Abstract
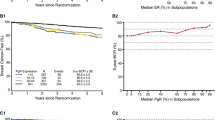
The predictivity of tumour size, oestrogen (ER) and progesterone (PgR) receptors, 3H-thymidine labelling index (TLI), c-erbB-2 and p27kip1 expression on clinical outcome was analysed on a consecutive series of 118 postmenopausal patients with ER-positive, node-positive tumours. All patients were treated with surgery ± radiotherapy and adjuvant tamoxifen (30mg/day) for at least 2 years. TLI, ER, c-erbB-2 and p27kip1 were generally unrelated to each other. PgR was directly related to ER and inversely to c-erbB-2. Tumour size was inversely related to both c-erbB-2 and p27kip1 expression. At a median follow-up of 75 months, 5-year relapse-free survival was significantly lower for patients with very rapidly proliferating (HR=2.61, 95% CI=1.34–5.08), PgR negative (HR=2.76, 95% CI=1.43–5.33) or relatively low ER content (HR=2.20, 95% CI=1.14–4.25) tumours than for patients with tumours expressing the opposite biological profiles. Overall survival was also significantly different as a function of TLI (HR=3.47, 95% CI=1.52–7.93) and PgR (HR=2.27, 95% CI=1.00–5.15). TLI and PgR maintained an independent relevance in multivariate analysis and together were capable of identifying subgroups of patients at significantly different risk of relapse and death.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Whelan SL, Ferlay J, Raymond L, Young J (eds): Cancer incidence in five continents. IARC Sci Publ VII(143): 446-742, 1997
Merkel DE, Osborne CK: Prognostic factors in breast cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 3(4): 641-652, 1989
Moustafa AS, Nicolson GL: Breast cancer metastasisassociated genes: prognostic significance and therapeutic implications. Oncol Res 9: 505-525, 1997
Goldhirsch A, Glick JH, Gelber RD, Senn, HJ: Commentary: Meeting highlights-International Consensus Panel on the Treatment of Primary Breast Cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 90(21): 1601-1608, 1998
Dhingra K, Hortobagyi GN: Critical evaluation of prognostic factor. Semin Oncol 23(4): 436-445, 1996
Révillion F, Bonneterre J, Peyrat JP: ERBB2 oncogene in human breast cancer and its clinical significance. Eur J Cancer 34(6): 791-808, 1998
Pegram MD, Konecny G, Slamon DJ: Use of HER2 for predicting response to breast cancer therapy. In: Harris JR, Lippman ME (eds). Disease of the Breast-update. Vol. 4, pp 1-9, 1999
Yokota T, Imamura M, Teshima S, Suzuki H, Tezuka F, Kikuchi S, Kunii Y, Yamauchi H: c-erbB-2, p53 protein expression and steroid hormone receptor in breast carcinomas: an immunohistochemical study. Anticancer Res 19(5B): 4007-4012, 1999
Elledge RM, Green S, Howes L, Clark GM, Berardo M, Allred DC, Pugh R, Ciocca D, Ravdin P, O'sullivan J, Rivkin S, Martino S, Osborne CK: bcl-2, p53, and response to tamoxifen in estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: a Southwest Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol 15(5): 1916-1922, 1997
Wu J, Shen ZZ, Lu JS, Jiang M, Han QX, Fontana JA, Barsky SK, Shao ZM: Prognostic role of p27kip1 and apoptosis in human breast cancer. Br J Cancer 79(9/10): 1572-1578, 1999
Cariou S, Catzavelos C, Slingerland JM: Prognostic implications of expression of the cell cycle inhibitor protein p27kip1. Breast Cancer Res Treat 52(1-3): 29-41, 1998
Clark GM: Prognostic and predictive factors. In: Harris JR, Lippman ME, Morrow M, Hellman S (eds) Disease of the Breast. 1996, Philadelphia, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, pp 461-485
Bernoux A, De Cremoux P, Laine-Bidron C, Martin EC, Asselain B, Magdelenat H: Estrogen receptor negative and progesterone receptor positive primary breast cancer: pathological characteristics and clinical outcome. Institut Curie Breast Cancer Study Group. Breast Cancer Res Treat 49(3): 219-225, 1998
Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group. Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet, 351(9114): 1451-1467, 1998
Osborne CK: Steroid hormone receptor in breast cancer management. Breast Cancer Res Treat 51(3): 227-238, 1998
Chang J, Powles TJ, Allred DC, Ashley SE, Clark GM, Makris A, Assersohn L, Gregory RD, Osborne CK, Dowsett M: Biologic markers as predictors of clinical outome from systemic therapy for primary operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 17(10): 3058-3063, 1999
Silvestrini R, Daidone MG, Mastore M, Di Fronzo G, Coradini D, Boracchi P, Squicciarini P, Salvadori B, Veronesi U: Cell kinetics as a predictive factor in node-positive breast cancer treated with adjuvant hormone therapy. J Clin Oncol 11(6): 1150-1155, 1993
Gardin G, Alama A, Rosso R, Campora E, Repetto L, Pronzato P, Merlini L, Naso C, Camoriano A, Meazza R: Relationship of variations in tumor cell kinetics induced by primary chemotherapy to tumor regression and prognosis in locally advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 32: 311-318, 1994
Bonetti A, Zaninelli M, Rodella S, Molino AM, Sperotto L, Piubello Q, Bonetti F, Nortilli R, Turazza M, Cetto GL: Tumor proliferative activity and response to first-line chemotherapy in advanced breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat 38: 289-297, 1996
MacGrogan G, Mauriac L, Durand M, Bonichon F, Trojani M, de Mascarel I, Coindre JM: Primary chemotherapy in breast invasive carcinoma: predictive value of the immunohistochemical detection of hormonal receptors, p53, c-erbB-2, MiB1, pS2 and GST pi. Br J Cancer 74(9): 1458-1465, 1996
Makris A, Powles TJ, Dowsett M, Osborne CK, Trott PA, Fernando IN, Ashley SK, Ormerod MG, Titley JC, Gregory RK, Allred DC: Prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemoendocrine therapy in primary breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 3(4): 593-600, 1997
Willsher PC, Pinder SE, Gee JM, Ellis IO, Chan SY, Nicholson RI, Blamey RW, Robertson JF: C-erbB-2 expression predicts response to preoperative chemotherapy for locally advanced breast cancer. Anticancer Res 18(5B): 3695-3698, 1998
Stal O, Skoog L, Rutqvist LE, Carstensen JM, Wingren S, Sullivan S, Andersson AC, Defmats M, Nordenskjold B: S-phase fraction and survival benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy of breast cancer. Br J Cancer 70(6): 1258-1262, 1994
Ferno M, Baldetorp R, Bendhal PO, Borg A, Ewers SB, Olsson H, Ryden S, Sigursson H, Killander D: Recurrence-free survival in breast cancer improved by adjuvant tamoxifenespecially for progesterone receptor positive tumors with a high proliferation. Breast Cancer Res Treat 36(1): 23-34, 1995
Sjöström J, Krajewski S, Franssila K, Niskanen E, Wasenius VM, Nordling S, Reed JC, Blomqvist C: A multivariate analysis of tumour biological factors predicting response to cytotoxic treatment in advanced breast cancer. Br J Cancer 78(6): 812-815, 1998
Koscielny S, Terrier P, Daver A, Wafflart J, Goussard J, Ricolleau G, Delvincourt C, Delarue JC: Quantitative determination of c-erbB-2 in human breast tumours: potential prognostic significance of low values. Eur J Cancer 34(4): 476-481, 1998
Ross JS, Fletcher JA: The HER-2/neu oncogene in breast cancer: prognostic factor, predictive factor, and target for therapy. Stem Cells 16: 413-428, 1998
Tan P, Cady B, Wanner M, Worland P, Cukor B, Magi-Galluzzi C, Lavin P, Draetta G, Pagano M, Loda M: The cell cycle inhibitor p27 is an independent prognostic marker in small (T1a,b) invasive breast carcinomas. Cancer Res 57: 1259-1263, 1997
Porter PL, Malone KE, Heagerty PJ, Alexander GM, Gatti LA, Firpo EJ, Daling JR, Roberts JM: Expression of cell-cycle regulators p27Kip1 and cyclin E, alone and in combination, correlate with survival in young breast cancer patients. Nat Med 3(2): 222-225, 1997
Catzavelos C, Bhattacharya N, Ung YC, Wilson JA, Roncari L, Sandhu C, Shaw P, Yeger H, Morava-Protzner I, Kapusta L, Franssen E, Pritchard KI, Singerland JM: Decreased level of the cell-cycle inhibitor p27kip1 prote in: prognostic implications in primary breast cancer. Nat Med 3(2): 227-230, 1997
Leong AC, Hanby AM, Potts HWW, Tan DSP, Skilton D, Ryder K, Harris WH, Liebmann RD, Barnes DM, Gillet CE: Cell cycle proteins do not predict outcome in grade I infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast. Int J Cancer (Pred Oncol) 89: 26-31, 2000
Reed W, Flörenes VA, Holm R, Hannisdal E, Nesland JM: Elevated levels of p27, p21 and cyclin D1 correlate with positive oestrogen and progesterone receptor status in node-negative breast carcinoma patients. Virchows Arch 435(2): 116-124, 1999
Volpi A, De Paola F, Nanni O, Granato AM, Bajorko P, Becciolini A, Scarpi E, Riccobon A, Balzi M, Amadori D: Prognostic significance of biologic markers in node-negative breast cancer patients: a prospective study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 63: 181-192, 2000
Silvestrini R: Feasibility and reproducibility of the 3H-TdR Labeling Index in breast cancer. The SICCAB Group for quality control of cell kinetic determination. Cell Prolif 21: 437-445, 1991
Piffanelli A, Pellizzola D, Giovannini G, Catozzi L, Faggioli L, Giganti M: Characterization of laboratory working standards for quality control of immunometric and radiometric estrogen receptor assays. Clinical evaluation of breast cancer biopsies. Tumori 75: 550-556, 1989
Kaplan EL, Meier P: Non parametric estimation for incomplete observation. J Am Stat Assoc 53: 457-481, 1958
Sancho-Garnier H, Delarue JC, Mouriesse H, Contesso G, May-Levin F, Gottelnad M, May E: Is the negative prognostic value of high oestrogen receptor (ER) levels in postmenopausal breast cancer patients due to a modified ER gene product? Eur J Cancer 31A: 1851-1855, 1995
Thorpe SM, Christensen IJ, Rasmussen BB, Rose C: Short recurrence-free survival associated with high oestrogen receptor levels in the natural history of postmenopausal, primary breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 29A: 971-977, 1993
Allred DC, Clark GM, Tandon AK, Molina R, Tormey DC, Osborne CK, Gilchrist KW, Mansour EG, Abeloff M, Eudey L: HER-2/neu in node-positive breast cancer: prognostic significance of overexpression influenced by the presence of in situ carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 10: 599-605, 1992
Amadori D, Nanni O, Marangolo M, Pacini P, Ravaioli A, Rossi A, Gambi A, Catalano G, Perroni D, Scarpi E, Casadei Giunchi D, Tienghi A, Becciolini A, Volpi A: DFS advantage of adjuvant CMF in node negative rapidly proliferating breast cancer patients: a randomised multicentre study. J Clin Oncol 18(17): 3125-3134, 2000
Silvestrini R, Luisi A, Zambetti M, Cipriani S, Valagussa P, Bonadonna G, Daidone MG: Cell proliferation and aoutcome following doxorubicin plus CMF regimens in node-positive breast cancer. Int J Cancer 87(3): 405-411, 2000
Cox DR: Regression models and life tables. J Royal Stat Soc 34: 187-220, 1972
Lawless JS: Statistical models and methods for life-time data. Wiley Publishers, New York, 1982
SAS Institute Inc. SAS/STATUser's Guide, version 6, 4th edn, Vol. 1, Cary NC: SAS Institute, 1989, pp 943.
Silvestrini R, Daidone MG, Benini E, Faranda A, Tomasic G, Boracchi P, Salvadori B, Veronesi U: Validation of p53 accumulation as a predictor of distant metastasis at 10 years of follow-up in 1400 node-negative breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res 2: 2007-2013, 1997
Korzeniowski S, Dyba T, Skolyszewski J: Classical prognostic factors for survival and loco-regional control in breast cancer patients treated with radical mastectomy alone Acta Oncol 33(7): 759-765, 1994
Amadori D, Volpi A, Callea A, Amaducci L, Morgagni S, Magni E, Nanni O: Clinical relevance of cell kinetics in breast cancer. Ann N.Y. Acad Sci 698: 186-192, 1993
Paradiso A, Tommasi S, Mangia A, Lorusso V, Simone G, De Lena M: Tumor proliferative activity, progesterone receptor status, estrogen receptor level, and clinical outcome of estrogen receptor positive advanced breast cancer. Cancer Res 50: 2958-2962, 1990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scarpi, E., Paola, F.D., Sarti, M. et al. Biomarker prediction of clinical outcome in operable breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res Treat 68, 101–110 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011975510181
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011975510181