Abstract
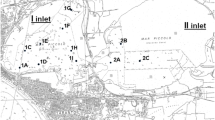
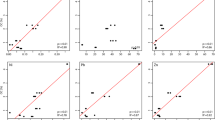
The release, bio-availability and toxicity of contaminants, when sediments are resuspended have been examined, studying concurrently their effects on the embryogenesis and on the larval growth of the Crassostrea gigas larvae and their bio-accumulation in those organisms. Three characteristic sediments have been selected (one contaminated by PAHs, a second by heavy metals and the last by the both pollutants). The organisms were directly exposed to elutriates obtained from each sediment or fed on algae (Isochrysis galbana) contaminated with the same elutriates. The elutriates used in this study show contamination levels similar to those observed in some polluted coastal and estuary environments. The larval growth test has appeared to be more sensitive that the embryotoxicity test. The biological effects and the contaminant bio-accumulation were more pronounced when larvae were directly exposed to different elutriates. In the case of PAHs, the contamination of algae was sufficient to lead to effect on the larval growth of the Crassostrea gigas. In all cases, a fraction of contaminants adsorbed on suspended particles was bio-available and accumulated by the larvae. This study has shown that resuspending polluted sediments constitutes a threat to pelagic organisms and than the C. gigas larval growth may be proposed as a test to protect the most sensitive areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ankley, G.T., Erickson, R.J., Phipps, G.L., Mattson, V.R., Kosian, P.A., Sheddy, B.R. and Cox, J.R. (1995). Effects of light intensity on the phototoxicity of fluoranthene to a benthic macroinvertebrate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 29, 2828–33.
Aminot, A. and Chaussepied, M. (1983). Manuel des analyses chimiques en milieu Marin. CNEXO, BNDO/Documentation Brest, 395pp.
Baldwin, B.S. and Newell, R.I.E. (1995). Relative importance of different size food particles in the natural diet of oyster larvae (Crassostrea virginica). Mar. Ecol.—Prog. Series 120, 135–45.
Baumard, P. (1997). Biogéochimie des composés aromatiques dans l'environnement marin. Thesis, University of Bordeaux I, Bordeaux France (290p).
Baumard, P. and Budzinski, H. (1997). Internal standard quantification method and gas chromatography—mass spectrometry (GS-MS): a reliable tool for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) quantification in natural matrices. Analusis 25, 246–52.
Baumard, P., Budzinski, H. and Garrigues, P. (1998). PAHs in Arcachon Bay, France: origin and biomonitoring with caged organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 36, 577–86.
Borgmann, U. (2000). Methods for assessing the toxicological significance of metals in aquatic ecosystems: bioaccumulation-toxicity relationships, water concentrations and sediment spiking approaches. Aquat. Ecosys. Health and Management 3, 277–89.
Brereton, A., Lord, H., Thornton, I. and Webb, J.S. (1973). Effect of zinc on growth and development of larvae of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Mar. Biol. 19, 96–101.
Budzinski, H., Papineau, A., Baumard, P. and Garrigues, P. (1995). Extraction assistée par chauffage microondes focalisées (MOF) à pression ambiante des composés organiques dans les matrices naturelles: application à l'analyse des composés aromatiques. Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences de Paris 321 (série IIb), 69–76.
Burgess, M. and Scott, K.J. (1992). The significance of in-place contaminated marine sediments on the water column: processes and effects. In G.A. Burton, Jr (ed.). Sediment Toxicity Assessment, pp. 129–65. London: Lewis Publishers.
Burgess, R.M., Schweitzer, K.A., McKinney, R.A. and Phelps, D.K. (1993). Contaminated marine sediment: water column and interstitial toxic effect. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12, 127–38.
Burton, G.A. (1992). Sediment Toxicity Assessment. 211p. London: Lewis Publishers.
Campanella, L., Conti, M.E., Cubadda, F. and Sucapane, C. (2001). Trace metals in seagrass, algae and molluscs from an uncontaminated area in the Mediterranean. Environ. Pollut. 111, 117–26.
Carr, R.S., Williams, J.W. and Fragata, C.T.B. (1989). Development and evaluation of a novel marine sediment pore water toxicity test with polychaete. Dinophilus gyrociliatus. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 8, 533–43.
Chapman, P.M. and Long, E.R. (1983). The use of bioassays as part of a comprehensive approach to marine pollution assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 14, 81–4.
Chapman, P.M. and Morgan, J.D. (1983). Sediment bioassays with oyster larvae. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 31, 438–44.
Chapman, P.M., Wang, F., Janssen, C., Persoone, G. and Allen, H.E. (1998). Ecotoxicology of metals in aquatic sediments: binding and release, bioavailability, risk assessment, and remediation. Canadian J. Fisheries Aquat. Sci. 55, 2212–43.
Ciarelli, S., Kater, B.J. and Van Straalen, N.M. (2000). Influence of bioturbation by the amphipod Corophium volutator on fluoranthene uptake in the marine polychaete Nereis virens. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 19(6), 1575–81.
Ciarelli, S., Van Straalen, N.M., Klap, V.A. and Van Wezel, A.P. (1999). Effects of sediment bioturbation by estuarine amphipod Corophium volutator on fluoanthene resuspension and transfert into the mussel (Mytilus edulis). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 18, 218–328.
Connell, D.W., Chaisuksant, Y. and Yu, J. (1999). Importance of internal biotic concentrations in risk evaluations with aquatic systems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 39, 54–61.
Danielsson, L.G., Magnusson, B., Westerlund, S. and Zhang, K. (1982). Trace metal determinations in estuarine waters by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry after extraction of dithiocarbamate complexes into freon. Analyt. Chim. Acta. 144, 183–8.
Davenport, R. and Spacie, A. (1991). Acute photoxicity of harbor and tributary sediments from lower Lake Michegan. J. Great Lakes Res. 17, 51–6.
Ettajani, H. (1994). Transfert des éléments traces essentiels ou toxiques dans la chaîne trophique marine à mollusque. Thèse, Université de Tours, France. 199pp.
Eertman, R.H.M., Groenink-van Emstede, M. and Sandde, B. (1993). The effects of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons fluorantrhene and benzo(a)pyrene on the mussel Mytilus edulis, the amphipod Bathyporeia sarsi and larva of the oyster, Crassostrea gigas. 50p. BEON-Efecten, DGW-NIOO.
Fernandes, M.B., Sicre, M.A., Boireau, A. and Tronczynski, Y. (1997). Polyaromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) distributions in the Seine river and its estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 34, 857–67.
Galtsoff, P.S. (1964). The American oyster, Crassostrea virginica Gmelin. US Fish and Wildlife Service, Fishery Bull. 64, 480p.
Geffard, O. (2001). Toxicité potentielle des sédiments marins et estuariens contaminés: evaluation chimique et biologique, biodisponibilité des contaminants sédimentaires. University of Bordeaux I, Bordeaux, France.
Geffard, O., Budzinski, H., Augagneur, S., Seaman, M.N.L. and His, E. (2001). Assessment of sediment contamination by spermiotoxicity and embryotoxicity bioassays with sea urchins (Paracentrotus lividus) and oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 20(7), 1605–11.
Geffard, A., Geffard, O., His, E. and Amiard, J.C. (2002). Relationships between metal bioaccumulation and metallothionein levels in larvae of Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to contaminated estuarine sediment elutriate. Mar. Ecol.—Prog. Series 233, 131–142.
Hatch, A. and Burton, G.A. Jr (1998). Effects of photoinduced toxicity of fluoranthene on amphibian embryos and larvae. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17(9), 1777–85.
His, E., Beiras, R. and Seaman, M.N.L. (1999b). The assessment of marine pollution—bioassays with bivalve embryos and larvae. Adv. Mar. Biol. 37, 1–178.
His, E., Heyvang, I., Geffard, O. and De Montaudouin, X. (1999a). A comparison between oyster (Crassostrea gigas) and sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) larval bioassays for toxicological studies. Water Res. 33, 1706–18.
His, E. and Robert, R. (1982). Le danger des traitements par le sulfate de cuivre en zone conchylicole: toxicité vis-à-vis des oeufs et des jeunes larves de. C. gigas. Rev. Trav. Inst. Pêches marit. 42(2), 117–25
His, E., Maurer, D. and Robert, R. (1983). Estimation de la teneur en acétate de tributyle-étain dans l'eau de mer par une méthode biologique. J. Moll. Stud. 12A, 60–8.
His, E., Seaman, M.N.L. and Beiras, R. (1997). A simplification of the bivalve embryogenesis larval development bioassay method for water quality assessment. Water Res. 31, 351–5.
Karickhoff, S.W., Brown, D.S. and Scott, T.A. (1979). Sorption of hydrophobic pollutants on natural sediments. Water Res. 13, 241–8.
Kwan, K.K. and Dukta, B.J. (1996). Development of reference sediment samples for solid phase toxicity screening tests. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 56, 696–702.
Landrum, P.F., Nihart, S.R., Eadie, B.J. and Herche, L.R. (1987). Reduction in bioavailabilty of organic contaminants to the amphipod Pontoporeia hoyi by dissolved organic matter of sediment interstitial waters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 6, 11–20.
Law, R.J., Dawes, V.J., Woohead, R.J. and Matthiessen, P. (1997). Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) in seawater around England and Wales. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 34, 306–22.
Long, E.R. (2000). Spatial extend of sediment toxicity in US estuaries and marines bays. Environ. Monitor. Assess. 64(1), 391–409.
Long, E.R., MacDonald, D.D., Smith, S.L. and Calder, F.D. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ. Management 19, 81–97.
Matthiessen, P., Bifield, S., Jarrett, F., Kirby, M.F., Law, R.J., McMinn, W.R., Sheahan, D.A., Thain, J.E. and Whale, G.F. (1998). An assessment of sediment toxicity in the River Tyne Estuary, UK by means of bioassays. Mar. Environ. Res. 45(1), 1–15.
McCauley, D.J., DeGraeve, G.M. and Linton, T.K. (2000). Sediment quality guidelines and assessment: overview and research needs. Environ. Sci. Policy 3, 133–44.
McPherson, C.A. and Chapman, P.M. (2000). Copper effects on potential sediment test organisms: the importance of appropriate sensitivity. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 40(8), 656–65.
Melzian, B.D. (1990). Toxicity assessment of dredged materials: acute and chronic toxicity as determined by bioassays and bioaccumulation tests. In C. Alzieu and B. Gallenne (eds). Proceedings of the International Seminar on Environmental Aspects of Dredging Activities, pp. 49–64. Nantes, France: Goubault Imprimeurs, s.a.
Michel, X.R., Beasse, C. and Narbonne, J.F. (1995). In vivo metabolism of benzo(a)pyrene in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Archiv. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 28, 215–22.
Pelletier, M.C., Burgess, R.M., Cantwell, M.G., Serbst, J.R., Ho, K.T. and Ryba, S.A. (2000). Importance of maternal transfer of the photoreactive polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon fluoranthene from benthic adult bivalves to their pelagic larvae. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 19(11), 2691–8.
Pelletier, M.C., Burgess, R.M., Ho, K.T., Kuhn, A., McKinney, R.A. and Ryba, A. (1997). Phototoxicity of individual polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and petroleum to marine invertebrate larvae and juveniles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 16, 2190–9.
Peterson, G.S., Ankley, G.T. and Leonard, E.N. (1996). Effects of bioturbation on metal-sulfide oxidation in surficial freshwater sediments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15, 2147–55.
Saulnier, I. and Mucci, A. (2000). Trace metal remobilization the resuspension of estuarine sediments: Saguenay Fjord, Canada. Appl. Geochem. 15, 203–22.
Slotten, D.G. and Reuter, J.E. (1995). Heavy metals in intact and resuspended sediments of a Califronia reservoir, with emphasis on potential bioavailability of copper and zinc. Mar. Freshwater Res. 46, 257–65.
Van Den Berg, G.A., Meijers, G.G.A., Van Der Heijdt, L.M. and Zwolsman, J.G. (2001). Dredging-related mobilisation of trace metals: a case study in the Netherlands. Water Res. 35, 1979–86.
Verrhiest, G., Clément, B., Blake, G. (2001). Single and combined effects of sediment-associated PAHs on three species of freshwater macroinvertebrates. Ecotoxicology 10(6), 363–372.
Walne, P.R. (1970). Present problems in the culture of the larvae of Ostrea edulis. Helgoländer Meeresunters 20, 514–25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geffard, O., Budzinski, H. & His, E. The Effects of Elutriates from PAH and Heavy Metal Polluted Sediments on Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg) Embryogenesis, Larval Growth and Bio-accumulation by the Larvae of Pollutants from Sedimentary Origin. Ecotoxicology 11, 403–416 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021024415695
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021024415695