Abstract
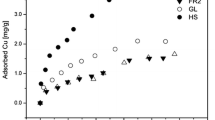
While sorbate/sorbent, sorbate/water, and sorbent/water (S/W)ratios in a batch system are known to affect the adsorption ofsorbate, the effect of different S/W ratios on the adsorptionof inorganic sorbates has seldom been addressed. This studyinvestigates the adsorption phenomena of Cu2+ in differentsorbate/sorbent/water ratios in a batch system. Batch experimentsare performed to examine the adsorption, and the linear (K D), Langmuir (K L), and Freundlich (K F) adsorption coefficients of Cu2+ in lateritic soil. These experiments are conducted using solutions with initial concentrations of 0.5 to 50 mg Cu2+ L-1 equilibratedwith an appropriate amount of soil to give S/W ratios of 0.1 to 2 g mL-1. Although the variations in the sorbed amountand adsorption coefficients apparently originate from a changein the sorbate/sorbent/water ratio, only the equilibrium concentration significantly affects adsorption. On the otherhand, the linear and Langmuir isotherm cannot adequately describethe adsorption data. In this study, the Freundlich equation gavean excellent fit to the adsorption data with a goodness-of-fit(R2) > 0.984. However, adsorption isotherms should be regarded as only a curve-fitting model or a mathematical tool and cannot be employed to interpret any particular adsorptionmechanism. Meanwhile, the solids effect reveals that K F andmaximum adsorption (b) of the Langmuir equation increase when S/W ratio decreases. The sorbate in the stagnant phase must beconsidered as part of the equilibrium concentration in the solidphase to avoid underestimating the sorbed amount at a lower S/Wratio and/or a higher sorbate concentration level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blake, G. R. and Hartge, K. H.: 1986, 'Particle Density', in A. Klute (2nd ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1. Physical and Mineralogical Methods, American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, U.S.A., pp. 377–382.
Bowman, B. T. and Sans, W. W.: 1985, 'Partitioning behavior of insecticides in soil-water systems: I. Adsorption Concentration Effects', J. Environ. Qual. 14, 265–269.
Brady, N. C. and Weil, P. R.: 1999, The Nature and Properties of Soils, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 881 pp.
Celorie, J. A., Woods, S. L., Vinson. T. S. and Istok, J. D.: 1989, 'A comparison of sorption equilibrium distribution coefficients using batch and centrifugation methods', J. Environ. Qual. 18, 307–313.
Chang, C. M., Wang, M. K., Chang, T. W. and Lin, C.: 2001, 'Transport modeling of copper and cadmium with linear and nonlinear retardation factors', Chemosphere 43, 1133–1139.
Chang, T. W.: 1995, 'Estimation of Distribution Coefficient by Miscible Displacement Experiments', in P. Binning, H. Bridgman and B. William (eds), Proceedings of the International Congress on Modeling and Simulation, Vol. 3: Water Resources and Ecology, Newcastle, Australia, 27-30 November 1995, pp. 169–172.
Chang, T. W.: 1996, 'The study of heavy metal copper distribution in soil at various water contents', J. Chin. Agric. Eng. 42(1), 92–97.
Cox, L., Hermosín, M. C. and Cornejo, J.: 1993, 'Adsorption of methomyl by soils of southern Spain and soil components', Chemosphere 27(5), 837–849.
Christensen, T. H.: 1984, 'Cadmium soil adsorption at low concentrations: 1. Effect of time, cadmium load, pH and calcium', Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 21, 105–114.
Di Toro, D. M.: 1985, 'A particle interaction model of reversible organic chemical sorption', Chemosphere 14, 1503–1538.
Farmer, W. J. and Aochi, Y.: 1974, 'Picloram sorption by soils', Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 38, 418–423.
Freundlich, H.: 1926, 'Colloid and Capillary Chemistry' (Translated from the third German edition by H. S. Hatfield), Methuen, London.
Garcia-Miragaya, J. and Page, A. L.: 1976, 'Influence of ionic strength and inorganic complex formation on the sorption of trace amounts of Cd by montmorillonite', Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 40, 658–663.
Gee, G. W. and Bauder, J. W.: 1986, 'Particle Size Analysis', in A. Klute (2nd ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1. Physical and Mineralogical Methods, American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, U.S.A., pp. 383–410.
Gee, G. W., Rai, D. and Serne, R. J.: 1983, 'Mobility of Radionuclides in Soil', in Soil Science Society of America (ed.), Chemical Mobility and Reactivity in Soil Systems, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, U.S.A., pp. 203–227.
Grover, R. and Hance, R. J.: 1970, 'Effect of ratio of soil to water on adsorption of linuron and atrazine', Soil Sci. 109, 136–138.
Hatano, R. and Sakuma, T.: 1991, 'A plate model for solute transport through aggregated soil columns. II. Experimental results and application of the model', Geoderma 50, 25–36.
Horzempa, L. M. and Di Toro, D. M.: 1983, 'PCB partitioning in sediment-water systems: the effect of sediment concentration', J. Environ. Qual. 12, 373–380.
Inskeep, W. P. and Baham, J.: 1983, 'Adsorption of Cd(II) and Cu(II) by Na-montmorillonite at low surface coverage', Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 47, 660–665.
Krishnamurti, G. S. R., Huang, P. M. and Kozak, L. M.: 'Sorption and desorption kinetics of cadmium from soils: influence of phosphate', Soil Sci. 164(12), 888–898.
Langmuir, I.: 1918, 'The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica, and platinum', J. Amer. Soc. 40, 1361–1403.
Lindsay, W. L.: 1979, 'Copper', in W. L. Lindsay (ed.), Chemical Equilibrium in Soils, John Wiley & Sons, New York, U.S.A., pp. 222–265.
Lion, L. W., Stauffer, T. B. and MacIntyre, W. C.: 1990, 'Sorption of hydrophobic compounds on aquifer materials: analysis methods and the effect of organic carbon', Contam. Hydrol. 5, 215–234.
Maraqa, M. A., Zhao, X., Wallace, R. B. and Voice, T. C.: 1998, 'Retardation coefficients of nonionic organic compounds determined by batch and column techniques', Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 62, 142–152.
McDonald Jr., L. M. and Evangelou, V. P.: 1997, 'Optimal solid-to-solution ratios for organic chemical sorption experiments', Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 61, 1655–1659.
McLaren, R. G., Backes, C. A., Rate, A. W. and Swift, R. S.: 1998, 'Cadmium and colbalt desorption kinetics from soil clays: effect of sorption period', Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 62, 332–337.
McLean, E. O.: 1982, 'Soil pH and Lime Requirement', in A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, and D. R. Keeney (2nd eds), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, U.S.A., pp. 199–224.
Nelson, D. W. and Sommers, L. E.: 1982, 'Total Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Organic Matter', in A. L. Page, R. H. Miller, and D. R. Keeney (2nd eds), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, U.S.A., pp. 539–579.
O'Connor, D. J. and Connolly, J. P.: 1980, 'The effect of concentration of adsorbing solids on the partition coefficient', Water Res. 14, 1517–1523.
Puls, R. W., Powell, R. M., Clark, D. and Eldred, C. J.: 1991, 'Effect of pH, solid/solution ratio, ionic strength, and organic acids on Pb and Cd sorption on kaolinite', Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 57-58, 423–430.
Rhodes, J. D.: 1982, 'Cation Exchange Capacity', in A. L. Page, R. H. Miller and D. R. Keeney (2nd eds), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, U.S.A., pp. 149–157.
Sanchez-Martin, M. J. and Sanchez-Camazano, M.: 1993, 'Adsorption and mobility of cadmium in natural, uncultivated soils', J. Environ. Qual. 22, 737–742.
Servos, M. R. and Muir, D. C. G.: 1989, 'Effect of suspended sediment concentration on the sediment to water partition coefficient for 1,3,6,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin', Environ. Sci. Technol. 23, 1302–1306.
Sidle, R. C. and Kardos, L. T.: 1977, 'Transport of heavy metals in a sludge-treated forested area', J. Environ. Qual. 6, 431–437.
Snoeyink, V. L. and Jenkins, D.: 1980, Water Chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp. 243–315.
Soil Survey Staff: 1996, Keys to Soil Survey Taxonomy, 7th ed., United States Department of Agriculture and Natural Resources Conservation Services, Washington, DC.
Sposito, G.: 1989, The Chemistry of Soils, Oxford University Press, New York, 277 pp.
van Genuchten, M. Th. and Wierenga, P. J.: 1976, 'Mass transfer studies in sorbing porous media. I. Analytical solutions', Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 40, 473–480.
Voice, T. C., Rice, C. P. and Weber Jr, W. J.: 1983, 'Effect of solids concentration on the sorptive partitioning of hydrophobic pollutants in aquatic systems', Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 789–796.
You, S., Yin, Y. and Allen, H. E.: 1999, 'Partitioning of organic matter in soils: Effects of pH and water/soil ratio', Sci. Total Environ. 227, 155–160.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, T.W., Wang, M.K. & Lin, C. Adsorption of Copper in the Different Sorbent/Water Ratios of Soil Systems. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 138, 199–209 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015551016833
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015551016833