Abstract
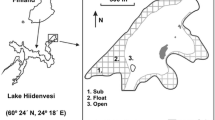
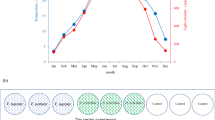
Shallow lake Agmon is a newly created subtropical wetland in north-eastern Israel. The lake is part of the Hula Project aimed at slowing down deterioration processes of the peat soils, to establish infrastructure for ecotourism as an income for the land owners, and nutrient removal from Lake Kinneret inputs. An onset of benthic filamentous macro-green algae during late winter–spring season, followed by submerged macrophytes vegetation during spring–summer was documented. The phosphorus summer loads are mostly plant–mediated internal fluxes and nitrogen intensively removed from lake waters by sedimentation and denitrification. The summer phytoplankton, mostly colonial cyanobacteria, are P limited. During 1995 and early 1996, dense Typha domingensisstands were developed in the southern half of the Lake (chalk-marl bottom sediments). The P-limited Typhavegetation collapsed within less than half a year and reappeared in the south-eastern part of the lake where sediments were exposed and oxidized. It is hypothesized that phosphorus cycle is a strong dependant of macrophyte mediation, and P deficiency in the sediments predominantly affected Typhadecline and an increase of P availability later enabled the reappearance of the Typhastands.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashkenazi, S., D. Markel & D. Kaplan, 1999. The catastrophic decline of cattail (Typha domingensis) in Lake Agmon: Possible machanisms and remedial measures J. Mediter. Ecol. 1: 85–100.
Armstrong, J., W. Armstrong, Z. Wu & F. Afreen-Zobayaed, 1996a. A role for phytotoxins in the Phragmites die-back syndrom? Folia Geobot. Phytotax. 31: 127–142.
Armstrong, J., W. Armstrong & W. H. Van Der Putten, 1996b. Phragmites die-back: bud and root death, blockages within the aeration and vascular systems and the possible role of phytotoxins. New Phytol. 1333: 399–414.
Armstrong, J., F. Afreen-Zobayed & W. Armstrong, 1996c. Phragmites die-back: sulfide-and acetic acid-induced bud and root death, lignifications, And blockageswithin aeration and vascular systems. New Phytol. 134: 601–614.
Armstrong, J. & W. Armstrong, 1999. Phragmites die-back: toxic effects of propionic, butyric and caproic acids in relation to pH. New Phytol. 142: 201–217.
Bradely, P. M. & J. T. Morris, 1990. Influence of oxygen and sulfide concentration on nitrogen uptake kinetics in Spartina alterniflora. Ecology 71 (1): 282–287.
Buurman, P., B. Van Lagen & E. J. Velthorst (eds), 1996. P-Olsen. In Manual for Soil and Water Analysis. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden: 62–64.
Christensen, K. K., 1997, Differences in iron, manganese and phosphorus binding in freshwater sediment vegetated with Litorrella uniflora and benthic microalgae. Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 99: 25–273.
Christensen, K. K. & F. O. Andersen, 1996, Influence of Litorella uniflora on phosphorus retenion in sediment supllied with artificial porewater. Aquat. Bot. 55: 183–197.
Christensen, K. K., F. O. Andersen & H. S. Jensen, 1997. Comparison of iron, manganese and phosphorus retention in freshwater litorral sediment with growth of Litorella uniflora and benthic microalgae. Biogeochemistry 38: 149–171.
Davis, S. M., 1997. Phosphorus inputs and vegetation sensitivity in the Everglades. In Davis, S. M. & J. C. Ogden (eds), Everglades the Ecosystem and its Restoration. St. Lucie Press: 357–378.
Davis, S. M., L. H. Gunderson, W. A. Park, J. R. Richardson & J. E. Mattson, 1997. Landscape dimension, composition and function in a changing Everglades Ecosystem. In Davis, S. M. & Ogden, J. C. (eds), Everglades the Ecosystem and its Restoration. St. Lucie Press: 419–444.
Dimentman, H., H. J. Bromely & F. D. Por, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998. Zooplankton and other Invertbrates. In Gophen, M. (ed.), Hula Project. Annual Reports 299–303. 124–136 (in Hebrew).
Dimentman, H., H. J. Bromley & F. D. Por, 1992. Lake Hula. Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities. 170 pp.
Geifinan, Y., H. Dexter & M. Shaw, 1970–1998. Nutrient fluxes into Lake Kinneret, Annual Reports. Mekorot, Water Supply Co.
Nazareth, Jordan District, Catchment area monitoring Uniy (in Hebrew).
Gophen, M. (ed.), 1995–1998. The Hula Project, Annual and semi-annual reports (in Hebrew).
Gophen, M. & L. Bar-Ilan, 1998. Water chemistry in Lake Agmon. In Gophen, M. (ed.), Hula Project, Annual Report: 3–39 (in Hebrew).
Hambright, K. D., W. Eckart & L. Bar-Ilan, 1996, 1997. General Chemistry and Water Quality in Lake Agmon. In Gophen, M. (ed.), Hula Project. Annual Reports: 214–226; 38–55.
Hambright, K. D., L. Bar Ilan & W. Eckart, 1998. General water chemistry and quality in newly-created subtropical wetland lake. Wetlands ecology and management 6 (2–3) 121–132.
Home, J. A. & C. R. Goldman, 1994. Limnology: Phosphorus cycling in the water column. McGraw-Hill Inc: 163–164.
Kaplan, D., 1997, 1998. Submerged Macrophytes in Lake Agmon. In Gophen, M. (ed.), Hula Project. Annual Report: 85–96 (in Hebrew).
Kaplan, D., T. Oron & M. Gutman, 1998. Development of macrophytic vegetation in the Agmon wetland of Israel by spontaneous colonization and reintroduction. Wetland ecology and management 6 (2–3) 143–150.
Koch, M. S. & I. A. Mendelsshon, 1989. Sulfide as a soil phytotoxin: differential response in two marsh species. J. Ecol. 77, 565–578.
Koch, M. S., I. A. Mendelsshon & K. L. McKee, 1990. Mechanism for the hydrogen sulfide-induced growth limitation in wetland macrophytes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 35(2): 399–408.
Koncalova, H. C., J. Kvet & K. Thompson, 1992. Carbon starvation: a kee to reed decline in eutrophic lakes. Aquat. Bot. 43: 105–113.
Shrestha K. M. & C. K. Lin, 1999. Effect of pond mud drying on mineralization and nutrients release. J. Aquat. Trop. 14(4): 277–287.
Mal, T. K., J. Lovett-Doust & L. Lovett-Doust, 1997. Time dependent competitive displacement of Typha angustifolia by Lythrum salicaria. Oikos 79: 26–33.
Markel, D., E. Sas, B. Lazar & A. Bein, 1996, 1997. Biogeochemistry. In Gophen, M. (ed.), Hula Project. Annual Reports: 194–213; 33–37 (in Hebrew).
Markel, D., E. Sas, B. Lazar & A. Bein, 1998. Biogeochemical evolution of a sulfur-iron rich aquatic system in a reflooded wetland environment (Lake Agmon, northern Israel). Wetland ecology and management 6 (2–3): 103–120.
Mendelsshon, I. A., K. L. McKee & W. H. Patrick, Jr., 1980. Oxygen deficiency in Spartina altern flora roots: metaboli adaptation to anoxia. Science Vol. 214, 23: 439–441.
Mendelsshon, I. A. & K. L. McKee, 1988. Spartina alterniflora dieback in Louisiana: time-course investigation of soil waterlogging effect. J. Ecol. 76: 509–521.
Miano, S. L. & W. F. DeBusk, 1999. Effects of phosphorus enrichment on structure and function of Sawgrass and Cattail communities in the everglades. In Reddy, K. R., G. A. O'Connor & C. L. Schelske (eds), Phosphorus Biogeochemistry in Subtropical Ecosystems. Lewis Publishers: 275–299.
Miano, S. L. & F. H. Sklar, 1998. Biomass and nutrient allocation of sawgrass and cattail along a nutrient gradient in Florida Everglades. Welland Ecosystem and Management (in press).
Moss, B., J. Stansfield & K. Irvine, 1990. Problems in the restoration of a hypertrophic lake by diversion of a nutrient-rich inflow. Verh. int. Ver. Theo. Ang. Limnol. 24: 568–572.
Paz, U. (ed.), 1975. The reconstruction of the Hula Reservation. In Nature Protection in Israel: 116–206 (in Hebrew).
Reddy, K. R. & E. M. D'Angelo, 1994. Soil processes regulating water quality in wetlands. InMitsch, W. J. (ed.), Global Wetlands Old World and New. Elsevier: 309–324.
Richardson, C. J., 1990. Biogeochemical Cycles: Regional. In Patten, B. C. (ed.), Wetlands and Shallow Continental Water Bodies. SPB Academic Publishing, The Hague. The Netherlands: 259–280.
Richardson, C. J., S. S. Cooper, R. G. Qian, R. G. Qualls, E. A. Romanowicz, R. J. Stevenson & P. Vaithiyanathan, 2000. Effects of phosphorus and hydroperiod alterations on ecosystem structure and functionin the Everglades. In Richardson, C. J. (ed.), The Everglades Experiments (in press).
Rom, M., 1999. The Kinneret water catchment: trends and chages in nutrient contribution Mekorot, national Water supply co. Water catchment unit, Jordan District. Special Report. 63 pp. (in Hebrew).
Scheffer, M., 1998. Managing the ecosystem. In Ecology of Shallow Lakes. Chapman and Hall: 298–300.
Smith, C. S. & M. S. Adam, 1986. Phosphorus transfer from sediments by Myriophyllum spicatum. Limnol. Oceanogr. 31: 1312–1321.
Smolders, A. J. R., J. G. M. Roelofs & C. Den-Hartog, 1996. Possible causes for the decline of the water soldier (Startiotes aloides L.) in the Netherlands. Archiv. Hydrobiol. 136 (3): 327–342.
Smolders, A. J. R. & J. G. M. Roelofs, 1993. Sulphate mediated iron limitation and eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems. Aquat. Bot. 46: 247–253.
Smolders, A. J. R. & J. G. M. Roelofs, 1995. Internal eutrophication, iron limitation and sulphide accumulation due to the inlet of river Rhine water in peaty shallow waters in the Nederlands. Arch. Hydrobiol. 133 (3): 349–365.
Smolders, A. J. P., R. C. Nijboer & J. G. M. Roelofs, 1995. Prevention of sulphide accumulation and phophate mobilization by the addition of iron (II) chloride to a reduced sediment: an enclosure experiment. Freshwat. Biol. 34: 559–568.
Snowden, R. E. D. & B. D. Wheeler, 1993. Iron toxicity to fen plant species. J. Ecol. vol. 81 (1): 35–46.
Standard Methods, 1995. In Eaton, A. D., L. S. Clesceri & A. E. Greenberg (eds), BOD, COD. Publishers: APHA, AWWA, and WEE, U.S.A. 19th edn: 5/3–5/6; 5/15–5/16.
Tzipris, Y., M. Meron & Y. Poker, 1996, 1997, 1998. Water Table measurements. In Gophen, M. (ed.), Annual Reports of Hula project: 67–73 (in Hebrew).
Van Oorscht, M. M. P., 1994. Plant production nutrient uptake and mineralization in river marginal wetlands: the impact of nutrient additions due to former land use. In Mitsch, W. J. (ed.), Global Wetlands Old World and New. Elsevier: 133–150.
Wade, D. D, J. J. Ewel & R. Hofstetter, 1980. Fire in south Florida ecosystems. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service. General Technical Report SE-17.
Washborn, R. & R. F. Jones, 1936. The Percy Sladen Expedition to Lake Huleh. Nature 137: 8552–855.
Weisner, S. E. B., 1996. Effects of an organic sediment on performance of young Phragmites australis clones at different water depth treatments. Hydrobiologia 330: 189–194.
Wetzel, R. G., 1983. Application of predictive models and data. In Limnology. Sounders College Publ: 292–295.
Wijck, C. V., C. J. De Groot & P. Grillas, 1992. The effect of anaerobic sediment on growth of Potamogeton pectinatus L: the role of organic matter, sulphide and ferrous iron. Aquat. Bot., 44: 31–49.
Yatom, S. & O. Rabinovitch, 1999. Fractionation of organic soils in the Hula valley. Hula Project, Annual report (M. Gophen ed.) for 1998: 86–99. (in Hebrew).
Zohary, M., 1955. Hydrophilic Vegetation in Israel. In Geobotany, Sifriyat Poalim Publ: 452–464 (in Hebrew).
Zohary, M. & G. Orshansky, 1947. The vegetation of the Huleh Plain. Pales. J. Bot. Jerusalem. Ser. 4: 90–104.
Zohary, T., B. Kaplan, T. Fishbein & U. Pollingher, 1995, 1996, 1997. Phytoplankton and benthic algae. In Gophen, M. (ed.), Hula Project. Annual Reports: 251–259; 8284 (in Hebrew).
Zohary, T., T. Fishbein, B. Kaplan & U. Pollingher, 1998. Phytoplankton-metaphyton seasonal dynamics in a newly created subtropical wetland lake. Wetland Ecol. Manage. 6 (2–3): 133–142.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gophen, M. Nutrient and plant dynamics in Lake Agmon Wetlands (Hula Valley, Israel): a review with emphasis on Typha domingensis (1994–1999). Hydrobiologia 441, 25–36 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017525804657
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017525804657