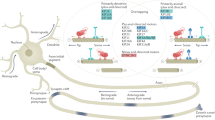
Abstract
The recent demonstration that the axonal transport motors kinesin and dynein participate in axonal transport of neurofilaments (NFs), and that the association of NFs with these motors is regulated by phosphorylation provides new insight into several aspects of axonal transport and NF biology. This review juxtaposes older and more recent findings on NF dynamics, and speculates on the organization of axonal NFs as suggested by real-time analyses of NF transport.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AHMAD, F. J., ECHEVERRI, C. J., VALLEE, R. B. & BAAS, P. W. (1998) Cytoplasmic dynein and dynactin are required for the transport of microtubules into the axon. Journal of Cell Biology 140, 391-401.
AHMAD, F. J., HUGHEY, J., WITTMANN, T., HYMAN, A., GREASER, M. & BAAS, P. W. (2000) Motor proteins regulate force interactions between microtubules and microfilaments in the axon. Nature Cell Biology 2, 276-280.
ANDERTON, B. H., BREINBURG, D., DOWNES, M. J., GREEN, P. J., TOMLINSON, B. E., ULRICH, J., WOOD, J. N., & KAHN, J. (1982) Monoclonal antibodies show that neurofibrillary tangles and neurofilaments share antigenic determinants. Nature 298, 84-86.
BORCHELT, D. R., WONG, P. C., BECHER, M. W., PARDO, C. A., LEE, M. K., XU, Z. S., THINAKARAN, G., JENKINS, N. A., COPELAND, N. G., SISODIA, S. S., CLEVELAND, D. W., PRICE, D. L. & HOFFMAN, P. N. (1998) Axonal transport of mutant superoxide dismutase 1 and focal axonal abnormalities in the proximal axons of transgenic mice. Neurobiology of Disease 5, 27-35.
BRADY, S. T. (1993) Motor neurons and neurofilaments in sickness and health. Cell 73, 1-3.
BRADY, S. T. (2000) Neurofilaments run sprints not marathons. Nature Cell Biology 2, E43-E45.
BROWN, A. (1998) Continguous phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated domains along axonal neurofilaments. Journal of Cell Science 111, 455-467.
BROWN, A. (2000) Slow axonal transport: Stop and go traffic in the axon. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 1, 153-156.
COOKSON, M. R. & SHAW, P. J. (1999) Oxidative stress and motor neurone disease. Brain Pathology 9, 165-186.
CHOU, Y.-H. & GOLDMAN, R. D. (2000) Intermediate filaments on the move. Journal of Cell Biology 150, F101-F105.
DILLMAN, III, J. F., DABNEY, L. P. & PFISTER, K. K. (1996) Functional analysis of dynactin and cytoplasmic dynein in slow axonal transport. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science 93, 141-144.
ELLURU, R. G., BLOOM, G. S. & BRADY, S. T. (1995) Fast axonal transport of kinesin in the rat visual system: functionality of kinesin heavy chain isoforms. Molecular Biology of the Cell 6, 21-40.
EYER, J. & LETERRIER, J. F. (1988) Influence of the phosphorylation state of neurofilament proteins on the interactions between purified filaments in vitro. Journal of Biochemistry 252, 655-660.
GALBRAITH, J. A., REESE, T. J., SCHLIEF, M. L. & GALLANT P. E. (1999) Slow transport of umpolymerized tubulin and polymerized neurofilament in the squid giant axon. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science 96, 11589-11594.
GIASSON, B. I. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1996) Aberrant stress-induced phosphorylation of perikaryal neurofilaments. Journal of Biological Chemistry 271, 30404-30409.
GIASSON, B. I. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1997) Study of proline-directed protein kinases involved in phosphorylation of the heavy neurofilament subunit. Journal of Neuroscience 17, 9466-9472.
GLASS, J. D. & GRIFFIN, J. W. (1991) Neurofilament redistribution in transected nerves: evidence for bidirectional transport of neurofilaments. Journal of Neuroscience 11, 3146-3154.
GLASS, J. D. & GRIFFIN, J. W. (1994) Retrograde transport of radiolabeled cytoskeletal proteins in transected nerves. Journal of Neuroscience 14, 3915-3921.
GOTOW, T. & TANAKA, J. (1994) Phosphorylation of neurofilament H subunit as related to arrangement of neurofilaments. Journal of Neuroscience Research 37, 691-713.
GUIDATO, S., TSAI, L.-H., WOODGETT, J. & MILLER, C. J. (1996) Differential cellular phosphorylation of neurofilament heavy side-arms by glycogen synthase kinase-3 and cyclin-dependent kinase-5. Journal of Neurochemistry 66, 1698-1706.
HAAFEZPARAST, M., WITHERDEN, A., NICHOLSON, S., BERMINGHAM, N., MACKIN, J., TEN ASBROEK, A., BALL, S., PETERS, J., BAAS, F., MARTIN, J. E. & FISHER, E. M. (1999) kinesin light chain gene: its mapping and exclusion in mouse and human forms of inherited motor neuron degeneration. Neuroscience Letters 273, 49-52.
HIROKAWA, N. (1993) Axonal transport and the cytoskeleton. Current Opinions in Neurobiology 3, 724-731.
JULIEN, J.-P. & MUSHYNSKI, W. E. (1998) Neurofilaments in health and disease. Progress in Nucleic Acid Research and Molecular Biology 61, 1-20.
JUNG, C., YABE, J. T., LEE, S. & SHEA, T. B. (2000a) Hypophosphorylated neurofilament subunits undergo axonal transport more rapidly than more extensively phosphorylated subunits in situ. Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 47, 120-129.
JUNG, C., YABE, J. T. & SHEA, T. B. (2000b) C-terminal phosphorylation of the high molecular weight neurofilament subunit correlates with decreased neurofilament axonal transport velocity. Brain Research 856, 12-19.
JUNG, C., YABE, J., WANG, F.-S. & SHEA, T. B. (1998) Neurofilaments are present within axonal neurites before incorporation into Triton-insoluble structures. Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 40, 44-58.
JUNG, C. & SHEA, T. B. (1999) Regulation of neurofilament axonal transport by phosphorylation in optic axons in situ. Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 43, 230-240.
JUNG, C., YABE, J. T. & SHEA, T. B. (2000) C-terminal phosphorylation of the heavy molecular weight neurofilament subunit correlates with decreased neurofilament axonal transport velocity. Brain Research 856, 12-19.
KOEHNLE, T. J. & BROWN, A. (1999) Slow axonal transport of neurofilament protein in cultured neurons. Journal of Cell Biology 144, 447-458.
LASEK, R. J., GARNER, J. A. & BRADY, S. T. (1985) Axonal transport of the cytoplasmic matrix. Journal of Cell Biology 99, 212s-221s.
LASEK, R. J., PAGGI, P. & KATZ, M. J. (1992) Slow axonal transport mechanisms move neurofilaments relentlessly in mouse optic axons. Journal of Cell Biology 117, 607-616.
LASEK, R. J., PAGGI, P. & KATZ, M. J. (1993) The maximum rate of neurofilament transport in axons: A view of molecular transport mechanisms continuously engaged. Brain Research 616, 58-64.
LETERRIER, J.-F. & EYER, J. (1987) Properties of highly viscous gels formed by neurofilaments in vitro. A possible consequence of specific inter-filament cross-bridging. Biochemical Journal 245, 93-101.
LETERRIER, J.-F., KÄS, J., HARTWIG, J., VEGNERS, R. & JANMEY, P. (1996) Mechanical effects of neurofilament cross-bridges. Journal of Biological Chemistry 271, 15687-15694.
LI, B. S., VEERANNA, GU, J., GRANT, P. & PANT, H. C. (1999) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (Erk1 and Erk2) cascade results in phosphorylation of NF-Mtail domains in transfectedNIH3T3 cells. European Journal of Biochemistry 262, 211-217.
LIAO, G. & GUNDERSEN, G. G. (1998) Kinesin is a candidate for cross-bridging microtubules and intermediate filaments. Selective binding of kinesin to detyrosinated tubulin and vimentin. Journal of Biological Chemistry 273, 9797-9803.
MA, D., HIMES, B. T., SHEA, T. B. & FISCHER, I. (2000) Axonal transport of microtubule-associated protein 1B (MAP1B) in the sciatic nerve of adult rat: Distinct transport rates for different isoforms. Journal of Neuroscience 20, 2122-2120.
NIXON, R. A. (1993) The regulation of neurofilament protein dynamics by phosphorylation: Clues to neurofibrillary pathology. Brain Pathology 3, 29-38.
NIXON, R. A. (1998) The slow transport of cytoskeletal proteins. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 10, 87-92.
NIXON, R. A. & LOGVINENKO K B (1986) Multiple fates of newly synthesized neurofilament proteins: Evidence for a stationary neurofilament network distributed non-uniformly along axons of retinal ganglion cell neurons. Journal of Cell Biology 102, 647-659.
OCHS, S. (1975) A unitary concept of axoplasmic transport based on the transport filament hypothesis. In Recent Advances in Myology (edited by BRADLEY, WG et al.,) Excerpta Medica 360 pp. 189-94, Amsterdam.
PANT, H. C. & VEERANNA (1995) Neurofilament phosphorylation. Biochemistry and Cell Biology 73, 575-592.
PRAHLAD, V., YOON, M., MOIR, R. D., VALE, R. D. & GOLDMAN, R. D. (1998) Rapid movement of vimentin on microtubule tracks: kinesin-dependent assembly of intermediate filament networks. Journal of Cell Biology 143, 159-170.
PRAHLAD, V., HEFLAND, G. T., LANGFORD G. M., VALE, R. D. & GOLDMAN, R. D. (1998) Fast transport of neurofilament proteins along microtubules in squid axoplasm. Journal of Cell Science 113, 3939-3946.
RATNER, N., BLOOM, G. S. & BRADY, S. T. (1998) A role for cyclin-dependent kinases(s) in the modulation of fast axonal transport: effects defined by olomoucine and the APC suppressor protein. Journal of Neuroscience 18, 7717-7726.
ROY, S., COFFEE, P., SMITH, G., LIEM, R. K. H., BRADY, S. T. & BLACK, M. M. (2000) Neurofilaments are transported rapidly but intermittently in axons: implications for slow axonal transport. Journal of Neuroscience 20, 6849-6861.
SANCHEZ, I., HASSINGER, L., SIHAG, R. K., CLEVELAND, D. W., MOHAN, P. & NIXON, R. A. (2000) Local control of neurofilament accumulation during radial growth of myelinating axons in vivo: selective role of site-specific phosphorylation. Journal of Cell Biology 151, 1013-1024.
SAXTON, W. M. (1994) Isolation and analysis of microtubule motor proteins. Methods in Cell Biology 44, 279-288.
SCHMIDT, M. L., CARDEN, M. J., LEE, V. M.-Y. & TROJANOWSKI, J. Q. (1987) Phosphate dependent and independent neurofilament epitopes in the axonal swellings of patients with motor neuron disease and controls. Laboratory Investigation 56, 282-294.
SHARMA, M., SHARMA, P. & PANT, H. C. (1999) CDK-5-mediated neurofilament phosphorylation in SHSY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Journal of Neurochemistry 73, 79-86.
SHAH, J. V., FLANAGAN, L. A., JANMEY, P. A. & LETERRIER, J.-FL. (2000) Bidirectional translocation of neurofilaments along microtubules mediated in part by dynein/dynactin. Molecular Biology of the Cell 11, 3495-3508.
SHAW, G. & HOU, Z.-C. (1990) Bundling and cross-linking of intermediate filaments of the nervous system. Journal of Neuroscience Research 25, 561-568.
SHEA, T. B. (1990) Neuritogenesis in mouse NB2a/d1 neuroblastoma cells: triggering by calcium influx and involvement of actin and tubulin dynamics. Cell Biology International Reports 14, 967-979.
SHEA, T. B. & YABE, J. T. (2000) Occam's razor slices through the mysteries of neurofilament axonal transport: can it really be so simple? Traffic 1, 522-523.
SHEA, T. B., SIHAG, R. K. & NIXON, R. A. (1990) Dynamics of phosphorylation and assembly of the high Axonal transport of neurofilaments molecular weight NF subunit in NB2a/d1 neuroblastoma. Journal of Neurochemistry 55, 1784-1792.
STRAUBE-WEST, K., LOOMIS, P. A., OPAL, P. & GOLDMAN, R. D. (1996) Alterations in neuronal intermediate filament organization, functional implications and the induction of pathological changes related to motor neuron disease. Journal of Cell Science 109, 2319-2329.
SUN, D, LEUNG, C. L. & LIEM, R. K. (1996) Phosphorylation of the high molecular weight neurofilament protein (NF-H) by cdk5 and p35. Journal of Biological Chemistry 271, 14245-14251.
TASHIRO, T. & KOMIYA, Y. (1989) Stable and dynamic forms of cytoskeletal proteins in slow axonal transport. Journal of Neuroscience 9, 760-768.
TOYOSHIMA, I., KATO, K., SUGAWARA, M., WADA, C. & MASAMUNE, O. (1998a) Kinesin accumulation in chick spinal axonal swellings with beta, beta'-iminodipropionitrile (IDPN) intoxication. Neuroscience Letters 249, 103-106.
TOYOSHIMA, I., SUGAWARA, M., KATO, K., WADA, C., HIROTA, K., HASEGAWA, K., KOWA, H., SHEETZ, M. P. & MASAMUNE, O. (1998b) Kinesin and cytoplasmic dynein in spinal spheroids with motor neuron disease. Journal of Neurological Science 159, 38-44.
TU, P. H., GURNEY, M. E., JULIEN, J.-P., LEEM, V. M.-Y. & TROJANOWSKI, J. Q. (1997) Oxidative stress, mutant SOD1, and neurofilament pathology in transgenic mouse models of human motor neuron disease. Laboratory Investigation 76, 441-456.
VEERANNA, SHETTY, K. T., LINK, W. T., JAFFE, H., WANG, J. & PANT, H. C. (1995) Neuronal cyclindependent kinase-5 phosphorylation sites in neurofilament protein (NF-H) are dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase 2A. Journal of Neurochemistry 64, 2681-2690.
VEERANNA, AMIN, N. D., AHN, N. G., JAFFE, H., WINTERS, C. A., GRANT, P. & PANT, H. C. (1998) Mitogen-activated protein kinases (Erk1, 2) phosphorylate Lys-Ser-Pro (KSP) repeats in neurofilament proteins NF-H and NF-M. Journal of Neuroscience 18, 4008-4021.
WANG, L., HO, C.-I., SUN, D., LIEM, R. K. H. & BROWN, A. (2000) Rapid movements of axonal neurofilaments interrupted by prolonged pauses. Nature Cell Biology 2, 137-141.
WATSON, D. F., GRIFFIN, J. W., FITTRO, K. P. & HOFFMAN, P. N. (1989) Phosphorylation-dependent immunoreactivity of neurofilaments increases during axonal maturation and β, β'-iminodipropionitrile intoxication. Journal of Neurochemistry 53, 1818-1829.
WATSON, D. F., GLASS, J. D. & GRIFFIN, J. W. (1993) Redistribution of cytoskeletal proteins in mammalian axons disconnected from their cell bodies. Journal of Neuroscience 13, 4354-4360.
WILLIAMSON, T. L. & CLEVELAND, D. W. (1999) Slowing of axonal transport is a very early event in the toxicity of ALS-linked SOD1 mutants to motor neurons. Nature Neuroscience 2, 50-56.
WINDORFFER, R. & LEUBE, R. E. (1999) Detection of keratin dynamics by time-lapse fluorescence microscopy in living cells. Journal of Cell Science 112, 4521-4534.
YABE, J. T., PIMENTA, A. & SHEA, T. B. (1999) Kinesinmediated transport of neurofilament protein oligomers. Journal of Cell Science 112, 3799-3814.
YABE, J. T., JUNG, C., CHAN, W. K.-H. & SHEA, T. B. (2000) Phospho-dependent association of neurofilament proteins with kinesin in situ. Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 45, 249-262.
YABE, J. T., CHAN, W. K.-H., CHYLINSKI, T. M., LEE, S., PIMENTA, A. F. & SHEA, T. B. (2001a) The predominant form in which neurofilament subunits undergo axonal transport varies during axonal initiation, elongation and maturation. Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 48, 61-83.
YABE, J. T., CHYLINSKI, T. M., WANG, F.-S., PIMENTA, A. F., KATTAR, S. D., LINSLEY, M.-D., CHAN, W. K.-H. & SHEA, T. B. (2001b) Neurofilaments consist of distinct populations that can be distinguished by Cterminal phosphorylation, bundling and axonal transport rate in growing axonal neurites. Journal of Neuroscience, in press.
ZHANG, J. H., SAMPOGNA, S., MORALES, F. R. & CHASE, M. H. (1997) Age-related alterations in immunoreactivity of the midsized neurofilament subunit in the brainstem reticular formation of the cat. Brain Research 769, 196-200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shea, T.B. Microtubule motors, phosphorylation and axonal transport of neurofilaments. J Neurocytol 29, 873–887 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010951626090
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010951626090