Abstract
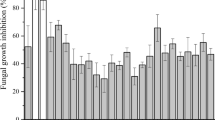
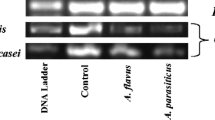
Antimutagenic activity of Lactobacillus plantarum KLAB21, isolated from Korean kimchi, was investigated against MNNG (N-methyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine), NQO (4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide), NPD (4-nitro-O-phenylenediamine) and aflatoxin B1 using Salmonella typhimurium strains TA100 and TA98. Although all the cell fractions including the culture supernatant, dry cells and cell-free extract exhibited antimutagenic activity against MNNG and NQO, the culture supernatant possessed the highest activity. The antimutagenic ratio of the culture supernatant was 98.4% against MNNG on strain TA100 and 57.3% against NQO on strain TA98. Its antimutagenic activity was reconfirmed by a Bacillus subtilis spore-rec assay. Levels of the antimutagenic ratios of other lactic acid bacteria originating from fermented milk ranged between 26.8 to 53% against MNNG and 28.5 to 43.4% against NQO. The antimutagenic activities of the strain KLAB21 against NPD were 72.6% on TA100 and 62.8% on TA98, and those against aflatoxin B1 were 82.5% on TA100 and 78.2% on TA98.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi S (1992) Lactic acid bacteria and the control of tumors. In: Wood BJB, ed. The Lactic Acid Bacteria in Health and Disease. London: Elsevier Applied Science, pp. 233-261.
Alm L (1982) Effect of fermentation of lactose, glucose and lactose content milk and suitability of fermented milk products for lactose intolerant individuals. J. Dairy Sci. 63: 346-351.
Carmeron E,Pauling L,Leibovitz B (1979) Ascorbic acid and cancer: a review. Cancer. Res. 39: 663-668.
Dodd HM,Gasson MJ (1994) Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. In: Gasson MJ, ed. Genetics and Biotechnology of Lactic Bacteria. London: Blackie Academic & Professional, pp. 211-251.
Hosono A,Sagae S,Tokita F (1986) Desmutagenic effect of cultured milk on chemically induced mutagenesis in Escherichia coli B/r LWP2 trp-hcr. Milchwissenschaft 41: 142-145.
Hosono A,Wardojo R,Otani H (1990) Inhibitory effects lactic acid bacteria from fermented milk on the mutagenicities of volatile nitrosamines. Agric. Biol. Chem. 54: 1639-1643.
Kada T,Kaneko K,Matsuzaki T,Hara T (1985) Detection and chemical identification of natural bio-antimutagens: a case of the green tea factor. Mutat. Res. 150: 127-132.
Kandler O,Weiss N (1986) Genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, 212AL. In: Krieg NR,Holt JG, eds. Bergey' Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Vol 2. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, pp. 1209-1234.
Kim ES,Chun HC,Kim BK,Rhee KC (1997) Garlic and cancer prevention. Korean J. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2: 180-190.
Maron DM,Ames BN (1983) Revised methods for the Salmonella mutagenicity test. Mutat. Res. 113: 173-219.
Nishioka K,Miyamoto T,Kataoka K,Nakae T (1989) Prelimmary studies on antimutagenic activities of lactic acid bacteria. Japan J. Zootech. Sci. 60: 491-494.
Parente E,Ricciardi A (1999) Production, recovery and purification of bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 52: 628-638.
Park KY,Baek KA,Rhee SH,Cheigh HS (1995) Antimutagenic effect of kimchi. Food Biotechnol. 4: 41-145.
Perdigon G,Nacer ME,Alvarez S,Oliver G,de Ruiz Golgado AP (1988) Systematic augmentation of the immune system response in mice feeding fermented milks with Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus acidophilus. Immunology 63: 17-23.
Rhee CH,Park HD (1999) Isolation and characterization of lactic acid bacteria producing antimutagenic substance from Korean kimchi. Korean J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 27: 15-22.
Rhee CH,Park HD (2001) Three glycoproteins with antimutagenic activity identified in Lactobacillus plantarum KLAB21. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., in press.
Sandine WE,Muralidhara KS,Elliker PR,England DC (1972) Lactic acid bacteria in food and health: a review with special reference to enteropathogenic Escherichia coli as well as certain enteric diseases and their treatment with antibiotics and lactobacilli. J. Milk Food. Technol. 35: 691-702.
Shun YL,Ayres JA,Winkler W,Sandine WE (1989) Lactobacillus effect on cholesterol: in vitro and in vivo results. J. Dairy Sci. 72: 2884-2889.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, HD., Rhee, CH. Antimutagenic activity of Lactobacillus plantarum KLAB21 isolated from kimchi Korean fermented vegetables. Biotechnology Letters 23, 1583–1589 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011921427581
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011921427581