Abstract
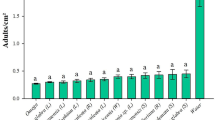
Fertile transgenic tobacco plants with leaves expressing avidin in the vacuole have been produced and shown to halt growth and cause mortality in larvae of two noctuid lepidopterans, Helicoverpa armigera and Spodoptera litura. Late first instar H. armigera larvae and neonate (<12-h-old) S. litura larvae placed on leaves excised from T0 tobacco expressing avidin at 3.1–4.6 μM (μmoles/kg of fresh leaf tissue) had very poor growth over their first 8 days on the leaves, significant numbers had died by days 11 or 12 and all were dead by day 22 (H. armigera) or day 25 (S. litura). Similar results were obtained when late first instar H. armigera larvae were placed on leaves from T1 plants expressing avidin at six different average concentrations, ranging from 3.7 to 17.3 μM. Two larvae on the lowest expressing leaves survived to pupation, but there was total mortality among the other groups and no relationship between avidin concentration and the effects on the larvae. Synergistic effects between avidin-expressing tobacco plants and a purified Bt toxin, Cry1Ba, were demonstrated. Late instar H. armigera larvae fed with leaves from T2 plants expressing avidin at average concentrations of either <5.3 or >12.9 μM, and painted with Cry1Ba protein at a rate equivalent to an expression level of 0.5% of total leaf protein, died significantly faster than larvae given either of the two treatments alone. Larvae fed with avidin-expressing leaves painted with the protease inhibitor, aprotinin, at a rate equivalent to 1% of total leaf protein had mortality similar to those given avidin-leaves alone. There was no evidence of antagonism between these two proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon (1985) Heliothis armigera Hubner, Noctuidae, Tomato noc-tuid. Fiches Techniques Sur les Ravageurs des Cultures Vivrieres Tropicales IRATCV, Montpellier, France.
Armes NJ, Wightman JA, Jadhav DR and Roa GVR (1997) Status of insecticide resistance in Spodoptera litura in Andhra Pradesh, India. Pesticide Sci 50: 240–248.
Ayyanna T, Subbaratnam GV and Dharmaraju E (1978) Pest complex on sunflower, Helianthus annus Lin in Andhra Pradesh. Indian J Entomol 40: 353–356.
Baker DH (1995) Vitamin bioavailability. In: Ammerman CB, Baker DH and Lewis AJ (eds), Bioavailability of Nutrients for Animals: Amino Acids, Minerals Vitamins. (pp. 399–431) Academic Press, San Diego.
Bell DE, Slaughter G, Roberts PM, Ellis CE, Willingham L, Cary T et al. (1999) The effects of over sprays on bt cotton. Proc Beltwide Cotton Conf. Orlando, Florida, USA, 3–7 January, 1999, Vol. 2, pp. 956–958.
Beuning LL, Spriggs TW and Christeller JT (1994) Evolution of the proteinase inhibitor I family and apparent lack of hyper-variability in the proteinase contact loop. J Mol Evol 39: 644–654.
Bruins BG, Scharloo W and Thorig GEW (1991) The harmful effect of light on Drosophila is diet-dependent. Insect Biochem 21: 535–539.
Christeller JT, Burgess EPJ, Mett V, Gatehouse HS, Markwick NP, Murray C et al. The expression of a mammalian proteinase inhibitor, bovine spleen trypsin inhibitor (SI), in tobacco and effects on Helicoverpa armigera larvae. Transgenic Res 11: 163–176.
Christeller J, Sutherland P, Murray C, Markwick N, Phung M, Burgess E et al. (2000) Chimeric polypeptides allowing expression of plant-noxious proteins. International Patent No. WO 00/04049. Viewable at http://www.delphion.com/details?&pn=WO00004049A1&abl=fr#ABST
Dadd RH (1985) Nutrition: organisms. In: Kerkut GA and Gilbert LL (eds), Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology. (pp. 313–390) Pergamon Press, New York.
Du C and Nickerson KW(1995) Insecticidal activity of avidin. Abstr 1995 Mtg Soc Invertebr Pathol p. 70.
Fitt GP, Mares CL, Llewellyn DJ, Hokkanen HMT and Deacon J (1994) Field evaluation and potential ecological impact of transgenic cottons Gossypium hirsutum in Australia. Biocontrol Sci Technol 4: 535–548.
Forrester NW (1997) The benefits of insect-resistant cotton. In: McLean GD, Waterhouse PM, Evans G and Gibbs MJ (eds), Commercialisation of Transgenic Crops: Risk, Benefit and Trade Considerations, Department of Primary Industries and Energy Bureau of Resource Sciences, Proceedings of a workshop held in Canberra, pp. 239–242.
Gleave AP (1992) A versatile binary vector system with a T-DNA organisational structure conducive to efficient integration of cloned DNA into the plant genome. Plant Mol Biol 20: 1203–1207.
Gope ML, Keinänen RA, Kristo PA, Conneely OM, Beattie WG, Zarucki-Schulz T et al. (1987) Molecular cloning of the chicken avidin cDNA. Nucl Acids Res 15: 3595–3606.
Guilin C and Yunxi L (1996) Cotton bollworm resistance and its development in northern cotton region of China 1984–1995. Resistant Pest Management 8: 32–33.
Hill D (1975) Agricultural Insect Pests of the Tropics and their Control. Cambridge University Press, London.
Hood EE, Witcher DR, Maddock S, Meyer T, Baszczynski C, Bailey Met al. (1997) Commercial production of avidin from transgenic maize: characterization of transformant, production, processing, extraction and purification. Mol Breed 3: 291–306.
Kalbfleisch JD and Prentice RL (1980) Statistical Analysis of Failure Time Data. Wiley, New York.
Knowles JR (1989) The mechanism of biotin-dependent enzymes. Ann Rev Biochem 58: 195–211.
Kopinski JS, Leibholz J and Love RJ (1989) Biotin studies with pigs. 5. The post-ileal absorption of biotin. Br J Nutr 62: 781–789.
Kramer KJ, Morgan TD, Throne JE, Dowell FE, Bailey M and Howard JA (2000) Transgenic avidin maize is resistant to storage insect pests. Nature Biotech 18: 670–674.
Kumble V and Reed W (1981) Heliothis: a global problem. Proc Int Workshop on Heliothis Management, ICRISAT Center, Patancheru, India, pp. 9–14.
Levinson HZ and Bergmann ED (1959) Vitamin deficiencies in the housefly produced by antivitamins. J Insect Physiol 3: 293–305.
Levinson HZ, Barelkovsky J and Bar Ilan AR (1967) Nutritional effects of vitamin omission and antivitamin administration on development and longevity of the hide beetle Dermestes maculatus Deg (Coleoptera, Dermestidae). J Stored Prod Res 3: 345–352.
Levinson HZ, Levinson AR and Offenberger M (1992) Effect of dietary antagonists and corresponding nutrients on growth and reproduction of the flour mite (Acarus siro L). Experientia 48: 721–729.
Li SQ and Rahmann H (1997) Cotton pest management in China. I: Insect pests. Zeitschrift fur Pflanzenkrankheiten und Pflanzenschutz 104: 611–621.
MacIntosh SC, Kishore GM, Perlak FJ, Marrone PG, Stone TB, Sims SR et al. (1990) Potentiation of Bacillus thuringirnsis insecticidal activity by serine protease inhibitors. J Agric Food Chem 38: 1145–1152.
Malone LA and Pham-Delègue MH (2001) Effects of transgene products on honey bees and bumblebees. Apidologie 32: 287–304.
Marek J and Navratilova M (1995) A new glasshouse pest, Helicoverpa armigera (Noctuidae, Lepidoptera). Ochrana Rostlin 31: 143–147.
Markwick NP, Christeller JT, Docherty LC and Lilley CM (2001) Insecticidal activity of avidin and streptavidin against four species of pest Lepidoptera. Entomol Exp Appl 98: 59–66.
McManus MT and Burgess EPJ (1995) Effects of the soybean (Kunitz) trypsin inhibitor on growth and digestive proteases of larvae of Spodoptera litura. J Insect Physiol 41: 731–738.
McManus MT, Burgess EPJ, Philip B, Watson L, Laing WA, Voisey CR et al. (1999) Expression of the soybean (Kunitz) trypsin inhibitor in transgenic tobacco: effects on larval development of Spodoptera litura. Transgenic Res 8: 383–395.
Morgan TD, Oppert B, Czapla TH and Kramer KJ (1993) Avidin and streptavidin as insecticidal and growth inhibiting dietary proteins. Entomol Exp Appl 69: 97–108.
Murray C and Christeller JT (1995) Purification of a trypsin inhibitor (PFTI) from pumpkin fruit phloem exudate and isolation of putative trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitor cDNA clones. Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler 376: 281–287.
Murray C, Sutherland PW, Phung MM, Lester MT, Marshall RK and Christeller JT (2001) Expression of biotin-binding proteins, avidin and streptavidin, in plant tissues using plant vacuolar targeting sequences. Transgenic Res 11: 201–216.
Olson RI (1999) Vitamin deficiency, dependency, and toxicity. In: Beers MH and Berkow R (eds), The Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy. The Centennial edn, Whitehouse Station, New York, pp. 35–51.
Payne RW, Lane PW, Digby PGN, Harding SA, Leech PK, Morgan GW et al. (1993) Genstat 5 Release 3 Reference Manual. Lawes Agricultural Trust, Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Pilcher CD and Rice ME (1998) Management of European corn borer (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) and corn rootworms (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) with transgenic corn: a survey of farmer perceptions. Am Entomol 44: 36–44.
Raju SSD, Hammerlindl JK, Panchuk B, Pelcher LE and Keller W (1992) Modified binary plant transformation vectors with the wild-type gene encoding NPTII. Gene 122: 383–384.
Reynolds D and Armes N (1994) When insecticides fail: the case of the cotton bollworm in India. In: Cartwright A (ed.), World Agriculture London. (pp. 39–42) Sterling Publications, London.
Sahayaraj K and Paulraj MG (1998) Screening the relative toxicity of some plant extracts to Spodoptera litura Fab. (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) of groundnut. Fresenius Environ Bull 7: 9–10; 557–560.
Sekhar PR, Roa NV, Rao BR and Venkataiah M (1995) Current status of synthetic pyrethroid resistance in Helicoverpa armigera populations on groundnut. Int Arachis Newslett 15: 62–63.
Shanower TG, Romeis J and Minja EM (1999) Insect pests of pigeonpea and their management. Ann Rev Entomol 44: 77–96.
Simpson RM, Burgess EPJ and Markwick NP (1997) Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin binding sites in two Lepidoptera, Wiseana spp. and Epiphyas postvittana. J Invertebr Pathol 70: 136–142.
Tsiropoulos GR (1985) Dietary administration of antivitamins affected the survival and reproduction of Dacus oleae. Z Ang Entomol 100: 35–39.
Van den Berg H (1997) Bioavailability of biotin. Eur J Clin Nutr 51: S60–S61.
Velázquez A, Zamudio S, Báez A, Murguía-Corral R, Rangel-Peniche and Carrasco A (1990) Indicators of biotin status: a study of patients on prolonged total parenteral nutrition. Eur J Clin Nutr 44: 11–16.
Venables WN and Ripley BD (1997) Modern Applied Statistics with S-Plus. 2nd edn, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Whalon ME and Norris D (1997) Bacillus thuringiensis transgenic plants: Will resistance kill the promise? In: McLean GD, Waterhouse PM, Evans G and Gibbs MJ (eds), Commercialisation of Transgenic Crops: Risk, Benefit and Trade Considerations, Department of Primary Industries and Energy Bureau of Resource Sciences, Proceedings of a workshop held in Canberra, pp. 243–258.
Wood HG and Barden RE (1977) Biotin enzymes. Ann Rev Biochem 46: 385–413.
Wurtele ES and Nikolau BJ (1990) Plants contain multiple biotin enzymes: discovery of 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA-carboxylase, propionyl-CoA carboxylase and pyruvate carboxylase in the plant kingdom. Arch Biochem Biophys 278: 179–186.
Zaz GM and Kushwaha KS (1984) Efficacy of Bacillus cereus Frankland and Frankland against different instars of Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) fed on treated cauliflower leaves. J Entomol Res 8: 216–219.
Zhang JH, Wang CZ and Qin JD (2000) The interactions between soybean trypsin inhibitor and delta-endotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis in Helicoverpa armigera larvae. J Invertebr Pathol 75: 259–266.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burgess, E.P., Malone, L.A., Christeller, J.T. et al. Avidin Expressed in Transgenic Tobacco Leaves Confers Resistance to Two Noctuid Pests, Helicoverpa Armigera and Spodoptera Litura . Transgenic Res 11, 185–198 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015297302990
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015297302990