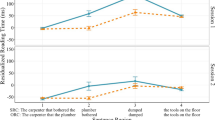
Abstract
Researchers frequently use data from monitoring tasks to argue that constraints on meaning facilitate lower-level processes. An alternate hypothesis is that the processing level that a monitoring task requires interacts with discourse-level processing. Subjects monitored spoken sentences for a synonym (semantic match), a nonsense word (phonological match), or a rhyme (phonologically and semantically constrained matching). The critical targets appeared at the beginning of the final clause in two-clause sentences that began with if, which signals a semantic analysis at the discourse level, or with though, which maintains a surface representation. Synonym-monitoring times were faster for if than for though, nonsense word-monitoring times were faster for though than for if, and rhyme-monitoring times did not differ for if and though. The results show that conjunctions influence how listeners allocate attention to semantic versus phonological information, implying that listeners form these kinds of information independently.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Cairns, H. S., Cowart, W., & Jablon, A. D. (1981). Effects of prior context upon the integration of lexical information during sentence processing. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 20, 445–453.
Crain, S., & Steedman, M. (1985). On not being led up the garden path: The use of context by the psychological syntax processor. In D. R. Dowty, L. Karttunen, & A. M. Zwicky (Eds.), Natural language parsing: Psychological, computational, and theoretical perspectives. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Elman, J. L., & McClelland, J. L. (1984). Speech perception as a cognitive process: The interactive activation model. In N. Lass (Ed.), Speech and language, Vol. 10. New York: Academic Press.
Green, D. W. (1975). The effects of tasks on the representation of sentences. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 14, 275–283.
Liberman, A. M., Cooper, F. S., Shankweiler, D. P., & Studdert-Kennedy, M. (1967). Perception of the speech code. Psychological Review, 74, 431–461.
Marslen-Wilson, W. D., & Tyler, L. K. (1975). Processing structure of sentence perception. Nature, 257, 784–786.
Marslen-Wilson, W., Tyler, L., & Seidenberg, M. (1978). Sentence processing and the clause boundary. In W. J. M. Levelt & G. B. Flores d'Arcais (Eds.), Studies in the perception of language (pp. 219–246). New York: Wiley.
Marslen-Wilson, W. D., & Welsh, A. (1978). Processing interactions and lexical access during word recognition in continuous speech. Cognitive Psychology, 10, 29–63.
McClelland, J. L., St. John, M., & Taraban, R. (1989). Sentence comprehension: A parallel distributed processing approach. Language and Cognitive Processes, 4, SI287–336.
Rubenstein, H., Garfield, L., & Milliken, J. A. (1970). Homographic entries in the internal lexicon. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 9, 487–492.
Samuel, A. (1981). Phonemic restoration: Insights from a new methodology. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 110, 474–494.
Townsend, D. J., & Bever, T. G. (1978). Inter-clause relations and clausal processing. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 17, 509–521.
Townsend, D. J., & Bever, T. G. (1991). The use of higher-level constraints in monitoring for a change in speaker demonstrates functionally distinct levels of representation during discourse comprehension. Language and Cognitive Processes, 6, 49–77.
Tyler, L. K., & Marslen-Wilson, W. D. (1977). The on-line effects of semantic context on syntactic processing. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 16, 683–692.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Townsend, D.J., Hoover, M. & Bever, T.G. Word-Monitoring Tasks Interact with Levels of Representation During Speech Comprehension. J Psycholinguist Res 29, 265–274 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005148104885
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005148104885