, M.S., M. Devic, M. Delseny & M. Lakshmikumaran, 2000. Identification of AFLP fragments linked to seed coat color in Brassica juncea and conversion to a SCAR marker for rapid selection. Theor Appl Genet 101: 146-152.
Page, R.D.M., 1996. TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Applic Biosci 12: 357-358.
Paran, I. & R.W. Michelmore, 1993. Development of reliable PCR-based markers linked to downy mildew resistance genes in lettuce. Theor Appl Genet 85: 985-993.
Parasnis, A.S., V.S. Gupta, S.A. Tamhankar & P.K. Ranjekar, 2000. A Highly Reliable Sex Diagnostic PCR Assay for Mass-Screening of Papaya Seedlings. Mol Breeding 6: 337-344.
Ruas, P.M., A. Bonifacio, C.F. Ruas, D.J. Fairbanks & W.R. Andersen, 1999. Genetic relationship among 19 accessions of six species of Chenoposium L. by Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA fragments (RAPD). Euphytica 105: 25-32.
Sanz-Cortés, F., M.L. Badenes, S. Paz, A. Iñiguez & G. Llacer, 2001. Molecular Characterization of Olive Cultivars Using RAPD Markers. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 126: 7-12.
Shah, M.m., Y. Yen, K.S. Gill & P.S. Baezinger, 2000. Comparisons of RFLP and PCR-based markers to detect polymorphism between wheat cultivars. Euphytica 114: 135-142.
Strimmer, K. & A. von Haeseler, 1996. Quartet-puzzling: a quartet maximum-likelihood method for reconstructing tree topologies. Mol Biol Evol 13: 964-969.
Vanichanon, A., N.K. Blake, J.M. Martin & L.E. Talbert, 2000. Properties of sequence-tagged-site primer sets influencing repeatability. Genome 43: 47-52.
Vergari, G., M. Patumi & G. Fontanazza, 1996. Utilización de los marcadores RAPDs para la caracterización del germoplasma de olivo. Olivae 60: 19-22.
Wiesman, Z., N. Avidan, S. Lavee & B. Quebedeaux, 1998. Molecular characterization of common olive varieties in Israel and the West-Bank using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 123: 837-841.
Williams, J.G.K., M.K. Hanafey, J.A. Rafalski & S.V. Tingey, 1993. Genetic analysis using random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Methods Enzymol 218: 704-740.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bautista, R., Crespillo, R., Cánovas, F.M. et al. Identification of olive-tree cultivars with SCAR markers. Euphytica 129, 33–41 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021528122049
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021528122049