Abstract
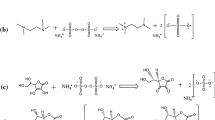
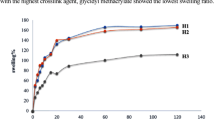
The thermal and mechanical properties of a new family of biodegradable hydrogels made of photocrosslinked dextran derivative of allyl isocyanate (dex-AI) and poly (D,L) lactide diacrylate macromer (PDLLAM) were studied. The changes of thermal and mechanical properties of the dex-AI/PDLLAM hydrogels as functions of dex-AI to PDLLAM composition ratio and immersion time in phosphate buffer solution at 37 °C were also investigated. Thermal property data showed that the chemical modification, crosslinking, swelling and hydrolytic degradation affected the glass transition and melting temperatures. Based on thermal data, no phase separation was observed in the bicomponent dex-AI/PDLLAM hydrogels. Mechanical property data showed that, by changing the composition ratio, dex-AI/PDLLAM hydrogels having a wide range of dry and swollen compression moduli could be obtained. The moduli of the dex-AI/DPLLAM hydrogels in dry state decreased with an increase in the PDLLAM composition due to the reduction in glass transition temperature of the hydrogels. The loss of mechanical strength in buffer solutions was attributed to the swelling-induced formation of 3D porous network structure in the early stage of immersion and the hydrolytic degradation of the PDLLAM in the late stage via the chain scission of ester linkages located in the PDLLAM backbone. Because swelling and degradation were composition dependent, the magnitude of the loss of mechanical strength was also composition-dependent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Park, W. S. W. Shalaby and H. Park, in “Biodegradable Hydrogels For Drug Delivery” (Technomic Publishing AG, 1993) Chapter 1, p. 6.
K. R. Kamath and K. Park, in “Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews” (Elsevier Science Publishers B.V. 1993), Chapter 11, p. 60.
K. W. Leong, in “Polymers for Controlled Drug Delivery”, edited by P. J. Tarcha (CRC Press, Boca Raton, Ann Arbor and Boston, 1991), Chapter 7, p. 129.
W. E. Hennink, H. Talsma, J. C. H. Borchert, S. C. De Smedt and J. Demeester, J. Controlled Release 39 (1996) 47.
W. N. E. Van Dijk-Wolthuis, J. A. M. Hoogeboom, M. J. Van Steenbergen, S. K. Y. Tsang and W. E. Hennink, Macromolecules 30 (1997) 4639.
S. Shah, K. J. Zhu and C. G. Pitt, J. Biomater. Sci. Polymer Edn. 5 (1994) 421.
T. K. Wang, I. Iliopoulos and R. Audebert, “ACS Symposium Series 467” (American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 1991) pp. 218-231.
M. E. Mcneill and N. B. Graham, J. Biomater. Sci. Polymer Edn. 5 (1993) 111.
Y. Zhang, C.-Y. Won and C.-C. Chu, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 37 (1999) 4554.
Y. L. Zhang, C. Y. Won and C. C. Chu, ibid. 38 (2000) 2392.
Y. Zhang and C. C. Chu, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 59 (2002) 318.
Y. L. Zhang and C. C. Chu, ibid. 54 (2001) 1.
Y. Zhang and C. C. Chu, J. Biomat. Appl. (Pending).
C. Migliaresi, L. Fambri and D. Cohn, J. Biomater. Sci. Polymer Edn. 5 (1994) 591.
F. Castelli, G. Pitarresi, V. Tomarchio and G. Giammona, J. Controlled Release 45 (1997) 103.
V. Carelli, G. D. Colo, E. Nannipieri and M. F. Serafini, Int. J. Pharm. 94 (1993) 103.
D. Mirejovsky, A. S. Patel and G. Young, Biomaterials 14 (1993) 1080.
S. S. Shah, K. J. Zhu and C. G. Pitt, J. Biomater. Sci. Polymer Edn. 5 (1994) 421.
O. Ariga, M. Kato, T. Sano, Y. Nakazawa and Y. Sano, J. Ferment. Bioeng. 76 (1993) 203.
Y. Miyachi, K. Jokei, M. Oka and T. Hayashi, J. Biomater. Sci. Polymer Edn. 7 (1996) 805.
Y. M. Lee and S. S. Kim, Polymer. 38 (1997) 2415.
S. P. Gorman, M. M. Tunney, P. F. Keane, K. Van Bladel and B. Bley, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 39 (1998) 642.
L. Vervoort, P. Rombaut, G. V. Den Mooter, P. Augustijns and R. Kinget, Int. J. Pharm. 172 (1998) 137.
J. Ch. Gayet, P. He and G. Fortier, J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 13 (1998) 179.
P. Ravichandran, K. L. Shantha and K. Panduranga Rao, Int. J. Pharm. 154 (1997) 89-94.
M. Kakizaki, H. Yamamoto, T. Ohe and T. Hideshima, “Molecular motions and dielectric relaxations in chitin, chitosan and related polymers, in Chitin and Chitosan”, edited by G. Skjak-Braek, T. Anthonsen and P. Sandford (Elsevier Applied Science, London and New York), p. 512.
Y. L. Zhang and C. C. Chu, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. In Medicine (in Press).
G. Pitarresi, V. Tomarchio and G. Cavallaro, J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 11 (1996) 328.
F. Rodriguez, “Principles of polymer systems” (Taylor & Francis, Washington, DC, 1996) Chapter 3, p. 56.
F. O. Eschbach and S. J. Huang, J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 9 (1994) 29.
Y. L. Zhang and C. C. Chu, Bioactive & Compatible Polym. (Pending).
C. C. Chu, J. A. Von Fraunhofer and H. P. Greisler, “Wound Closure Biomaterials and Devices” (CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, Florida, 1997) pp. 107-128
Z. Q. Gu, J. M. Xiao and X. H. Zhang, Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 8 (1998) 75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Chu, CC. Thermal and mechanical properties of biodegradable hydrophilic-hydrophobic hydrogels based on dextran and poly (lactic acid). Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 13, 773–781 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016123125046
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016123125046