Abstract
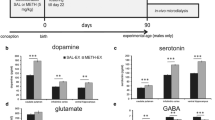
Mercury is a neurotoxin that exists in a number of physical and chemical forms, producing different effects in the brain. In the present work, we have studied the effects of intrastriatal administration of different doses (40 μM, 400 μM, and 4 mM) of organic mercury (methylmercury, MeHg) on the dopaminergic system of rat striatum, in conscious and freely-moving animals, using microdialysis coupled to Liquid Chromatography. In previous works, we have discussed the effects of chronic and acute administration of MeHg on striatal dopaminergic system assessing changes in both release and metabolism of striatal dopamine (DA). In the present study we report that the intrastriatal administration of different doses of MeHg (40 μM, 400 μM, and 4 mM) produced significant increases (907 ± 31%, 2324 ± 156%, and 9032 ± 70% of basal levels, respectively for the different doses) in DA release from rat striatal tissue associated with significant decreases in extracellular levels of its main metabolites dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) and homovallinic acid (HVA) using the dose of 4 mM MeHg (35 ± 3% and 48 ± 1%, respectively), whereas non-significant changes in metabolite levels were observed with the doses of 40 μM and 400 μM MeHg. We explain these effects as a result of stimulated DA release and/or decreased DA intraneuronal degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aschner, M. and Aschner, J. L. 1990. Mercury neurotoxicity: Mechanisms of blood-brain barrier transport. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 14:169–176.
Atchison, W. D. 1987. Effects of activation of sodium and calcium entry on spontaneous release of acetylcholine induced by methylmercury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 241:131–139.
Atchison, W. D. and Hare, M. F. 1994. Mechanism of methylmercury-induced neurotoxicity. FASEB J. 8:622–629.
Bondy, S. C., Anderson, C. L., Harrington, M. E., and Prasad, K. N. 1979. Effects of organic and inorganic lead and mercury on neurotransmitter high-affinity transport and release mechanisms. Environ. Res. 19:102–111.
Chang, L. W. 1975. Neurotoxic effects of mercury: A Review. Environ. Res. 14:329–373.
Faro, L. R. F., Durán R., do Nascimento, J. L. M., Alfonso. M., and Picanço-Diniz C. W. 1997. Effects of methylmercury on the in vivo release of dopamine and its acidic metabolites DOPAC and HVA from striatum of rats. Ecol. Environ. Saf. 38:95–98.
Faro, L. R. F., do Nascimento, J. L. M., Alfonso. M., and Durán, R. 1998. Acute administration of methylmercury changes the in vivo dopamine release from rat striatum. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 60:632–638.
Imperato, A. and Di Chiara, G. 1984. Trans-striatal dialysis coupled to reverse-phase high perfomance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection: A new method for the study of the in vivo release of endogenous dopamine and metabolites. J. Neurosci. 4:966–977.
Komulainen, H. and Bondy, S. 1987. Increased free intrasynaptosomal Ca2+ by neurotoxic organometals: Distinctive mechanisms. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 88:77–86.
Komulainen, H. and Tuomisto, J. 1981. Interference of methylmercury with monoamine uptake and release in rat brain synaptosomes. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 48:214–222.
Minnema, D. J., Cooper, G. P., and Greenland, R. D. 1989. Effects of methylmercury on neurotransmitters release from rat brain synaptosomes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 99:510–521.
Moller-Madsen, B. 1994. Localization of mercury in CNS of the rat. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 75:1–41.
Pellegrino, L. J., Pellegrino, A. S., and Cushman, A. J. 1979. A stereotaxic atlas of the rat brain. New York: Plenum Publishing Corporation.
Westerink, B. H. C. 1985. Sequence and significance of dopamine metabolism in the rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 7:221–227.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faro, L.R.F., do Nascimento, J.L.M., San José, J.M. et al. Intrastriatal Administration of Methylmercury Increases In Vivo Dopamine Release. Neurochem Res 25, 225–229 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007571403413
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007571403413