Abstract
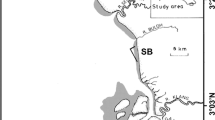
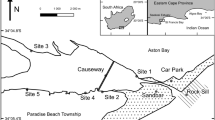
The structure and functioning of salt marsh fish communities in the overall ecology of southern African estuaries is poorly understood. This study compares the ichthyofauna associated with a salt marsh creek and eelgrass bed in an attempt to evaluate the relative importance of these habitats to fishes. Taylor's salt marsh creek and adjacent eelgrass bed in the Kariega Estuary were sampled twice per season between the winter of 1992 and the autumn of 1994. The average density and standing stock of fishes were found to be considerably higher in the eelgrass bed than in the intertidal creek. Both habitats had similar fish diversities but were dominated by different taxa, the most notable of which was the dominance of mugilids in the creek and their scarcity in the eelgrass. Taylor's intertidal creek and adjacent eelgrass beds were dominated by juvenile fish, with both habitats functioning as nursery areas for juvenile fish, albeit for totally different ichthyofaunal communities. The similar fish diversities but lower abundances in the intertidal creek compared to the eelgrass beds are in contrast to similar North American studies, and refute the hypothesis that intertidal salt marsh creeks have higher fish densities but lower diversities than eelgrass beds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Adams, S.M. 1976. The ecology of eelgrass, Zostera marina (L.), fish communities. 1. Structural analysis. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 22: 269–291.
Allanson, B.R. & G.H.L. Read. 1995. Further comment on the response of south east coast estuaries to variable freshwater flows. S. Afr. J. aquat. Sci. 21: 56–70.
Beckley, L.E. 1983. The ichthyofauna associated with Zostera capensis Setchell in the Swartkops Estuary, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Zool. 18: 15–24.
Bell, J.D. & D.A. Pollard. 1989. Ecology of fish assemblages and fisheries associated with seagrasses. pp. 565–609. In: A.W.D. Larkum, A.J. McComb & S.A. Shepard (ed.) Biology of Seagrasses, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Bozeman, E.L. & J.M. Dean. 1980. The abundance of estuarine larval and juvenile fish in a South Carolina intertidal creek. Estuaries 3: 89–97.
Branch, G.M. & J.R. Grindley. 1979. Ecology of southern African estuaries, Part XI. Mngazana: a mangrove estuary in the Transkei. S. Afr. J. Zool. 14: 149–170.
Cain, R.L. & J.M. Dean. 1976. Annual occurrence, abundance and diversity of fish in a South Carolina intertidal creek. Mar. Biol. 36: 369–379.
Caulton, M.S. 1978. The importance of habitat temperatures for growth in the tropical cichlid Tilapia rendalli Boulenger. J. Fish Biol. 13: 99–112.
Chamberlain, R.H. & R.A. Barnhart. 1993. Early use by fish of a mitigation salt marsh, Humboldt Bay, California. Estuaries 16: 769–783.
Clarke, K.R. & R.M. Warwick. 1994. Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. Natural Environment Research Council, Plymouth. 144 pp.
Connolly, R.M. 1994a. A comparison of fish assemblages from seagrass and unvegetated areas of a southern Australian estuary. Aust. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 45: 1033–1044.
Connolly, R.M. 1994b. Comparison of fish catches from buoyant pop net and a beach seine net in a shallow seagrass habitat. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 109: 305–309.
Cyrus, D.P. & S.J.M. Blaber. 1987. The influence of turbidity on juvenile marine fish in the estuaries of Natal, South Africa. Continental Shelf Research 7: 1411–1416.
Ferell, D.J. & J.D. Bell. 1991. Differences among assemblages of fish associated with Zostera capricorni and bare sand over a large spatial scale. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 72: 15–24.
Fowler, J. & L. Cohen. 1993. Practical statistics for field biology. Wiley and Sons, New York. 213 pp.
Hanekom, N. & D. Baird. 1984. Fish community structures in Zostera and non-Zostera regions of the Kromme Estuary, St Francis Bay. S. Afr. J. Zool. 19: 295–301.
Harrison, T.D. & A.K. Whitfield. 1995. Fish community structure in three temporarily open/closed estuaries on the Natal coast. Ichthyol. Bull. Smith Inst. Ichthyol. 64: 1–80.
Heck, K.L., K.W. Able, M.P. Fahay & C.T. Roman. 1989. Fishes and decapod crustaceans of Cape Cod eelgrass meadows: species composition, seasonal abundance patterns and comparison with unvegetated substrates. Estuaries 12: 59–65.
Knieb, R.T. 1997. The role of tidal marshes in the ecology of estuarine nekton. Oceanography and Marine Biology: an Annual Review 35: 163–220.
Orth, R.J. 1992. A perspective on plant animal interactions in seagrasses: physical and biological determinants influencing plant and animal abundance. pp. 147–164. In: D.M. John, S.J. Hawkins & J.H. Price (ed.) Plant Animal Interactions in the Marine Benthos, Systematics Association Special Volume 46, Claredon Press, Oxford.
Orth, R.J., K.L. Heck & J. van Montfrans. 1984. Faunal communities in seagrass beds: a review of the influence of plant structure and prey characteristics on predator prey relationships. Estuaries 4: 339–350.
Paterson, A.W. 1998. Aspects of the ecology of fishes associated with salt marshes and adjacent habitats in a temperate South African estuary. Ph.D. Thesis, Rhodes University, Grahamstown. 200 pp.
Paterson, A.W. & A.K. Whitfield. 1996. The fishes associated with an intertidal salt marsh creek in the Kariega Estuary, South Africa. Trans. Roy. Soc. S. Afr. 51: 195–218.
Pollard, D.A. 1984. A review of ecological studies on seagrass-fish communities, with particular reference to recent studies in Australia. Aquat. Bot. 18: 3–42.
Reis, R.R. & J.M. Dean. 1981. Temporal variation in the utilization of an intertidal creek by the bay anchovy (Anchoa mitchilli). Estuaries 4: 16–23.
Rountree, R.A. & K.W. Able. 1993. Diel variation in decapod crustacean and fish assemblages in New Jersey polyhaline marsh creeks. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 37: 181–201.
Shenker, J.M & J.M. Dean. 1979. The utilisation of an intertidal salt marsh creek by larval and juvenile fishes: abundance, diversity and temporal variation. Estuaries 2: 154–163.
Smith, S.M., J.G. Hoff, S.P. O'Neil & M.P. Weinstein. 1984. Community and trophic organisation of nekton utilising shallow marsh habitats, York River, Virginia. U.S. Fish. Bull. 82: 455–467.
Sogard, S.M. & K.W. Able. 1991. A comparison of eelgrass, sea lettuce, macroalgae and marsh creeks as habitats for epibenthic fishes and decapods. Est. Coast. Shelf Sci. 33: 501–519.
Sogard, S.M., G.V.N. Powell & J.G. Holmquist. 1989. Utilization by fishes of shallow, seagrass-covered banks in Florida Bay: 2. Diel and tidal patterns. Env. Biol. Fish. 24: 81–92.
Taylor, D.I. & B.R. Allanson. 1995. Organic carbon fluxes between a high marsh and estuary, and the inapplicability of the outwelling hypothesis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 120: 263–270.
Ter Morshuizen, L.D. & A.K. Whitfield. 1994. The distribution of littoral fish associated with eelgrass Zostera capensis beds in the Kariega Estuary, a southern African system with a reversed salinity gradient. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 14: 95–105.
Washington, H.G. 1984. Diversity, biotic and similarity indices. A review with special relevance to aquatic ecosystems. Water Res. 18: 653–694.
Weinstein, M.P. & H.A. Brooks. 1983. Comparative ecology of nekton residing in a tidal creek and adjacent seagrass meadow: community composition and structure. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 12: 15–27.
West, R.J. & R.J. King. 1996. Marine, brackish, and freshwater fish communities in the vegetated and bare shallows of an Australian coastal river. Estuaries 19: 31–41.
Whitfield, A.K. 1994a. A review of ichthyofaunal biodiversity in southern African estuarine systems. Ann. Mus. R. Afr. Centr. Zool. 275: 149–163.
Whitfield, A.K. 1994b. Fish species diversity in southern African estuarine systems: an evolutionary perspective. Env. Biol. Fish. 40: 37–48.
Whitfield, A.K. 1988. The fish community of the Swartvlei Estuary and the influence of food availability on resource utilization. Estuaries 11: 160–170.
Whitfield, A.K., L.E. Beckley, B.A. Bennett, G.M. Branch, H.M. Kok, J.C. Potter & R.P. van der Elst. 1989. Composition, species richness and similarity of ichthyofaunas in eelgrass Zostera capensis beds of southern Africa. S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 8: 251–259.
Whitfield, A.K., A.W. Paterson, A.H. Bok & H.M. Kok. 1994. A comparison of the ichthyofaunas in two permanently open eastern Cape estuaries. S. Afr. J. Zool. 29: 175–185.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The first author is also the senior author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paterson, A.W., Whitfield, A.K. The Ichthyofauna Associated with an Intertidal Creek and Adjacent Eelgrass Beds in the Kariega Estuary, South Africa. Environmental Biology of Fishes 58, 145–156 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007629328937
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007629328937