Abstract
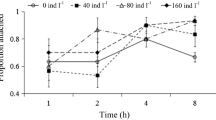
A hypothesis that size selection of prey by predators elicits size-specific responses from prey was examined. Freshwater snails, Pomacea canaliculata, ages 1, 3, 7, 15, 30, or 60 days, were given an extract of 3-day-old snails, and 3-day-old snails were given extracts of snails of the other ages or eggs. Snails 15 days or younger crawled out of the water in response to the 3-day-old snail extract, but older ones did not. The 3-day-old snails responded to the extracts of snails of all examined ages, but not to the extract of eggs. Snails of four size classes, 3-days-old, small (shell lengths 8–12 mm), medium (13–20 mm), and large (>28 mm) were given extracts of snails of each of these four classes. The 3-day-old snails crawled out of the water in response to the extract of 3-day-old snails, but showed a lower or no response to other extracts. Larger snails buried themselves in the soil in response to the extract of snails of similar sizes. These responses are discussed in the context of the evolution of the snail's avoidance behavior in response to the size-dependent prey choice by the predator.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Alexander, J. E. and Covich, A. P. 1991a. Predation risk and avoidance behavior in two freshwater snails. Biol. Bull. 180: 387–393.
Alexander, J. E., and Covich, A. P. 1991b. Predator avoidance by the freshwater snail Physella virgata in response to the crayfish Procambarus simulans. Oecologia 87:435–442.
Ball, S. L. and Baker, R. L. 1996. Predator-induced life history changes: antipredator behavior costs or facultative life history shifts? Ecology 77: 1116–1124.
Beissinger, S. R. 1983. Hunting behavior, prey selection, and energetics of snail kite in Guyana: consumer choice by a specialist. Auk 100:84–92.
Beltzer, A. H. 1985. Ecological alimentaria de Aramides ypecana (Aves: Rallidae) en el valle aluvial del Rio Parana medio (Argentina). Rev. Asoc. Cienc. Nat. Lit. 16: 73–83.
Boersma, M, Spaak, P., and De Meester, L. 1998. Predator-mediated plasticity in morphology, life history, and behavior of Daphnia: the uncoupling of responses. Am. Nat. 152: 237–248.
Buskirk, J. V. 2000. The costs of an inducible defense in anuran larvae. Ecology 81: 2813–2821.
Chivers, D. P. and Mirza, R. S. 2001. Importance of predator diet cues in responses of larval wood frogs to fish and invertebrate predators. J. Chem. Ecol. 27: 45–51.
Chivers, D. P. and Smith, R. J. F. 1998. Chemical alarm signalling in aquatic predator-prey systems: A review and prospectus. Écoscience 5: 338–352.
Chivers, D. P., Kiesecker, J. M., Marco, A., De Vito, J., Anderson, M. T., and Blaustein, A. R. 2001. Predator-induced life history changes in amphibians: egg predation induces hatching. Oikos 92: 135–142.
Cook, A. 1989. Factors affecting prey choice and feeding technique in the carnivorous snail Euglandina rosea Ferussac. J. Moll. Stud. 55: 469–477.
Covich, A. P., Crowl, T. A., Alexander, J. E., and Vaughn, C. C. 1994. Predator-avoidance responses in freshwater decapod-gastropod interactions mediated by chemical stimuli. J. North Am. Benthol. Soc. 13: 283–290.
Crowl, T. A. and Covich, A. P. 1990. Predator-induced life-history shifts in a freshwater snail. Science 247: 949–951.
De Castellanos, Z. J. A. and FernÁndez, D. 1976. Fauna de Agua Dulce de la Republica Argentina. Volumen XV Moluscos Gasteorpodos Fasciculo 1 Ampullariidae. FECIC, Buenos Aires, p. 33.
Dodson, S. I., Crowl, T. A., Peckarsky, B. L., Kats, L. B., Covich, A. P., and Culp, J. M. 1994. Non-visual communication in freshwater benthos: an overview. J. North Am. Benthol. Soc. 13: 268–282.
Donnay, T. J. and Beissinger, S. R. 1993. Apple snail (Pomacea doliodes) and freshwater crab (Dilocarcinus dentatus) population fluctuations in the llanos of Venezuela. Biotropica 25: 206–214. AGE INFLUENCE ON ALARM RESPONSE 2027
Estebenet, A. L. and Cazzaniga, N. J. 1992. Growth and demography of Pomacea canaliculata (Gastropoda: Ampullariidae) under laboratory conditions. Malacol. Rev. 25: 1–12.
GarcÍa, E. N. 1996. Invertebrates exploiting terrestrial and freshwater mollusks. Walkerana 8: 139–148.
GuimarÃes, C. T. 1981. Algumas observa¸cões de laboratório sobre biologia ecologia de Pomacea haustrum (Reeve, 1856). Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 76: 33–46.
Halwart, M. 1994. Fish As Biocontrol Agents in Rice: The Potential of Common Carp Cyprinus carpio (L.) and Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (L:): Margalef Verlag, Filderstadt, p. 169.
Kai, S., Ando, S., and Shiozaki, N. 2001. Predation on the golden apple snail, Pomacea canaliculata, by common carp under laboratory condition. Kyushu Agr. Res. 63: 85 (in Japanese).
Kats, L. B. and Dill, L. M. 1998. The scent of death: chemosensory assessment of predation risk by prey animals. Écoscience 5: 361–394.
Lardner, B. 2000. Morphological and life history responses to predators in larvae of seven anurans. Oikos 88: 169–180.
Laurila, A. 2000. Behavioural responses to predator chemical cues and local variation in antipredator performance in Rana temporaria tadpoles. Oikos 88: 159–168.
Lewis, D. B. 2001. Trade-offs between growth and survival: responses of freshwater snails to predatciouis crayfish. Ecology 82: 758–765.
Mondor, E. B., Baird, D. S., Slessor, K. N., and Roitberg, B. D. 2000. Ontogeny of alarm pheromone section in pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. J. Chem. Ecol. 26: 2875–2882.
Murphy, R. C. 1955. Feeding habits of the everglade kite (Rostramus sociabilis). Auk 72: 204–205.
NystrÖm, P. and Åbj Örnsson, K. 2000. Effects of fish chemical cues on the interactions between tadpoles and crayfish. Oikos 88: 181–190.
Pettersson, L. B., Nilsson, P. A., and BrÖnmark, C. 2000. Predator recognition and defence strategies in crucian carp, Carassius carassius. Oikos 88: 200–212.
Rahman, Y. J., Forward, R. B., JR., and Rittschof, D. 2000. Responses ofmudsnails and periwinkles to environmental odors and disaccharide mimics of fish odor. J. Chem. Ecol. 26: 679–696.
Rittschof, D. 1990. Peptide-mediated behaviors in marine organisms. J. Chem. Ecol. 16: 261–272.
Rowe, R. J. 1987. Predatory versatility in a larval dragonfly, Hemianax papuensis (Odonata: Aeshnidae). J. Zool. 211: 193–207.
Santos, S. A., Niagara, M. S., Campos, P., M. S., Magnusson, Z.W. E., and Mourao, G.M. 1996. Diets of Caiman crocodilus yacare from different habitats in the Brazilian Pantanal. Herpetol. J. 6: 11–117.
Skelly, D. K. and Werner, E. E. 1990. Behavioral and life-historical responses of larval American toads to an odonate predator. Ecology 71: 2313–2322.
Slootweg, R. 1987. Prey selection by molluscivorous cichlids foraging on a schistosomiasis vector snail, Biomphalaria glabrata. Oecologia 74: 193–202.
Snyder, N. F. R. and Snyder, H. A. 1971. Defenses of the Florida apple snail Pomacea paludosa. Behavior 40: 175–215.
Stevens, A. J., Stevens, N. M., Darby, P. C., and Percival, H. F. 1999. Observations of the fire ants (Solenopsis invicta Buren) attacking apple snails (Pomacea paludosa) exposed during dry down conditions. J. Moll. Stud. 65: 507–510.
Turner, A. M., Fetterolf, S. A., and Bernot, R. J. 1999. Predator identity and consumer behavior: differential effects of fish and crayfish on the habitat use of a freshwater snail. Oecologia 118: 242–247.
Turner, A. M., Bernot, R. J., and Boes, C.M. 2000. Chemical cues modify species interactions: the ecological consequences of predator avoidance by freshwater snails. Oikos 88: 148–158.
Vaz-Ferreira, R., Paulete, J., and Paulete de, S. S. 1965. Ecoetolog a alimentaria de Rostrhamus sociabilis sociabilis (Vieill). Rev. Fac. Human. Cienc. 22: 191–202. 2028 ICHINOSE
Von Elert, E., and Pohnert, G. 2000. Predator specificity of kairomones in diel vertical migration of Daphnia: a chemical approach. Oikos 88: 119–128.
Warkentin, K. M. 1995. Adaptive plasticity in hatching age: a response to predation risk trade-offs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 3507–3510.
Watt, P. J. and Young, S. 1992. Genetic control of predator avoidance behaviour in Daphnia. Freshwater Biol. 28: 263–367.
Zimmer, R. K. and Butman, C. A. 2000. Chemical signaling processes in the marine environment. Biol. Bull. 198: 168–187.
Zimmer, R. K., Commins, J. E., and Brozne, K. 1999. Regulatory effects of environmental chemical signals on search behavior and foraging success. Ecology 80: 1432–1446.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ichinose, K. Influence of Age and Body Size on Alarm Responses in a Freshwater Snail Pomacea canaliculata . J Chem Ecol 28, 2017–2028 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020749911877
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020749911877