Abstract
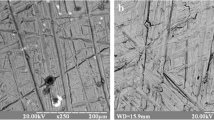
In the biomedical field, the synthetic hydroxyapatite [Ca10(PO)4(OH)2], with similarity to the inorganic component of bone but brittle, has been considered as the appropriate coating on stronger implant materials, such as metallic implants, for presenting a surface which is conductive to bone formation. Many industrial and laboratory techniques were developed to apply hydroxyapatite onto metallic substrates, such as electrophoretic deposition, ion sputtering, hot isostatic pressing, pulsed laser deposition and the only widely used method commercially available: plasma spraying. This work presents a new approach on how to bind calcium phosphate (CaP) to the Ti alloy with a well-known technique in the metallurgical field: laser surface alloying, in order to overcome the drawbacks of plasma spraying. The analysis of the results obtained and the description of the phenomena that take place in the coating process will complete this explorative study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Z. Legeros, Adv. Dent. Res. 2 (1988) 164.
L. L. Hench and J. Wilson, in “An Introduction to Bioceramics”, edited by L. L. Hench and J. Wilson (World Scientific, Singapore, 1993) pp. 1-24.
J. F. Kay, Dent. Clin. North. Amer. 36 (1992) 1.
B. Koch, J. G. C. Wolke and K. De Groot, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 24 (1990) 655.
S. R. Radin and P. Ducheine, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 3 (1992) 33.
M. J. Filiaggi, R. M. Pilliar and N. A. Coombs, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 27 (1993) 191.
H. Ji and P. M. Marquis, Biomaterials 14 (1993) 64.
P. Cheang and K. A. Khor, J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 48 (1995) 429.
J. G. C. Wolke, K. Van Dijk, H. G. Schaeken, K. De Groot and J. A. Jansen, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 28 (1994) 1477.
T. S. Chen and W. R. Lacefield J. Mater. Res. 9 (1994) 1284.
M. Shirkhanzadeh, M. Azadegan, V. Stack and S. Schreyer, Mater. Lett. 18 (1994) 211.
C. M. Cotell, D. B. Chrisey, K. S. Grabowski, J. A. Sprague and C. R. Gossett, J. Appl. Biomat. 3 (1992) 87.
P. Baeri, L. Torrisi, N. Marino and G. Foti, Appl. Surf. Sci. 54 (1992) 210.
G. Sardin, M. Varela and J. L. Morenza, in “Hydroxyapatite and Related Materials”, edited by P. W. Brown and B. Constanz (CRC Press, Boca Raton, U.S.A. 1994), p. 225.
E. N. Antonov, V. N. Bagratashvili, E. N. Sobol, R. Smith and S. M. Howdle, J. Phys. IV (1994) C4-183.
F. J. GarcÍa-Sanz, M. B. Mayor, J. L. Arias, J. Pou, B. LeÓn and M. PÉrez-Amor, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 8 (1997) 861-865.
Z. Yaping, C. Jiacheng, T. Jifu and Z. Zhirong, Surface and Coating Technol 58 (1993) 125-127.
“Phase diagrams for ceramists”, American Ceramic Society, 12 Volumes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lusquiños, F., Pou, J., Arias, J.L. et al. Alloying of hydroxyapatite onto Ti6Al–4V by high power laser irradiation. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 13, 601–605 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015187129141
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015187129141