Abstract
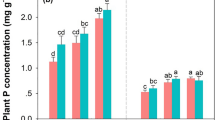
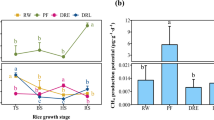
Recent work in seasonally snow covered ecosystems has identifiedthawed soil and high levels of heterotrophic activity throughout the winterunder consistent snow cover. We performed measurements during the winter of1994 to determine how the depth and timing of seasonal snow cover affectsoil microbial populations, surface water NO\({\text{NO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }} \) loss during snowmelt, and plant Navailability early in the growing season. Soil under early accumulating,consistent snow cover remained thawed during most of the winter and bothmicrobial biomass and soil inorganic N pools gradually increased under thesnowpack. At the initiation of snowmelt, microbial biomass N pools increasedfrom 3.0 to 5.9 g n m-2,concurrent with a decrease in soil inorganic N pools. During the latterstages of snowmelt, microbial biomass N pools decreased sharply without aconcurrent increase in inorganic N pools or significant leaching losses. Incontrast, soil under inconsistent snow cover remained frozen during most ofthe winter. During snowmelt, microbial biomass initially increased from 1.7to 3.1 g N m-2 and thendecreased as sites became snow-free. In contrast to smaller pool sizes,NO\({\text{NO}}_{\text{3}}^{\text{ - }} \) export during snowmeltfrom the inconsistent snow cover sites of 1.14 (±0.511) g N m-2 was significantly greater (p< 0.001) than the 0.27 (±0.16) g N m-2 exported from sites with consistent snowcover. These data suggest that microbial biomass in consistentlysnow-covered soil provides a significant buffer limiting the export ofinorganic N to surface water during snowmelt. However, this buffer is verysensitive to changes in snowpack regime. Therefore, interannual variabilityin the timing and depth of snowpack accumulation may explain the year toyear variability in inorganic N concentrations in surface water theseecosystems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron JS (1991) Biogeochemistry of a Subalpine Ecosystem: Loch Vale Watershed, Ecological Studies Ser. 90. Springer-Verlag
Baron JS, Ojima DS, Holland EA & Parton WJ (1994) Analysis of nitrogen saturation potential in Rocky Mountain tundra and forest: Implications for aquatic systems. Biogeochemistry 27: 61–82
Bowman WD, TA Theodose, JC Schardt & RT Conant (1993) Constraints of nutrient availability on primary production in two alpine communities. Ecology 74: 2085–2097
Bowman WD (1992) Inputs and storage of nitrogen in winter snowpack in an alpine ecosystem. Arctic and Alpine Res. 24: 211–215
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G & Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 17: 837–842
Brooks PD, SK Schmidt & MW Williams (1995a) Snowpack controls on soil nitrogen dynamics in the Colorado alpine. In: Tonnessen K, Williams M & Tranter M (Eds) Biogeochemistry of Snow-Covered Catchments (pp 283–292). International Association of Hydrological Sciences Publication 228, Wallingford, UK
Brooks PD, Schmidt SK, Walker, DA & Williams MW (1995b) The Niwot Ridge snow fence experiment: Biogeochemical responses to changes in the seasonal snowpack. In: Tonnessen K, Williams M & Tranter M (Eds) Biogeochemistry of Snow-Covered Catchments (pp 293–302). International Association of Hydrological Sciences Publication 228, Wallingford, UK
Brooks PD, Williams MW & Schmidt SK (1996) Microbial activity under alpine snow packs, Niwot Ridge, CO. Biogeochemistry 32: 93–113
Brooks PD, Schmidt SK & Williams MW (1997) Winter production of CO2 and N2O from alpine tundra; environmental controls and relationship to intersystem C and N fluxes. Oecologia 110: 403–413
Burns SF (1980) Alpine Soil Distribution and Development, Indian Peaks, Colorado Front Range. PhD Dissertation, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO
Cline D (1995) Snow surface energy exchanges and snowmelt at a continental alpine site. In: Tonnessen K, Williams M & Tranter M (Eds) Biogeochemistry of Snow-covered Catchments (pp 157–166). International Association of Hydrological Sciences Publication 228, Wallingford, UK
Creed IF, Band LE, Foster NW, Morrison IK, Nicholson JA, Semkin RS & Jeffries DS (1996) Regulation of nitrate-N release from temperate forests: A test of the N flushing hypothesis. Water Resour. Res. 32: 3337–3354
Davidson EA, Eckert RW, Hart SC & Firestone MK (1989) Direct extraction of microbial biomass nitrogen from forest and grassland soils of California. Soil Biol. Biochem. 21: 773–778
DiStephano JF & Gholz HL (1986) A proposed use of ion exchange resins to measure nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in intact soil cores. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 17: 989–998
Fisk, MC (1995) Nitrogen dynamics in an alpine landscape. PhD Dissertation, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO
Fisk MC & Schmidt SK (1995) Nitrogen mineralization and microbial biomass N dynamics in three alpine tundra communities. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 59: 1036–1043
Grant MC & Lewis WM (1982) Chemical loading rates from precipitation in the Colorado Rockies. Tellus 34: 74–88
Greenland D (1989) The climate of Niwot Ridge, Front Range, Colorado. Arctic and Alpine Research 21: 380–391
Hart SC & Gunther AT (1989) In situ estimates of annual net mineralization and nitrification in a subarctic watershed. Oecologia. 80: 284–288
Kendall C, Campbell DH, Burns DA, Shanley JB, Silva RA & Chang CC (1995) Tracing sources of nitrate in snowmelt runoff using the oxygen and nitrogen isotopic concentrations of nitrate: Pilot studies at three catchments. In: Tonnessen K, Williams M & Tranter M (Eds) Biogeochemistry of Snow-covered Catchments (pp 339–348). International Association of Hydrological Sciences Publication 228, Wallingford, UK
Lewis WM & Grant MC (1980) Relationship between snow cover and winter losses of dissolved substances from a mountain watershed. Arctic and Alpine Research 12: 11–17
Lewis WM Jr, Grant MC & Saunders JF III (1984) Chemical patterns of bulk atmospheric deposition in the State of Colorado. Water Resour. Res. 20: 1691–1704
Mullen RB & Schmidt SK (1993) Mycorrhizal infection, phosphorus uptake, and phenology in Ranunculus adoneus: Implications for the functioning of mycorrhizae in alpine systems. Oecologia 94: 229–234
Oberbauer S & Billings WD (1981) Drought tolerance and water use by plants along an alpine topographical gradient. Oecologia 50: 325–331
Rascher CM, Driscoll CT & Peters NE (1987) Concentration and flux of solutes from snow and forest floor during snowmelt in the West-Central Adirondack region of New York. Biogeochemistry 3: 209–224
Schimel JP, Kielland K & Chapin FS III (1994) Nutrient Availability and Uptake by Tundra Plants. In: Reynolds JF & Tenhunen JD (Eds) Landscape Function: Implications for Ecosystem Response to Disturbance: A Case Study in Arctic Tundra (pp 203–221). Springer-Verlag
Sievering H, Burton D & Caine N (1992) Atmospheric loading of nitrogen to alpine tundra in the Colorado Front Range. Global Biogeochemical Cycles. 6: 339–346
Sommerfeld RA, Musselman RC, Ruess JO & Mosier AR (1991) Preliminary measurements of CO2 in melting snow. Geophysical Research Letters 18: 1225–1228
Sommerfeld RA, Mosier AR & Musselman RC (1993) CO2, CH4, and N2O flux through a Wyoming snowpack. Nature 361: 140–143
Sommerfeld RA, Massman WJ & Musselman RC (1996) Diffusional flux of CO2 through snow: Spatial and temporal variability among alpine-subalpine sites. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 10: 473–482
Walker DA, Halfpenny JC, Walker MD & Wessman CA (1993) Long-Term studies on snowvegetation interactions. Bioscience 43: 287–301
Walker MD, Webber PJ, Arnold EH & Ebert-May D (1994) Effects of inter-annual climate variation on above ground phytomass in alpine vegetation. Ecology 75: 393–408
Williams MW & Melack JM (1991) Solute chemistry of snowmelt and runoff in an alpine basin, Sierra Nevada. Water Resources Research. 27: 1575–1588
Williams MW, Caine N, Baron J, Sommerfeld RA & Sanford RL (1993) Regional assessment of nitrogen saturation in the Rocky Mountains. EOS, Transactions of the American Geophysical Meeting, 1993 Fall Meeting 74(Supplement): 257
Williams MW, Bales RC, Brown AD & Melack JM (1995) Fluxes and transformations of nitrogen in a high-elevation catchmen, Sierra Nevada. Biogeochemistry 28: 1–31
Williams MW, Brooks PD, Mosier AR & Tonnessen KA (1996a) Mineral N transformations in and under seasonal snow in a high-elevation catchment, Rocky Mountains, USA. Water Resources Research 32: 3175–3185
Williams MW, Losleben M, Caine N & Greenland D (1996b) Changes in climate and hydrochemical responses in a high elevation catchment, Rocky Mountains. Limnol. Oceanogr. 41: 939–946
Zak DR, Groffman PM, Pregitzer KS, Chreistensen S & Tiedje JM (1990) The vernal dam: Plant-microbe competition for nitrogen in northern hardwood forests. Ecology 7: 651–656
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brooks, P.D., Williams, M.W. & Schmidt, S.K. Inorganic nitrogen and microbial biomass dynamics before and during spring snowmelt. Biogeochemistry 43, 1–15 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005947511910
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005947511910