Abstract
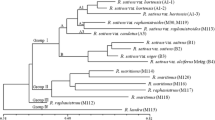
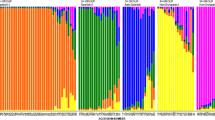
The wild progenitor of the cultivated flax (Linumusitatissimum L.) has been long hypothesized to beL. angustifolium Huds., largely fromseveral phytogeographic cytogenetic and phenotypic studies, but no molecularstudies on the issue are found. In this study, we genotyped 12 flax accessionsrepresenting seven flax species in the genus Linum with 527RAPD loci from 29 informative RAPD primers and analyzed their geneticrelationships with simple matching, Dice's and Jaccard's similaritycoefficients. Large RAPD variations were found among the flax species.L. usitatissimum andL. angustifolium had a higher RAPDsimilarity than the other pairs of flax species and these two species wereconsistently clustered in the same group with all of the similarity coefficientsused. This molecular finding provides an additional support for the hypothesisof L. angustifolium as the wildprogenitor of cultivated flax.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldrich J. and Cullis C.A. 1993. RAPD analysis in flax: optimization of yield and reproducibility using Klen Tag 1 DNA polymerase, Chelex 100, and gel purification of genomic DNA. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 11: 128–141.
Apostol B.L., Black IV C.W., Miller B.R., Reiter P. and Beaty B.J. 1993. Estimation of the number of full sibling families at an oviposition site using RAPD-PCR markers: applications to the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86: 991–1000.
Campbell C.D., Procunier J.D., Oomah B.D., Kenaschuk E.O., Dribnenki J.C.P. and Rashid K.Y. 1995. Analysis of genetic relationships in flax (Linum usitatissimum) using RAPD markers Proceedings of 56th Flax Institute of the United States., pp. 177–181.
Chaudhary B.D., Singh V.P. and Kumari R. 1986. Genetic diver gence in species of genus Linum. Acta Agronomica Hungarica 35: 235–238.
Chennaveeraiah M.S. and Joshi K.K. 1983. Karyotypes in cultivated and wild species of Linum. Cytologia 48: 833–841.
Cullis C.A., Swami S. and Song Y. 1999. RAPD polymorphisms detected between flax genotrophs. Plant Mol. Biol. 41: 795–800.
Dice L.R. 1945. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26: 297–302.
Diederichsen A. and Hammer K. 1995.Variation of cultivated flax (Linum usitatissimum L. subsp. usitatissimum) and its wild progenitor pale flax (subsp. angustifolium (Huds.) Thell.). Genet. Resear. Crop Evol. 42: 263–272.
Diederichsen A. and Richards K.W. 2001. Cultivated flax and the genus Linum L.--Taxonomy and germplasm conservation. In: Muir A. and Westscott N. (eds), Flax, The Genus Linum. Hardwood Academic Publishers, Amsterdam (in press).
Dillman A.C. 1953. Classification of flax varieties. USDA, Technical Bulletin No. 1064.
Dos Santos J.B., Nienhuis J., Skroch P., Tivang J. and Slocum M.K. 1994. Comparison of RAPD and RFLP genetic markers in determining genetic similarity among Brassica oleracea L. genotypes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 87: 909–915.
Fu Y.B., Diederichsen A., Richards K.W. and Peterson G. 2001. Genetic diversity of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) cultivars and landraces as revealed by RAPDs. Genet. Resear. Crop Evol. 47:5, pp. 569. (in press).
Gill K.S. and Yermanos D.M. 1967. Cytogenetic studies on the genus Linum. Crop Science 7: 623–631.
Gill K.S. 1987. Linseed. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi.
Hammer K. 1986. Linaceae. In: Schultze-Motel J. (ed.), Rudolf Mansfelds Verzeichnis landwirtschaftlicher und gärtnerischer Kulturpflanzen Vol. 2. Akademie-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 710–713.
Hammer K., Filatenko A.A. and Korzun V. 2000. Microsatellite markers--a new tool for distinguishing diploid wheat species. Genet. Resear. Crop Evol. 47: 497–505.
Heer O. 1872. Über den Flachs und die Flachskultur im Altertum. Neujahrsblatt der Naturforschenden Gesellschaft Zürich 74: 1–26.
Hickey M. 1988. 100 Families of Flowering Plants. 2nd edn. University Press, Cambridge.
Hjelmquist H. 1950. The flax weeds and the origin of cultivated flax. Botaniska Notiser 1950: 257–298.
Jaccard P. 1908. Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale. Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sci. Nat. 44: 223–270.
Link W., Dixkens C., Singh M., Schwall M. and Melchinger A.E. 1995. Genetic diversity in European and Mediterranean faba bean germ plasm revealed by RAPD markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 90: 27–32.
Mace E.S., Lester R.N. and Gebhardt C.G. 1999. AFLP analysis of genetic relationships among the cultivated eggplant, Solanum melongena L. and wild relatives (Solanaceae). Theor. Appl. Genet. 99: 626–633.
Nei M. and Li W.H. 1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76: 5269–5273.
Nicolosi E., Deng Z.N., Gentile A., La Malfa S., Continella G. and Tribulato E. 2000. Citrus phylogeny and genetic origin of important species as investigated by molecular markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 100: 1155–1166.
Ockendon D.J. 1968. Biosystematic studies in the Linum perenne group. New Phytol. 67: 787–813.
Ockendon D.J. and Walters S.M. 1968. Linum L. In: Tutin T.G. and Heywood V.H. (eds), Flora Europaea Vol. 2. University Press, Cambridge, pp. 206–211.
Oh T.J., Gorman M. and Cullis C.A. 2000. RFLP and RAPD mapping in flax (Linum usitatissimum). Theor. Appl. Genet. 101: 590–593.
Rohlf F.J. 1997. NTSYS-PC 2.1. Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System. Exeter Software, New York.
SAS Institute Inc. 1995. SAS user guide, version 6.12 edition. SAS Institute Incorporated, Cary, North Carolina.
Smouse P.E., Long J.C. and Sokal R.R. 1986. Multiple regression and correlation extensions of the Mantel test of matrix correspondence. Syst. Zool. 35: 627–632.
Sokal R.R. and Michener C.D. 1958. A statistical method for evaluating systematic relationships. Univ. Kansas Sci. Bull. 38: 1409–1438.
Tammes T. 1923. Das genotypische Verhältnis zwischen wildemLinum angustifolium und dem Kulturlein, Linum usitatissimum. Genetica 5: 61–76.
Thellung A. 1912. Neues aus der Adventivflora von Montepellier. Feddes Repertorium 11: 69–80.
Vidal J.R., Coarer M. and Defontaine A. 1999. Genetic relationships among grapevine varieties grown in different French and Spanish regions based on RAPD markers. Euphytica 109: 161– 172.
Whitkus R., Doebley J. and Wendel F. 1994. Nuclear DNA markers in systematics and evolution. In: Philips R.L. and Vasil J.K. (eds), DNA-Based Markers in Plants. Kluwer Academic Publ., Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 116–141.
Williams J.K.G., Kubelik A.R., Livak K.J., Rafalski J.A. and Tingey S.V. 1990. DNA polymorphism amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 18: 6531–6535.
Winkler H. 1931. Linaceae, Trib. I. 3. Linoideae-Eulineae. In: Engler A. (ed.), Die natürlichen Pflanzenfamilien nebst ihren Gattungen und wichtigeren Arten, Insbesondere den Nutzpflanzen. 2nd edn. W. Engelmann, Leipzig, pp. 111–120.
Yuzepchuk S.V. 1949. Genus 863 Linum. [Russ.]. In: Shishkin B.K. and Bobrov E.G. (eds), Flora SSSR, Izdatel'stvo Akademii Nauk Vol. 14. Moskva, Leningrad, pp. 86–146.
Zohary D. 1999. Monophyletic and polyphyletic origin of the crops on which agriculture was formed in the Near East. Genet. Resear. Crop Evol. 46: 133–142.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, YB., Peterson, G., Diederichsen, A. et al. RAPD analysis of genetic relationships of seven flax species in the genus Linum L. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 49, 253–259 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015571700673
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015571700673