Abstract
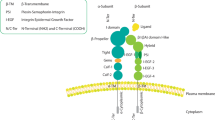
The integrins are a family of cell surfaceadhesion receptors that mediate adhesion to eithercomponents of the extracellular matrix or to othercells. The β1 family of integrinsrepresent the major class of cell substrate receptors withspecificities primarily for collagens, laminins, andfibronectins. The role of the integrin family of cellsurface adhesion receptors in normal mammary glandmorphogenesis and the contributions of altered integrinreceptor expression to the invasive and metastaticphenotype have been the primary focus of our lab, aswell as a number of other laboratories. Theα2 β1 integrin is expressed at high levels by normaldifferentiated epithelial cells including those of thenormal breast. Using breast cancer as a model, weevaluated changes in integrin expression in malignancy. We and other investigators made the keyobservation that α2 β1integrin expression is decreased in adenocarcinoma ofthe breast in a manner that correlates with the stage ofdifferentiation. Studies of other adenocarcinomas have yielded similarresults. When the α2 β1integrin was reexpressed in a poorly differentiatedmammary carcinoma that expressed no detectableα2 integrin subunit, a dramatic reversion of malignant phenotype to adifferentiated epithelial phenotype was observed,indicating a critical role forα2β1 expression inmammary gland differentiation. Other laboratories using monoclonal antibodies to competitivelyinhibit α2 β1 integrinadhesion or oncogenic transformation using c-erb2 haveconfirmed the important role of that α2β1 integrin in mammary gland morphogenesis. Re-expression of theα2 β1 integrin alsoresults in upregulation of both the α6and β4 integrin subunits. To determinethe contribution of enhanced α6 andβ4 integrin expression to the abrogation of the malignantphenotype by α2 β1integrin expression, we have now separately re-expressedthe human α6 or β4integrin subunit in the breast cancer model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. H. Barcellos-Hoff, J. Aggeler, T. G. Ram, and M. J. Bissell (1989). Functional differentiation and alveolar morphogenesis of primary mammary cultures on reconstituted basement membrane. Development 105: 223-235.
C. H. Damsky and Z. Werb (1992). Signal transduction by integrin receptors for extracellular matrix: cooperative processing of extracellular information. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 4: 772-781.
C. D. Roskelley, P. Y. Desprez, and M. J. Bissell (1994). Extra-cellular matrix-dependent tissue-specific gene expression in mammary epithelial cells requires both physical and biochemical signal transduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91: 12378-12382.
V. M. Weaver, O. W. Petersen, F. Wang, C. A. Larabell, P. Briand, C. Damsky, and M. J. Bissell (1997). Reversion of the malignant phenotype of human breast cells in three-dimensional culture and in vivo by integrin blocking antibodies. J. Cell. Biol. 137 (1): 231-245.
E. Ruoslahti (1991). Integrins. J. Clin. Invest. 87: 1-5.
R. O. Hynes (1992). Integrins: Versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 69: 11-25.
S. M. Albelda (1993). Biology of disease. Role of integrins and other cell adhesion molecules in tumor progression and metastasis. Lab. Invest. 68: 4-17.
S. Dedhar, W. S. Argraves, S. Suzuki, E. Ruoslahti E, and M. D. Pierschbacher (1987). Human osteosarcoma cells resistant to detachment by an Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptide overproduce the fibronectin receptor. J. Cell Biol. 105: 1175-1182.
L. F. Reichardt and K. J. Tomaselli (1991). Extracellular matrix molecules and their receptors: function in neural development. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 14: 531-570.
Z. Werb, P. M. Tremble, O. Behrendsten, E. Crowley, and C. H. Damsky (1989). Signal transduction through the fibronectin receptor induces collagenase and stromelysin gene expression. J. Cell Biol. 109: 877-899.
M. A. Schwartz and K. Denninghoff (1994). αv integrins mediate the rise in intracellular calcium in endothelial cells on fibronectin even though they play a minor role in adhesion. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 11133-11137.
P. J. Keely, A. M. Fong, M. M. Zutter, and S. A. Santoro (1995). Alteration of collagen-dependent adhesion, motility, and morphogenesis by the expression of antisense α2 integrin mRNA in mammary cells. J. Cell. Sci. 108: 595-607.
E. U. M. Saelman, P. J. Keely, and S. A. Santoro. (1995). Loss of MDCK cell α2β1 integrin expression results in reduced cyst formation, failure to hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factorinduced branching morphogenesis, and increase apoptosis. J. Cell. Sci. 108: 3531-3540.
A. R. Howlett, N. Bailey, C. Damsky, O. W. Petersen, and M. J. Bissell (1995). Cellular growth and survival are mediated by β1 integrins in normal human breast epithelium but not in breast carcinoma. J. Cell. Sci. 108 (5): 1945-1957.
F. Berdichevsky, C. Gilbert, M. Shearer, and J. Taylor-Papadimitriou (1991). Collagen-induced morphogenesis of human mammary epithelial cells: The role of the α2β1 integrin. J. Cell. Sci. 102: 437-446.
S. A. Santoro and M. M. Zutter (1995). The α2β1 integrin: A collagen receptor on platelets and other cells. Thrombosis and Haemostasis 74: 813-821.
M. J. Elices and M. E. Hemler (1989). The human integrin VLA-2 is a collagen receptor on some cells and a collagen/laminin receptor on others. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86: 9906-9910.
L. R. Languino, K. R. Gehlsen, E. A. Wayner, W. G. Carter, E. Engvall, and E. Ruoslahti (1989). Endothelial cells use α2β1 integrin as a laminin receptor. J. Cell Biol. 109: 2455-2462.
D. Kirchofer, L. R. Languino, E. Ruoslahti, and M. D. Pierschbacher (1990). α2β1 integrins from different cell types show different binding specificities. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 615-618.
M. M. Zutter and S. A. Santoro (1990). Widespread histologic distribution of the α2β1 integrin cell surface collagen receptor. Am. J. Pathol. 137: 113-120.
V. Quaranta (1991). Epithelial integrins. Cell. Diff. Devel. 32: 361-366.
M. E. Hemler, C. Crouse, and A. Sonnenberg (1989). Association of the VLA subunit α6 with a novel protein. A possible alternative to the common VLA β1 subunit on certain cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 6529-6535.
W. G. Carter, P. Kaur, S. G. Gil, P. J. Gahr, and E. A. Wayner (1990). Distinct functions for integrins α3β1 in focal adhesions and α6β4/bullous pemphigoid antigen in a new stable anchoring contact (SAC) of keratinocytes: relation to hemidesmosomes. J. Cell. Biol. 111: 3141-3154.
M. A. Stepp, S. Spurr-Michaud, A. Tisdale, J. Elwell, and I. K. Gipson (1990). α6β4 integrin heterodimer is a component of hemidesmosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87: 8970-8974.
J. C. R. Jones, M. A. Kurpakus, H. M. Cooper, and V. Quaranta (1991). A function for the integrin in α6β4 in the hemidesmosome. Cell. Reg. 2: 427-438.
A. Sonnenberg, J. Calafat, H. Janssen, H. Daams, L. M. van der Raaij-Hemler, R. Falcioni, S. J. Kennel, J. D. Aplin, J. Baker, and M. Loizidou (1991). Integrin α6β4 complex is located in hemidesmosomes, suggesting a major role in epidermal cell-basement membrane adhesion. J. Cell. Biol. 113: 907-917.
J. R. Starkey (1990). Cell matrix interactions during tumor invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 9: 113-123.
L. A. Liotta, P. S. Steeg, and W. G. Stetler-Stevenson (1991). Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: An imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell 64: 327-336.
J. Behrens (1993). The role of cell adhesion molecules in cancer invasion and metastasis. Br. Cancer. Res. Treat. 24: 125-184.
F. G. Giancotti and F. Mainiero (1994). Integrin-mediated adhesion and signaling tumorigenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1198: 47-64.
L. C. Plantefaber and R. O. Hynes (1989). Changes in integrin receptors on oncogenically transformed cells. Cell 56: 281-290.
S. Dedhar and R. Saulnier (1990). Alterations in integrin receptor expression on chemically transformed human cells: Specific enhancement of laminin and collagen receptor complexes. J. Cell. Biol. 110: 481-489.
M. M. Zutter, G. Mazoujian, and S. A. Santoro (1990). Decreased expression of integrin adhesive protein receptors in adenocarcinoma of the breast. Am. J. Pathol. 137: 863-870.
M.M. Zutter, H. R. Krigman, and S. A. Santoro (1993). Altered integrin expression in adenocarcinoma of the breast. Analysis by in situ hybridization. Am. J. Pathol. 142: 1438-1439.
G. K. Koukoulis, I. Virtanen, M. Korhonen, L. Laitnen, V. Quaranta, and V. E. Gould (1991). Immunohistochemical localization of integrins in the normal, hyperplastic and neoplastic breast: Correlation with their functions as receptors and cell adhesion molecules. Am. J. Pathol. 139: 787-799.
M. Pignatelli, A. M. Hanaby, and G. W. H. Stamp (1991). Low expression of β1, α2, and α3 subunits of VLA integrins in malignant mammary tumors. J. Pathol. 165: 25-32.
M. Pignatelli, M. R. Cardillo, A. Hanaby, and G. W. Stamp (1992). Integrins and their accessory adhesion molecules in mammary carcinomas: Loss of polarization in poorly differentiated tumors. Human Pathol. 23: 1159-1166.
K. Koretz, P. Schlag, L. Boumsell, and P. Moller (1991). Expression of VLA-α2, VLA-α6, and VLA-β1 chains in normal mucosa and adenomas of the colon, and in colon carcinomas and their liver metastasis. Am. J. Pathol. 138: 741-750.
A. Stallmach, B. Von Lampe, H. Matthes, G. Bornhoft, and E. O. Riecken (1992). Diminished expression of integrin adhesion molecules on human colonic epithelial cells during the benign to malignant tumor transformation. Gut 33: 342-346.
P. A. Hall, P. Coates, N. R. Lemoine, and M. A. Horton (1991). Characterization of integrin chains in normal and neoplastic human pancreas. J. Pathol. 165: 33-41.
H. Bonkoff, U. Stein, and K. Remberger. (1993). Differential expression of α6 and α2 very late antigen integrins in the normal, hyperplastic and neoplastic prostate: Simultaneous demonstration of cell surface receptors and their extracellular ligands. Human Pathol. 24: 243-248.
G. W. H. Stamp and M. Pignatelli (1991). Distribution of β1, α2, and α3 integrin chains in basal cell carcinomas. J. Pathol. 163: 307-313.
M. Pignatelli (1990). Integrin cell adhesion molecules and colorectal cancer. J. Pathol. 162: 95-97.
M. Pignatelli, M. E. F. Smith, and W. F. Bodmer (1991). Low expression of collagen receptors in moderate and poorly differentiated colorectal adenocarcinomas. Brit. J. Cancer 61: 636-638.
G. K. Koukoulis, I. Virtanen, R. Moll, V. Quaranta, and V. E. Gould (1993). Immunolocaliz ation of integrins in the normal and neoplastic colonic epithelium. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 63: 373-383.
M. Korhonen, L. Laitinen, J. Ylanne, G. K. Koukolis, V. Quaranta, H. Juusela, V. E. Gould, and I. Virtanen (1992). Integrin distributions in renal cell carcinomas of various grades of malignancy. Am. J. Pathol. 141: 1161-1171.
R. J. Weinel, A. Rosendahl, K. Neumann, B. Chaloupka, O. Erb, M. Rothmund, and S. A. Santoro (1992). Expression and function of VLA α2, α3, α5, α6 integrin receptors in pancreatic carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 52: 827-833.
L. Damjanovich, S. M. Albelda, S. A. Mette, and C. A. Buck (1992). Distribution of integrin cell adhesion receptors in normal and malignant lung tissue. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 6: 197-206.
J. A. Varner and D. A. Cheresh (1996). Integrins and cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 8: 724-730.
S. Kajiiji, R. N. Tamura, and V. Quaranta (1989). A novel integrin (αEβ4) from human epithelial cells suggests a fourth family of integrin adhesion receptors. EMBO J. 8: 673-680.
A. Sonnenberg, C. J. T. Linders, J. H. Daams, and S. J. Kennel (1990). The α6β1 (VLA-6) and α6β4 protein complexes: tissue distribution and biochemical properties. J. Cell Sci. 96: 207-217.
G. P. Gui, C. A. Wells, P. D. Browne, P. Yeomans, S. Jordan, J. R. Puddefoot, G. P. Vinson, and R. Carpenter (1995). Integrin expression in primary breast cancer and its relation to axillary nodal status. Surgery 117: 102-108.
A. M. Hanaby, E. E. Gillett, M. Pignatelli, and G. W. Stamp (1993). β1 and β4 integrin expression in methacarn and formalin-fixed material from in situ ductule carcinoma of the breast. J. Pathol. 171: 257-262.
K. Friedrichs, P. Ruiz, F. Franke, I. Gille, H. J. Terpe, and B. A. Imhof (1995). High expression level of α6 integrin in human breast carcinoma is correlated with reduced survival. Cancer Res. 55: 901-906.
J. D. Knox, A. E. Cress, V. Clark, L. Manriquez, K. S. Affinito, B.L. Dalkin, and R.B. Nagle (1994). Differential expression of extracellular matrix molecules and the α6 integrins in the normal and neoplastic prostate. Am. J. Pathol. 145: 167-174.
R. B. Nagle, J. Hao, J. D. Knox, B. L. Dalkin, V. Clark, and A. E. Cress (1995). Expression of hemidesmosomal and extracellular matrix proteins by normal and malignant human prostate tissue. Am. J. Pathol. 146: 1498-1507.
J. J. Korman and S. L. Hrabovsky (1993). Basal cell carcinomas display extensive abnormalities in the hemidesmosome anchoring fibril complex. Exp. Dermatol. 2: 139-144.
P. Savoia, L. Trusolino, E. Pepino, O. Cremona, and P. C. Marchisio (1993). Expression and topography of integrins and basement membrane proteins in epidermal carcinomas: basal but not squamous cell carcinomas display loss of α6β4 and BM-600/nicein. J. Invest. Dermatol. 101: 352-358.
G. P. H. Gui, C. A. Wells, P. D. Browne, P. Yeomans, S. Jordan, J. R. Puddefoot, G. P. Vinson, and R. Carpenter (1995). Integrin expression in primary breast cancer and its relation to axillary nodal status. Surgery 117: 102-108.
G. P. H. Gui, J. R. Puddefoot, G. P. Vinson, C. A. Wells, and R. Carpenter (1995). Modulation of very late activation-2 laminin receptor function in breast cancer metastasis. Surgery 118: 245-250.
G. Lindmark, B. Gerdin, L. Pahlman, B. Glimelius, K. Gehlsen, and K. Rubin (1993). Interconnection of integrins alpha 2 and alpha 3 and structure of the basal membrane in colorectal cancer: Relation to survival. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 19: 50-60.
M. M. Zutter, S. A. Santoro, W. D. Staatz, and Y. L. Tsung (1995). Re-expression of the α2β1 integrin abrogates the malignant phenotype of breast carcinoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92: 7411-7415.
N. J. Tawil, M. Houde, R. Blacher, F. Esch, L. F. Reichardt, D. C. Turner, and S. Carbonetto (1990). α1β1 integrin heterodimer functions as a dual laminin/collagen receptor in neural cells. Biochemistry 29: 6540-6544.
F. Giancotti and E. Ruoslahti (1990). Elevated levels of the α5β1 fibronectin receptor suppress the transformed phenotype of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell 60: 349-350.
M. J. Bissell and H. G. Hall (1987). Form and function in the mammary gland: The role of extracellular matrix. The Mammary Gland: Development, Regulation and Function Plenum Press, New York, pp. 97-146.
B. D'Souza, F. Berdichevsky, N. Kyprianou, and J. Taylor-Papadimitrious (1993). Collagen-induced morphogenesis and expression of the alpha 2-integrin subunit is inhibited in c-erbB2-transfected human mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene 8 1797-1806.
D. A. Lauffenburger and A. F. Horwitz (1996). Cell migration: A physically integrated molecular process. Cell 84: 359-369.
A. S. Clarke, M. M. Lotz, C. Chao, and A. M. Mercurio (1995). Activation of the p21 pathway of growth arrest and apoptosis by the β4 integrin cytoplasmic domain. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 22673-22676.
C. Choa, M.M. Lotz, A. C. Clarke, and A. M. Mercurio (1996). A function for the integrin α6β4 in the invasive properties of colorectal carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 56: 4811-4819.
L. M. Shaw, C. Chao, U. M. Wewer, and A. M. Mercurio (1996). Function of the integrin α6β1 in metastatic breast carcinoma cells assessed by expression of a dominant-negative receptor. Cancer Res. 56: 959-963.
P. E. Hughes, M. W. Renshaw, M. Pfaff, J. Forsyth, V. M. Keivens, M. A. Schwartz, and M. H. Ginsberg (1997). Suppression of integrin activation: A novel function of a Ras/Rafinitiated MAP kinase pathway. Cell 88: 521-530.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zutter, M.M., Sun, H. & Santoro, S.A. Altered Integrin Expression and the Malignant Phenotype: The Contribution of Multiple Integrated Integrin Receptors. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 3, 191–200 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018798907544
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018798907544