Abstract
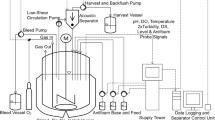
The isolation of a new type of thrombin inhibitor, called triabin, from the saliva of the hematophagous bug Triatoma pallidipennis, has recently been described. In the in vitro platelet aggregation inhibition assay triabin has a similar potency as the thrombin inhibitor hirudin now in phase III clinical trials. However, in another in vitro assay using a low molecular weight substrate for thrombin, triabin does not inhibit thrombin completely even at 6 fold higher molar doses in comparison with hirudin. This means that triabin has a novel mode of action towards thrombin making triabin into an interesting candidate as a therapeutic agent. Recently it has been shown that a recombinant baculovirus can be efficiently used for the triabin production in insect cells and that the yields in adherent cultures of High Five™ cells (approx. 20 mg l-1) were about 7 fold higher than in adherent cultures of Sf9 cells (approx. 3 mg l- 1). To optimize the triabin yield from the baculovirus/insect cell expression system, experiments were performed with suspension adapted cultures of High Five™ cells to investigate the effects of the state of the host cell, of the multiplicity of infection, of the cell density at the time of infection and of supplementation of the medium with nutrients and oxygen. Triabin yields of up to 200 mg l-1, as determined by an activity assay, could finally be obtained here.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bober H (1986) Über Möglichkeiten der HPLC zur Trennung und Bestimmung von Aminosäuren. Technical Report, Beckman Instruments, München.
Chico E, Kobold A, Haase B and Jaeger V (1997) Characterization of growth and recombinant protein production of the insect cell line BTI-Tn-5B1-4 (High Five™) in suspension culture. In: Carrondo MJT, Griffiths B, Moreira JCP (eds) Animal Cell Technology — from Vaccines to Genetic Medicine, (pp. 755-760) Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
Church FC, Phillips J and Woods JL (1991) Chimeric antithrombin peptide, characterization of an arg-gly-asp (RGD)-and hirudin carboxy terminus-containing synthetic peptide. J. Biol. Chem. 288(18): 11975-11979.
Davis TR, Wickham TJ, McKenna KA, Granados RR, Shuler ML and Wood HA (1993) Comparative recombinant protein production of eight insect cell lines. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 29A: 388-390.
Fuentes-Prior P, Noeske-Jungblut C, Donner P, Schleuning WD, Huber R and Bode W (1997) Structure of the thrombin complex with triabin, a lipocalin-like exosite-binding inhibitor derived from a triatomine bug. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 11845-11850.
Kioukia N, Nienow AW; Emery AN and Al-Rubeai M (1995) Physiological and environmental factors affecting the growth of insect cells and infection with baculovirus. J. Biotechnol. 38: 243-251.
Noeske-Jungblut C, Haendler B, Donner P, Alagon A, Possani L and Schleuning WD (1995) Triabin, a highly potent exosite inhibitor of thrombin. J. Biol. Chem. 270(48): 28629-28634.
Petri T, Neukamm B, Isernhagen M, Ockert B and Noeske-Jungblut, C. (1997) Expression of triabin, a novel highly potent inhibitor of thrombin, in Sf9 and High Five™ insect cells using a recombinant baculovirus. In: Carrondo MJT, Griffiths B and Moreira JCP (eds) Animal Cell Technology — from Vaccines to Genetic Medicine (pp. 525-528) Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
Reid S, Greenfield PF, Power J, Radford KM, Nielsen LK, Wong TKK and Peter C (1995) The use of very low multiplicities of infection with the baculovirus expression vector system. In: Beuvery EC, Griffiths JB and Zeijlemaker WP (eds) Animal Cell Technology — Developments towards the 21st Century (pp. 73-77) Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1995.
Scott RI, Blanchard JH and Ferguson CHR (1992) Effects of oxygen on recombinant protein production by suspension cultures of Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf-9) insect cells. Enzyme Microbial Technol. 14: 798-804.
Vonach B, Hess B, Streiff M and Leist C (1997) Expression of a protein A-fucosyltransferase III fusion protein in insect cells. In: Carrondo MJT, Griffiths B, Moreira JCP (eds) Animal Cell Technology — from Vaccines to Genetic Medicine (pp. 703-707) Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
Whiting JP, Wafford KA, Pribilla I and Petri T (1995) Channel cloning, mutagenesis and expression — baculovirus expression. In: Ashley RH (ed) Ion Channels, a Practical Approach (pp. 133-169) Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Wickham TJ, Davis T, Granados RR, Shuler ML and Wood HA (1992) Screening of insect cell lines for the production of recombinant proteins and infectious virus in the baculovirus expression system. Biotechnol. Prog. 8: 391-396.
Wickham TJ and Nemerow GR (1993) Optimization of growth methods and recombinant protein production in BTI-Tn-5B1-4 insect cells using the baculovirus expression system. Biotechnol. Prog. 9: 25-30.
Woehe G (1990) Einführung in die allgemeine Betriebswirtschaftslehre. Verlag Franz Vahlen GmbH, München, 17th edition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vallazza, M., Petri, T. Optimization of the production of triabin, a novel thrombin inhibitor, in High Five™ insect cells infected with a recombinant baculovirus. Cytotechnology 29, 85–92 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008008023779
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008008023779