Abstract
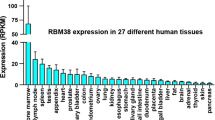
A 2860-bp cDNA was isolated from a human fetal brain cDNA library by high throughput cDNA sequencing, which encodes a putative protein with 186 amino acids. The putative protein shares 90.7% identity with rat pBOG (3403163) and shares 93.4% identity with human RBBP9 (NPA conserved RB binding domain, L × C × E, located between residue 63 and 68 was recognized. Therefore, it was named RBBP10. Mapviewer analysis locates it on human chromosome 20q11.22. RBBP10 spans about 9.6 kb of the genome and consists of six exons and five introns. RT-PCR revealed that the gene was expressed widely in various human tissues, and the expression level is somewhat higher in tumor tissues than in normal tissues. But subsequent sequencing analysis did not found any mutation of this in tumor tissues. The COS 7 cell transfected with the ORF of RBBP10 showed that the protein was distributed both in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus. Our results suggest that RBBP10 is the orthologue of the rat BOG gene (AF025819) and a paralogue of human RBBP9 (AF039564).
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bookstein, R., Shew, J. Y., Chen, P. L., Scully, P., and Lee, W. H. (1990). Suppression of tumorigenicity of human prostate carcinoma cells by replacing a mutated RB gene. Science 247:712–715.
Chen, C., and Okayama, H. (1995). High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7:2745–2752.
Dyson, N., Guida, P., McCall C., and Hariow, E. (1992). Adenovirus E1A makes two distinct contacts with retinoblastoma protein. J. Virol. 66:4606–4611.
Elena, R.-P., Qi, X., Maria, B. B., and Crisanto G. (1999). The cloning of plant E2F, a retinoblastomabinding protein, reveals unique and conserved features with animal G1/S regulators. Nucleic Acids Res. 27:3527–3533.
Figge, J., Breese, K., Vajda, S., Zhu, Q. L., Eisele, L., Andersen, T. T., MacColl, R., Friedrich, T., and Smith, T. F. (1993). The binding domain structure of retinoblastoma-binding proteins. Protein Sci. 2:155–164.
Friend, S. H., Bernards, R., Rogelj, S., Wenberg, R. A., Rapaporet, J. M., Albert, D. M., and Dryjia, T. P. (1986). A human DNA segment with properities of the gene that predisposed to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature 323:643–646.
Goodrich, D. W., Chen, Y., Scully, P., and Lee, W. H. (1992). Expression of the retinoblastoma gene product in bladder carcinoma cells associates with a low frequency of tumor formation. Cancer Res. 52:1968–1973.
Hall, M., and Peters, G. (1996). Genetic alteractions of cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and cdk inhibitors in human cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 68: 67–108.
Helin, K. (1998). Regulation of cell proliferation by the E2F transcription factors. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 8:28–35.
Helin, K., Lees, J. A., Vidal, M., Dyson, N., Harlow, E., and Fattaey, A. (1992). A cDNA encoding a pRB-binding protein with properties of the transcription factor E2F.Cell 70:337–350.
Hiehert, S.W., Chellappan, S. P., Horowitz, J. M., and Nevins, J. R. (1992). The interaction of RB with E2F coincides with an inhibition of the transcriptional activity of E2F. Genes Dev. 6:177–185.
Huang, H. J., Yee, J. K., Shew, J. Y., Chen, P. L., Bookstein, R., Friedmann, T., Lee, E. Y., and Lee, W. H. (1988). Suppression of the neoplastic phenotype by replacement of the RB gene in human cancer cells. Science 242:1563–1566.
Kaelin, W. G. Jr., Krek, W., Sellers, W. R., DeCaprio, J. A., Ajchenbaum, F., Fuchs, C. S., Chittenden, T., Li, Y., Farnham, P. J., Blanar, M. A., Livingston, D. M., and Flemington, E. K. (1992). Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell 70:351–364.
Kundsen, E. S., Buckmaster, C., Chen, T.-T., Feramisco, J. R., and Wang, J.-Y. (1998). Inhibition of DNA synthesis by RB: Effects on G/S transition and S-phase progression. Genes Dev. 12:2278–2292.
Lee, J. O., Russo, A. A., and Pavletich, N. P. (1998). Structure of the retinoblastoma tumor-suppressor pocket domain bound to a peptide from HPV E7. Nature 391:859–865.
Lee, W. H., and Shew, J. Y. (1987). Human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene: Cloning, identification and sequence. Science 235:1394–1399.
Lipinski, M. M., and Jack, T. (1999). The retinoblastoma gene family in differentiation and development. Oncogene 18:7873–7882.
Nevins, J. R. (1992). E2F: A link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science 258:424–429.
Sellers, W. R., Rodgers, J.W., and Kaelin, W. G. (1995). A potent transrepression in the retinoblastoma protein induces a cell cycle arrest when bound to E2F sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:11544–11548.
Wang, H., Grand, R. J. A., Milner, A. E., Armitage, R. J., and Grogory, C. D. (1996). Repression of apotosis in human B lymphoma cells by CD40 ligand and BCL2: Relationship to the cell cycle and role of the retinoblastoma protein. Oncogene 13:373–379.
Weinberg, R. A. (1995). The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell 81:323–330.
Welch, P. J., and Wang, J.Y. (1992).AC-terminal protein-binding domain in the retinoblastoma protein regulates nuclear c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the cell cycle. Cell. 75:779–790.
Wen, H., and Ao, S. (2001). Identification and characterization of a novel human cDNA encoding a 21 kDa pRb-assocoated protein. Gene 263:85–92.
Woitach, J. T., Hong, R., Keck, C. L., Zimonjic, D. B., Popescu, N. C., and Thorgeirsson, S. S. (1999). Assignment of the Bog gene (RBBP9) to syntenic regions of mouse chromosome 2G1-H1 and human chromosome 20p11.2 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 85:252–253.
Yang, M., Wu, Z., and Fields, S. (1995). Protein-peptide interactions analyzed with the yeast two-hybrid system. Nucleic Acids Res. 23:1152–1156.
Zhang, M., Niu, C. H., and Thorgeirsson, S. S. (1998). A retinoblastoma-binding protein that affects cell-cycle control and confers transforming ability. Nature Genet. 19:371–374.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, JZ., Yang, QS., Wang, S. et al. Cloning and Expression of a Novel Retinoblastoma Binding Protein cDNA, RBBP10. Biochem Genet 40, 273–282 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019886918029
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019886918029