Abstract
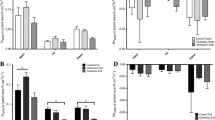
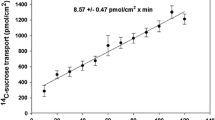
Rates of glucose, amino acid and dipeptide absorption by the intestine of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) were measured in vitro at 10 °C as functions of concentration and region using intact tissues (everted sleeve method). Salmon (weight range 300–1300 g) fed a commercial, extruded salmon feed, were kept at 12–13 °C in freshwater. Maximum rates (V max) of glucose and dipeptide transport were low compared to most amino acid V max values. There was a declining proximal-to-distal gradient of absorption along the post-gastric intestinal tract. A saturable component of absorption was not evident for proline and glycyl-proline in the distal intestine, and glycyl-sarcosine in any region. `Apparent diffusion', which may include low affinity, high capacity carrier systems and carrier-independent influx, appears to account for the majority of total uptake at higher concentrations of amino acids and dipeptides. There was competition between the dipeptides for transporter sites in the pyloric ceca and mid intestine, suggesting a common carrier. There was also indication of hydrolysis of these dipeptides by brush border membrane enzymes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adibi, S.A. 1997. The oligopeptide transporter (Pept-1) in human intestine: biology and function. Gastroenterology 113: 332-340.
Anderson, J.S., Lall, S.P., Anderson, D.M. and McNiven, M.A. 1995. Availability of amino acids from various fish meals fed to Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 138: 291-301.
Balocco, C., Bogé, G. and Roche, H. 1993. Neutral amino acid transport by marine fish intestine: role of the side chain. J. Comp. Physiol. B 163: 340-347.
Bogé, G., Rigal, A. and Peres, G. 1979a. A study of intestinal absorption in vivo and in vitro of different concentrations of glycine by the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri Richardson). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 62A: 831-836.
Bogé, G., Rigal, A. and Peres G. 1979b. A study of energized transport mechanisms of glycine absorption by the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri Richardson). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 64A: 537-541.
Bogé, G., Rigal, A. and Peres, G. 1981. Rates of in vivo intestinal absorption of glycine and glycylglycine by rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri R.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 69A: 455-459.
Buddington, R.K. and Diamond, J.M. 1987. Pyloric ceca of fish: a 'new' absorptive organ. Am. J. Physiol. 252 (Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 15): G65-G76.
Buddington, R.K., Chen, J.W. and Diamond, J.M. 1987. Genetic and phenotypic adaption of intestinal nutrient transport to diet in fish. J. Physiol. 393: 261-281.
Buddington, R.K., Chen, J.W. and Diamond, J.M. 1991. Dietary regulation of intestinal brush-border sugar and amino acid transport in carnivores. Am. J. Physiol. 261 (Regulatory Integrative Comp. Physiol. 30): R793-R801.
Buddington, R.K., Krogdahl, Å. and Bakke-McKellep, A.M. 1997. The intestines of carnivorous fish: structure and functions and the relations with diet. Acta Physiol. Scand. 161 (Suppl. 638): 67-80.
Christensen, H.N. 1990. Role of amino acid transport and countertransport in nutrition and metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 70: 43-77.
Coady, M.J., Pajor, A.M. and Wright, E.M. 1990. Sequence homologies among intestinal and renal NaC/glucose cotransporters. Am. J. Physiol. 259 (Cell Physiol. 28): C605-C610.
Collie, N.L. 1985. Intestinal nutrient transport in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) and the effects of development, starvation, and seawater adaption. J. Comp. Physiol. B 156: 163-174.
Collie, N.L. and Ferraris, R.P. 1995. Nutrient fluxes and regulation in fish intestine. In: Metabolic Biochemistry. pp. 221-239. Edited by P.W. Hochachka and T.P. Mommsen. Elsevier Science B.V., Amsterdam.
Ferraris, R.P. and Ahearn, G.A. 1983. Intestinal glucose transport in carnivorous and herbivorous marine fishes. J. Comp. Physiol. B 152: 79-90.
Ferraris, R.P. and Ahearn, G.A. 1984. Sugar and amino acid transport in fish intestine. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 77A: 397-413.
Ferraris, R.P. and Diamond, J.M. 1986. A method for measuring apical glucose transporter site density in intact intestinal mucosa by means of phlorizin binding. J. Membr. Biol. 94: 65-75.
Ferraris, R.P., Lee, P.P. and Diamond, J.M. 1989. Origin of regional and species differences in intestinal glucose uptake. Am. J. Physiol. 257 (Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 20): G689-G697.
Ferraris, R.P. 1994. Regulation of intestinal nutrient transport. In: Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract, Third Edition. pp. 1773-1794. Edited by L.R. Johnson. Raven Press, New York.
Ganapathy, V., Brandsch, M. and Leibach, F.H. 1994. Intestinal transport of amino acids and peptides. In: Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract, third edition. pp. 1773-1794. Edited by L.R. Johnson. Raven Press, New York.
Hemre, G.I., Sandnes, K., Lie, Ø. Torrissen, O. and Waagbø, R. 1995. Carbohydrate nutrition in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. growth and feed utilization. Aquacult. Res. 26: 149-154.
Ingh, T.S.G.A.M. van den, Krogdahl, Å., Olli, J., Hendricks, H.G.C.J.M. and Koninkx, J.F.J.G. 1991. Effects of soybeancontaining diets on the proximal and distal intestine in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): a morphological study. Aquaculture 94: 297-305.
Ingham, L. and Arme, J.C. 1977. Intestinal absorption of amino acids by rainbow trout Salmo gairdneri (Richardson). J. Comp. Physiol. 117: 323-334.
Karasov, W.H. and Diamond, J.M. 1983. A simple method for measuring intestinal solute uptake in vitro. J. Comp. Physiol. 152: 105-116.
Krogdahl, Å., Nordrum, S., Sørensen, M., Brudeseth, L. and Røsjø, C. 1999. Effects of diet composition on apparent nutrient absorption along the intestinal tract and of subsequent fasting on mucosal disaccharidase activities and plasma nutrient concentration in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. Aquacult. Nutr. 5: 121-133.
Maffia, M., Verri, T., Danieli, A., Thamotharan, M., Pastore, M., Ahearn, G.A. and Storelli, C. 1997. HC-glycyl-L-proline cotransport in brush-border membrane vesicles of eel (Anguilla anguilla) intestine. Am. J. Physiol. 272 (Regulatory Integrative Comp. Physiol. 41): R217-R225.
Munilla-Morán, R. and Stark, J.R. 1990. Metabolism in marine flatfish-VI. Effect of nutritional state on digestion in turbot, Scophthalmus maximus (L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 95B: 625-634.
Reshkin, S.J. and Ahearn, G.A. 1991. Intestinal glycyl-Lphenylalanine and L-phenylalanine transport in a euryhaline teleost. Am. J. Physiol. 260 (Regulatory Integrative Comp. Physiol. 29): R563-R569.
Sabapathy, U. and Teo, L.H. 1993. A quantitative study of some digestive enzymes in the rabbitfish, Siganus canaliculatus and the sea bass, Lates calcarifer. J. Fish Biol. 42: 595-602.
Schep, L.J., Tucker, I.G., Young, G. and Butt, A.G. 1997. Regional permeability differences between the proximal and distal portions of the isolated salmonid posterior intestine. J. Comp. Physiol. 167: 370-377.
Sire, M.F. and Vernier, J.-M. 1992. Intestinal absorption of protein in teleost fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 103A: 771-781.
Smith, B.W. and Lovell, R.T. 1973. Determination of apparent protein digestibility in feeds for channel catfish. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 4: 831-835.
Storelli, C., Vilella, S. and Cassano, G. 1986. Na-dependent Dglucose and L-alanine transport in eel intestinal brush border membrane vesicles. Am. J. Physiol. 251 (Regulatory Integrative Comp. Physiol. 20): R463-R469.
Storelli, C., Vilella, S., Romano, M.P., Maffia, M. and Cassano, G. 1989. Brush-border amino acid transport mechanisms in carnivorous eel intestine. Am. J. Physiol. 257 (Regulatory Integrative Comp. Physiol. 26): R506-R510.
Thamotharan, M., Gomme, J., Zonno, V., Maffia, M., Storelli, C. and Ahearn, G.A. 1996. Electrogenic, proton-coupled, intestinal dipeptide transport in herbivorous and carnivorous teleosts. Am. J. Physiol. 270 (Regulatory Integrative Comp. Physiol. 39): R939-R947.
Vilella, S., Ahearn, G.A., Cassano, G., Maffia, M. and Storelli, C. 1990. Lysine transport by brush border membrane vesicles of eel intestine: interaction with neutral amino acids. Am. J. Physiol. 259 (Regulatory Integrative Comp. Physiol. 28): R1181-R1188.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakke-McKellep, A., Nordrum, S., Krogdahl, Å. et al. Absorption of glucose, amino acids, and dipeptides by the intestines of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 22, 33–44 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007872929847
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007872929847