Abstract
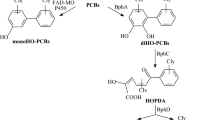
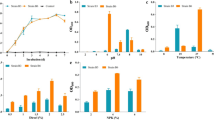
A bioemulsifier excreting bacterium of the species Peudomonas cepacia was isolated after a screeningprocedure using n-dodecane as carbon source. Thepartly purified bioemulsifier was preliminarily identifiedas a mixture of glycolipids. A decrease of the surfacetension to 37 mN/m and a CMC of 5 mg/l could bemeasured with the bioemulsifier GL-K12. Usingsunflower oil as main carbon source, up to 7.1 g/lbioemulsifier could be produced in oxygen and nitrogenlimited fermentations on a scale of 300 l. Thebiodegradation of Aroclor 1242 in liquid cultures by abacterial mixed population was enhanced by GL-K12when added at biosurfactant concentrations of 0.2 g/l ormore. The most positive effect was noted in thedegradation of PCB congeners with 3 Cl atoms with anincrease of up to 100%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovicz J (1990) Aerobic and anaerobic biodegradation of PCBs: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 10: 241–250
Ballschmiter K, Schäfer W & Buchert H (1987) Isomerspecific identification of PCB congeners in technical mixtures and environmental samples by HRGC-ECD and HRGC-MSD. Fresen. Z. Anal. Chem. 326: 253–257
Brandes B (1988) Der Einflußvon Glycolipiden auf die Abbaubarkeit vonNaphthalin, Phenanthren und Anthracen durch Pseudomonas putidaNCIB 9816. Diplomarbeit TU Braunschweig
Clarke AN, Plumb PD & Subramanyan TK (1991) Soil clean-up by surfactant washing. I. Laboratory results and mathematical modeling. Sep. Sci. Technol. 25: 301–343
Cooper DG, Zajic JE & Gerson DF (1979) Production of surface active lipids by Corynebacterium lepus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 37: 4–10
Davila A-M, Marchal R & Vandecasteele J-P (1992) Kinetics and balance of a fermentation free from product inhibition: sophorose lipid production by Candida bombicola. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 38: 6–11
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hammilton JK, Rebers PA & Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 28: 350–356
Fiebig R & Dellweg H (1985) Comparison between the process performance of an UASB reactor and an UASB fixed film combination with an acetic acid enrichment culture. Biotechnol. Lett. 7: 487–492
Fiebig R, Schulze D, Erlemann P, Slawinski M & Dellweg H (1993) Microbial degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls in contaminated soil. Biotechnol. Lett. 15: 93–98
Fiechter A (1992) Biosurfactants: Moving towards industrial application. TIBTECH 10: 208–217
Foght JM, Gutnick DL & Westlake WS (1989) Effect of Emulsan on biodegradation of crude oil by pure and mixed bacterial cultures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 36–42
Georgiou G, Lin S-C & Sharma MM (1992) Surface active compounds from microorganisms. Bio/Technol. 10: 60–65
Häusler A, Müller-Hurtig R & Wagner F (1992) Influence of chemical and biosurfactants on the microbial degradation of a fuel oil spill. In: Kreysa G & Driesel AJ (Eds) DECHEMA Biotechnol. Conf. Vol 5/B 10th Ann. Meeting of Biotechnologist Karlsruhe (pp 1037–1041). Dech., Frankf./M, FRG
Krupc'ik A, Kocan J, Petrik J, Leclercq PA & Ballschmiter K (1992) On the use of reference standards for quantitative trace analysis of PCBs by HRGC. Analysis of technical PCB formulations by HRGC/FID. Chromatographia 33: 514–520
Kohler H-PE, Kohler-Staub D & Focht DD (1988) Cometabolism of polychlorinated biphenyls: Enhanced transformation of Aroclor 1254 by growing bacterial cells. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54: 1940–1945
McDermott JB, Unterman R, Brennan MJ, Brooks RE, Mobley DP, Schwartz CC & Dietrich DK (1989) Two strategies for PCB soil remediation: Biodegradation and surfactant extraction. Environ. Progr. 8: 46–51
Mulligan CN, Cooper DG & Neufeld RJ (1984) Selection of microbes producing biosurfactants in media without hydrocarbons. J. Ferment. Technol. 62: 311–314
Neu TR & Poralla K (1990) Emulsifying agents from bacteria isolated during screening for cells with hydrophobic surfaces. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32: 521–525
Oberbremer A, Müller-Hurtig R & Wagner F (1990) Effect of the addition of microbial surfactants on hydrocarbon degradation in a soil population in a stirred reactor. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32: 485–489
Poremba K, Gunkel W, Lang S & Wagner F (1991) Marine biosurfactants. III. Toxicity testing with marine microorganisms and comparison with synthetic surfactants. Zeitschr. f. Naturforsch. 46c: 210–216
Robert M, Mercade ME, Bosch MP, Parra JL, Espuny MJ, Manresa MA & Guinea J (1989) Effect of the carbon source on biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa44 T1. Biotechnol. Lett. 11: 871–874
Schulz D, Passeri A, Schmidt M, Lang S, Wagner F, Wray V & Gunkel W (1991) Marine surfactants, I. Screening for biosurfactants among crude oil degrading marine microorganisms from the North Sea. Z. Naturforsch. 46c: 197–203
Siegmund I & Wagner F (1991) New method for detecting rhamnolipids excreted byPseudomonasspeciesduringgrowthonmineral agar. Biotechnol. Techn. 5: 265–268
Shabtai Y & Wang DIC (1990) Production of Emulsan in a fermentation process using soybean oil (SBO) in a carbon nitrogen coordinated feed. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 35: 753–765
Syldatk C, Lang S & Wagner F (1985a) Chemical and physical characterization of four interfacial active rhamnolipids from Pseudomonasspecies DSM 2874 grown on alkanes. Z. Naturforsch. 40c: 51–60
Syldatk C, Lang S, Matulovic U & Wagner F (1985b) Production of four interfacial active rhamnolipids from n-alkanes or glycerol by resting cells of Pseudomonasspecies DSM 2874. Z. Naturforsch. 40c: 61–67
Syldatk C & Wagner F (1987) Production of biosurfactants. In: Kosaric N, Cairns WC & Gray NCC (Eds) Surfactant Science Series 25 (pp 21–45). Marcel Dekker Inc., New York
Van Bernem K-H (1984) Experimentelle Untersuchungen zur Wirkung von Rohöl und Rohöl/Tensid-Gemischen im ÖkosystemWattenmeer. II. Eindringverhalten und Persistenz von Rohölkohlenwasserstoffen in Sedimenten nach experimenteller Kontamination. Senkenb. Marit. 16: 13–30
Van Dyke MI, Gulley SL, Lee H & Trevors JT (1993a) Evaluation of microbial surfactants for recovery of hydrophobic pollutants from soil. J. Ind. Microbiol. 11: 163–170
Van Dyke MI, Couture P, Brauer M, Lee H & Trevors JT (1993b) Pseudomonas aeruginosaUG2 rhamnolipids biosurfactants: structural characterization and their use in removing hydrophobic compounds from soil. Can. J. Microbiol. 39: 1071–1078
Wagner F (1987) Strategies for biosurfactant production. Fat Sci. Technol. 89: 586–591
Zajic JE, Guignard H & Gersson DF (1977) Emulsifying and surface active agents from Corynebacterium hydrocarboblastus. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 14: 1285–1301
Zhang Y & Miller RM (1992) Enhanced octadecane dispersion and biodegradation by a Pseudomonasrhamnolipid surfactant (biosurf.). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 3276–3282
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiebig, R., Schulze, D., Chung, JC. et al. Biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in the presence of a bioemulsifier produced on sunflower oil. Biodegradation 8, 67–75 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008256110136
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008256110136