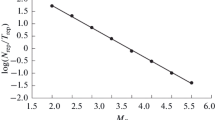
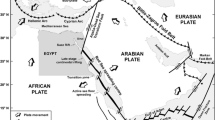
Abstract
A total of 235 potential seismic sources in Iran and neighboring regions are delineated based on available geological, geophysical, tectonic and earthquake data for seismic hazard assessment of the country. In practice, two key assumptions are considered; first, the assumption of earthquake repeatedness, implying that major earthquakes occur preferentially near the sites of previous earthquakes; second, the assumption of tectonic analogy, which implies that structures of analogous tectonic setting are capable of generating same size earthquakes. A two-step procedure is applied for delineation of seismic sources: first, demarcation of seismotectonic provinces; second, determination of potential seismic sources. Preferentially, potential seismic sources are modeled as area sources, in which the configuration of each source zone is controlled, mainly, by the extent of active faults, the mechanism of earthquake faultings and the seismogenic part of the crust.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambraseys, N.N., 1974, The historical seismicity of North-Central Iran, Geol. Surv. Iran, Rep. 29, 47–96.
Ambraseys, N.N., 1978, The relocation of epicenters in Iran, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 53, 117–121.
Ambraseys, N.N. and Melville, C.P., 1977, The seismicity of Kuhistan, Iran, Geogr. J. 143, 179–199.
Ambraseys, N.N. and Melville, C.P., 1982, A History of Persian Earthquakes, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 219 pp.
Ambraseys, N.N. and Tchalenko, J.S., 1969, The Dasht-e-Bayaz (Iran) earthquake of August 31, 1968: a field report, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 59, 1751–1792.
Ambraseys, N.N., Arsovski, M. and Moinfar, A., 1979, The Gisk earthquake of 19 December 1977 and the seismicity of the Kuhbanan Fault-zone, UNESCO Publ. No. FMR/SC/GEO/79/192, Paris.
Asudeh, I., 1983, ISC mislocation of earthquakes in Iran and geometrical residuals, Tectonophysics 95, 61–74.
Baker, C., Jackson, J. and Priestley, K., 1993, Earthquakes on the Kazeron line in the Zagros mountains of Iran: strike-slip faulting within a fold and-thrust belt, Geophys. J. Int. 115, 41–61.
Berberian, M., 1976a, Contribution to the seismotectonics of Iran (part II), Geol. Surv. Iran, Rep. 39.
Berberian, M., 1976b, Seismotectonic map of Iran (1:2 500 000), Geol. Surv. Iran, Rep. 39.
Berberian, M., 1977a, Contribution to the seismotectonics of Iran (part III), Geol. Surv. Iran, Rep. 40.
Berberian, M., 1977b, Isoseismal map of Iran (1900–1977), 1:5 000 000, Geol. Surv. Iran, Rep. 40.
Berberian, M., 1979a, Evaluation of the instrumental and relocated epicenters of Iranian earthquakes, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 58, 625–630.
Berberian, M., 1979b, Earthquake faulting and bedding thrust associated with the Tabas-e-Golshan (Iran) earthquake of September 16, 1978, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 69, 1861–1887.
Berberian, M., 1981, Active faulting and tectonics of Iran. In: Gupta, H.K. and Delany, F.M. (eds), Zagros-Hindukush-Himalaya Geodynamic Evolution, Am. Geophys. Union and Geol. Soc. Am., Geodyn. Ser. 3, 33–69.
Berberian, M., 1982, Aftershock tectonics of the 1978 Tabas-e-Golshan(Iran) earthquake sequence: a documented active 'thin and thick-skinned tectonic' case, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 68, 499–530.
Berberian, M., 1983, Continental deformation in the Iranian plateau (contribution to the seismotectonics of Iran, part IV), Geol. Surv. Iran, Rep. 52.
Berberian, M., 1995, Master 'blind' thrust faults hidden under the Zagros folds: active basement tectonics and surface morphotectonics, Tectonophysics 241, 193–224.
Berberian, M. and Arshadi, S., 1976, On the evidence of the youngest activity of the North Tabriz Fault and the seismicity of Tabriz city, Geol. Surv. Iran, Rep. 39, 397–418.
Berberian, M. and Qorashi, M., 1994, Coseismic fault-related folding during the South Golbaf earthquake of November 20, 1989, in southeast Iran, Geology 22, 531–534.
Berberian, M., Asudeh, I. and Arshadi, S., 1979, Surface rupture and mechanism of the Bob-Tangol (south-eastern Iran) earthquake of 19 December 1977, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 42, 456–462.
Berberian, M., Jackson, J.A., Qorashi, M. and Kadjar, M.H., 1984, Field and teleseismic observations of the 1981 Golbaf-Sirch earthquakes in SE Iran, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 77, 809–838.
Berberian, M., Qorashi, M., Jackson, J.A., Priestley, K.F. and Wallace, T., 1992, The Rudbar-Tarom Earthquake of 20 June 1990 in NW Persia: Preliminary field and seismological observations and its tectonic significance, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 82, 1726–1755.
Bonilla, M.G., Mark, R.K. and Lienkaemper, J., 1984, Statistical relations among earthquake magnitude, surface rupture length and surface fault displacement, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 74, 2379–2411.
Byrne, D.E., Sykes, L.R. and Davis, D.M., 1992, Great thrust earthquakes and aseismic slip along the plate boundry of Makran subduction zone, J. Geophys. Res. 79, 449–478.
Carver, G.A. and McCalpin, J.P., 1996, Paleoseismology of compressional tectonic environments. In: McCalpin, J.P. (ed.), Paleoseismology, Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, California, pp. 183–270.
Chandra, U., 1981, Focal mechanism solutions and their tectonic implication for the eastern Alpine-Himalayan region. In: Gupta, H.K. and Delany, F.M. (eds), Zagros-Hindukush-Himalaya Geodynamic Evolution, Am. Geophys. Union and Geol. Soc. Am., Geodynamic Ser. 3, 243–271.
Chandra, U., 1984, Focal mechanism solutions for earthquakes in Iran, Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 34, 9–16.
Dziewonski, A.M., Ekstrom, G., Salganik, M.P., 1994, Centroid-moment tensor solutions for January–March 1994, Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 86, 253–261.
Dziewonski, A.M., Ekstrom, G., Salganik, M.P., 1995, Centroid-moment tensor solutions for April–June 1994, Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 88, 69–78.
EERI Committee on Seismic Risk, 1989, The basics of seismic risk analysis, Earthquake Spectra 5, 675–702.
Gao, L. and Wallace, T.C., 1995, The 1990 Rudbar-Tarum Iranian earthquake sequence: evidence for slip partitioning, J. Geophys. Res. 100, 15317–15332.
Haghipour, A., 1992, Seismotectonic map of Middle East (1: 5 000 000), Geol. Surv. Iran and CGMW.
Haghipour, A. and Amidi, M., 1980, The November 14 to December 25, 1979 Ghaenat earthquakes of northeast Iran and their tectonic implications, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 70, 1751–1757.
He, H., Zhang, Y. and Zhou, B., 1994, Delineation of potential seismic sources in continent of China. In: Proc. Workshop on Implementation of GSHAP in Central and Southern Asia, Beijing, China, pp. 169–183.
Jackson, J.A., 1980a, Errors in focal depth determination and the depth of seismicity in Iran and Turkey, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 57, 209–229.
Jackson, J.A., 1980b, Reactivation of basement faults and crustal shortening in orogenic belts, Nature 283, 343–346.
Jackson, J.A. and Fitch, T.J., 1979, Seismotectonic implications of relocated aftershock sequences in Iran and Turkey, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 57, 209–229.
Jackson, J.A. and Fitch, T.J., 1981, Basement faulting and the focal depth of the large earthquakes in the Zagros mountains (Iran), Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 64, 561–586.
Jackson, J.A. and McKenzi, D.P., 1984, Active tectonics of the Alpine-Himalayan belt between Western Turkey and Pakistan, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 77, 185–264.
Jackson, J.A. and McKenzi, D.P., 1988, The relation between plate motions and seismic moment tensors, and the rates of active deformation in the Mediterranean and the Middle East, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 93, 45–73.
Jackson, J., Haines, J. and Holt, W., 1995, The accommodation of Arabia-Eurasia plate convergence in Iran, J. Geophys. Res. 100, 15205–15219.
Kadinsky-Cade, K. and Barazangi, M., 1982, Seismotectonics of southern Iran: The Oman line, Tectonics 1, 389–412.
Kagan, Y.Y. and Jackson, D.D., 1994, Long-term probabilistic forecasting of earthquakes, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 13685–13700.
Karakhanian, A.S., 1993, Map of active faults and seismotectonics of Armania Upland territory and adjacent regions of the West Asia, National survey of seismic protection, Armania.
Karnik, V., 1969, Seismicity of the European Area, Part 1, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht-Holland, 364 pp.
Knuepfer, P.L.K., 1989, Implications of the characteristics of endpoints of historical surface fault ruptures for the nature of fault segmentation. In: Schwartz, D.P. and Sibson, R.H. (eds), Fault Segmentation and Controls of Rupture Initiation and Termination, U.S. Geol. Surv. Open File Rep. pp. 89–315, 193–228.
McCalpin, J.P., 1996, Application of paleoseismic data to seismic hazard assessment and neotectonics research. In: McCalpin, J.P. (ed.), Paleoseismology, Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, California, pp. 439–493.
McKenzi, D.P., 1972, Active tectonics of Mediterranean region, Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 30, 109–185.
Mirzaei, N., Gao, M. and Chen, Y.T., 1997a, Evaluation of uncertainty of earthquake parameters for the purpose of seismic zoning of Iran, Earthquake Research in China 11, 197–212.
Mirzaei, N., Gao, M. and Chen, Y.T., 1997b, Seismicity in major seismotectonic provinces of Iran, Earthquake Research in China 11(4), in press.
Mirzaei, N., Gao, M. and Chen, Y.T., 1997c, Seismic source regionalization for seismic zoning of Iran: Major seismotectonic provinces, Submitted to Earthquake Research in China.
Mirzaei, N., Gao, M., Chen, Y.T. and Wang, J., 1997d, A uniform catalog of earthquakes for seismic hazard assessment in Iran, Acta Seismol. Sinica 10, 713–726.
Moinfar, A., 1976, The importance of macroseismic studies of past earthquakes. In: Proc. CENTO Semin. Recent Advances in Earthq. Hazard Minimization, Tehran, pp. 65–69.
Ni, J. and Barazangi, M., 1986, Seismotectonics of the Zagros continental collision zone and a comparison with the Himalayas, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 8205–8218.
Nogole Sadat, M.A.A., 1993, Seismotectonic map of Iran (scale 1:1 000 000), Geol. Surv. Iran (proof print).
Nowroozi, A.A., 1971, Seismotectonics of the Persian plateau, Eastern Turkey, Caucasus and Hindu-Kush region, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 61, 317–341.
Nowroozi, A.A., 1972, Focal mechanism of earthquakes in Persia, Turkey West Pakistan, and Afganistan and plate tectonics of the Middle East, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 62, 823–850.
Priestley, K., Baker, C. and Jackson, J., 1994, Implications of earthquake focal mechanism data for the active tectonics of the south Caspian basin and surrounding regions, Geophys. J. Int. 118, 111–141.
Reiter, L., 1990, Earthquake Hazard Analysis, Colombia University Press, New York, 254 pp.
Schwartz, D.P. and Coppersmith, K.J., 1984, Fault behavior and characteristic earthquakes: Examples from the Wasatch and San Andreas fault zones, J. Geophys. Res. 89, 5681–5698.
Shaw, J.H. and Suppe, J., 1996, Earthquake hazards of active blind-thrust faults under the central Los Angles basin, California, J. Geophys. Res. 101, 8623–8642.
Slemmons, D.B., Bodin, P. and Zhang, X., 1987, Determination of earthquake size from surface faulting events. In: Proc. International Seminar on Seismic Zonation, Guangzhou, China, 157–169.
Synder, D.B. and Barazangi, M., 1986, Deep crustal structure and flexure of the Arabian plate beneath the Zagros collisional mountain belt as inferred from gravity observation, Tectonics 5, 361–373.
Tchalenko, J.S., 1975, Seismicity and structure of the kopet Dagh (Iran, USSR), Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 278, 1–28.
Tchalenko, J.S. and Berberian, M., 1975, Dasht-e-Bayaz fault, Iran: earthquake and earlier related structures in bedrock, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 86, 703–709.
Tchalenko, J.S. and Braud, J., 1974, Seismicity and structure of the Zagros (Iran): the main recent fault between 33° and 35° N, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 227, 1–25.
Thenhause, P.C., EERI, M., Perkins, D.M., Algermissen, S.T., EERI, M. and Hanson, S.L., 1987, Earthquake hazard in the Eastern United States: consequences of alternative seismic source zones, Earthquake Spectra 3, 227–261.
Wells, D.L. and Coppersmith, K.J., 1994, New empirical relationship among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement, Bull. Seism. Soc. Am. 84, 974–1002.
Wyss, M., 1979, Estimating maximum expectable magnitude of earthquakes from fault dimensions, Geology 7, 336–340.
Ye, H., Chen, G. and Zhou, Q., 1995, Study on the intraplate potential seismic sources. In: Proc. Fifth International Conf. Seismic Zonation, 2, Nice, France, pp. 1424–1430.
Ye, H., Zhou, Y., Zhou, Q., Yang, W., Chen, G. and Hao, C., 1993, Study on potential seismic sources for seismic zonation and engineering seismic hazard analysis in continental areas. In: Continental Earthquakes, IASPEI Publication Series for the IDNDR 3, pp. 473–478.
Yucemen, M.S. and Gulkan, P., 1994, Seismic hazard analysis with randomly located sources, Natural Hazards 9, 215–233.
Yousefi, E., 1989, Total intensity map (1:1 000 000), Geol. Surv. Iran.
Zhang, Y., 1993, Principles and methods on delineation of potential earthquake source area. In: Proc. PRC/USSR Workshop on Geodynamics and Seismic Risk Assessment, Beijing, China, pp. 201–207.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirzaei, N., Gao, M. & Chen, Yt. Delineation of potential seismic sources for seismic zoning of Iran. Journal of Seismology 3, 17–30 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009737719013
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009737719013