Abstract
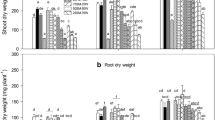
The effects of earthworms (Lumbricidae) on plant biomass production and N allocation in model intercropping systems of winter wheat and white clover were evaluated in two pot experiments. Wheat and wheat-clover mixtures were grown in a low-organic loam soil, earthworms were added at densities comparable to field population densities and the experiments were terminated 48 and 17 d after earthworm introductions. In both experiments, earthworms significantly increased the biomass and N uptake of wheat while they had generally no effects on clover. As a result, earthworm activity increased the proportion of wheat biomass in the total plant biomass of the mixture. Nitrogen budgets of the experiment lasting 48 d indicated that additional N in the system made available by earthworm activity was primarily taken up by the wheat. Earthworms also affected intra-plant N allocation in wheat which had significantly higher shoot:root N ratios when earthworms were present. When clover was labelled with 15N in the experiment which lasted 17 d, endogeic earthworms significantly reduced the amounts of 15N excess transferred from living or decomposing clover roots to accompanying wheat plants. Earthworms assimilated small quantities of 15N tracer from decomposing clover roots but not from living clover roots. The results of these model experiments suggest that earthworms can affect the balance between intercropped cereals and legumes by altering intra- and inter-plant N allocation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amijee F, Stribley D P and Lane P W 1993 The susceptibility of roots to infection by an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in relation to age and phosphorus supply. New Phytol. 125, 581–586.
Baker G H, Williams P M L, Carter P J and Long N R 1997 Influence of lumbricid earthworms on yield and quality of wheat and clover in glasshouse trials. Soil Biol. Biochem. 29, 599–602.
Barley K P 1961 The abundance of earthworms in agricultural land and their possible significance in agriculture. Adv. Agron. 13, 249–268.
Baylis J P 1984 Studies on root feeding by animals with particular emphasis on Trifolium repens L. Ph.D. thesis, University College of North Wales, Bangor, UK. 169 p.
Boller B C and Nösberger J 1987 Symbiotically fixed nitrogen from field-grown white and red clover mixed with ryegrass at low levels of 15N-fertilization. Plant Soil 104, 219–226.
Cassel D K and Nielsen D R 1986 Field capacity and available water capacity. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 1: Physical and Mineralogical Methods, 2nd ed. Ed A Klute. pp. 901–926. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America, Madison.
Clements B and Donaldson G 1997 Clover and cereals-low input bi-cropping. Farming and Conservation 3(4), 12–14.
Collins R P, Fothergill M and Rhodes I 1996 Interactions between seedlings of perennial ryegrass and white clover cultivars in establishing swards. Grass Forage Sci. 51, 163–169.
Conry M J, Hammond R F and O'Shea T 1970 Soils of County Kildare. National Soil Survey of Ireland, An Foras TalÚntais, Dublin. 92 p.
Cope W C 1916 Kjeldahl modification for determination of nitrogen in nitro substitution compounds. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 8, 592–593.
Cortez J and Bouché M B 1992 Do earthworms eat living roots? Soil Biol. Biochem. 24, 913–915.
Curry J P and Byrne D 1992 The role of earthworms in straw decomposition and nitrogen turnover in arable land in Ireland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 24, 1409–1412.
Doube B M, Ryder M H, Davoren C W and Stephens P M 1994 Enhanced root nodulation of subterranean clover (Trifolium subterraneum) by Rhizobium leguminosarium biovar trifolii in the presence of the earthworm Aporrectodea trapezoides (Lumbricidae). Biol. Fertil. Soils. 18, 169–174.
Edwards C A and Bohlen P J 1996 Biology and Ecology of Earthworms, 3rd ed. Chapman and Hall, London. 426 p.
Farnham D E and George J R 1993 Dinitrogen fixation and nitrogen transfer among red clover cultivars. Can. J. Plant Sci. 73, 1047–1054.
Francis C A 1989 Biological efficiencies in multiple-cropping systems. Adv. Agron. 42, 1–42.
Gunn A and Cherrett J M 1993 The exploitation of food resources by soil meso-and macro-invertebrates. Pedobiologia 37, 303–320.
Halpin U 1992 Physical, micromorphological and associated properties of soil crusts and the effect of soil amendments on sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) seedling emergence and growth. Ph.D. thesis, National University of Ireland, Dublin. 318 pp.
Hamel C, Barrantes-Cartín U, Furlan V and Smith D L 1991 Endomycorrhizal fungi in nitrogen transfer from soybean to maize. Plant Soil 138, 33–40.
Handley L L, Daft M J, Wilson J, Scrimgeour C M, Ingleby K and Sattar M A 1993 Effects of the ecto-and VA-mycorrhizal fungi Hydnagium carneum and Glomus clarum on the δ15N and δ13C values of Eucalyptus globulus and Ricinus communis. Plant Cell Environ. 16, 375–382.
Hart P B S, Rayner J H and Jenkinson D S 1986 Influence of pool substitution on the interpretation of fertilizer experiments with 15N. J. Soil Sci. 37, 389–403.
Hatch D J and Murray P J 1994 Transfer of nitrogen from damaged roots of white clover (Trifolium repens L.) to closely asscociated roots of intact perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Plant Soil 166, 181–185.
Haystead A, Malajczuk N and Grove T S 1988 Underground transfer of nitrogen between pasture plants infected with vesiculararbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 108, 417–423.
Höflich G 1989 Symbiotische N2-Fixierung. In Methoden der Bodenbiologie. Eds W Dunger and H J Fiedler. pp. 152–160. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Jena.
Høgh-Jensen H and Schjoerring JK 1997 Interactions between white clover and ryegrass under contrasting nitrogen availability: N2 fixation, N fertilizer recovery, N transfer and water use efficiency. Plant Soil 197, 187–199.
Hoogerkamp M, Rogaar H and Eijsackers H J P 1983 Effect of earthworms on grassland on recently reclaimed polder soils in the Netherlands. In Earthworm Ecology: From Darwin to Vermiculture. Ed. J E Satchell. pp. 85–105. Chapman and Hall, London.
Janzen H H and Gilbertson C 1994 Exchange of 15N among plants in controlled environment studies. Can. J. Soil Sci. 74, 109–110.
Johansen A and Jensen E S 1996 Transfer of N and P from intact or decomposing roots of pea to barley interconnected by an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. Soil Biol. Biochem. 28, 73–81.
Jones L 1992 Preliminary trials using a white clover (Trifolium repens L.) understorey to supply the nitrogen requirements of a cereal crop. Grass Forage Sci. 47, 366–374.
Jones L and Clements R O 1993 Development of a low input system for growing wheat (Triticum vulgare) in a permanent understorey of white clover (Trifolium repens). Ann. Appl. Biol. 123, 109–119.
Jørgensen F V and Jensen E S 1997 Short-term effects of a dung pat on N2 fixation and total N uptake in a perennial ryegrass/white clover mixture. Plant Soil 196, 133–141.
Kang BT 1988 Nitrogen cycling in multiple cropping systems. In Advances in Nitrogen Cycling in Agricultural Ecosystems. Ed. J R Wilson. pp. 333–348. CAB International, Wallingford.
Knight D, Elliott P W and Anderson J M 1989 Effects of earthworms upon transformations and movement of nitrogen from organic matter applied to agricultural soils. In Nitrogen in OrganicWastes Applied to Soils. Eds J A Hansen and K Henriksen. pp. 59–80. Academic Press, London.
Lee K E 1985 Earthworms: Their Ecology and Relationships with Soils and Land Use. Academic Press, Sydney. 411 p.
Makeschin F 1980 Einfluß von Regenwürmern (Lumbricidae, Oligochaeta) auf den Boden sowie auf Ertrag und Inhaltsstoffe von Nutzpflanzen. Ph.D. thesis, University of Giessen, Germany. 119 p.
Marinissen J C Y and de Ruiter P C 1993 Contribution of earthworms to carbon and nitrogen cycling in agro-ecosystems. Agric. Ecosys. Environ. 47, 59–74.
Mohr R M, Janzen H H and Entz M H 1998 Nitrogen dynamics under greenhouse conditions as influenced by method of alfalfa termination. 1. Volatile N losses. Can. J. Soil Sci. 78, 253–259.
Murray P J and Hatch D J 1994 Sitona weevils (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) as agents for rapid transfer of nitrogen from white clover (Trifolium repens L.) to perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Ann. Appl. Biol. 125, 29–33.
Ruz Jerez B E, Ball P R and Tillman R W 1988 The role of earthworms in nitrogen release from herbage residues. In Nitrogen Efficiency in Agricultural Soils. Eds D S Jenkinson and K A Smith. pp. 355–370. Elsevier Applied Science, London and New York.
Scheu S 1994 There is an earthworm mobilizable nitrogen pool in soil. Pedobiologia 38, 243–249.
Schmidt O, Scrimgeour C M and Handley L L 1997 Natural abundance of 15N and 13C in earthworms from a wheat and a wheat-clover field. Soil Biol. Biochem. 29, 1301–1308.
Sharpe R R and Harper L A 1997 Apparent atmospheric nitrogen loss from hydroponically grown corn. Agron. J. 89, 605–609.
Sims R W and Gerard B M 1985 Earthworms: Keys and Notes for the Identification and Study of the Species. Synopses of the British Fauna (New Series) No. 31. The Linnean Society of London and The Estuarine and Brackish-Water Sciences Association, London. 171 p.
Stern W R 1993 Nitrogen fixation and transfer in intercrop systems. Field Crops Res. 34, 335–356.
Subler S, Parmelee R W and Allen M F 1998 Earthworms and nitrogen mineralization in corn agroecosystems with different nutrient amendments. Appl. Soil Ecol. 9, 295–301.
Thompson L, Thomas C D, Radley J M A, Wiliamson S and Lawton J H 1993 The effect of earthworms and snails in a simple plant community. Oecologia 95, 171–178.
Tomm G O, van Kessel C and Slinkard A E 1994 Bi-directional transfer of nitrogen between alfalfa and bromegrass: short and long term evidence. Plant Soil 164, 77–86.
Vallis I, Haydock K P, Ross P J and Henzell E F 1967 Isotopic studies on the uptake of nitrogen by pasture plants. III. The uptake of small additions of 15N-labelled fertilizer by rhodes grass and Townsville lucerne. Aust. J. Agr. Res. 18, 865–877.
van Rhee J A 1965 Earthworm activity and plant growth in artificial cultures. Plant and Soil 22, 45–48.
Vinther, FP 1998 Biological nitrogen fixation in grass-clover affected by animal excreta. Plant Soil 203, 207–215.
Walley F L, Tomm G O, Matus A, Slinkard A E and van Kessel C 1996 Allocation and cycling of nitrogen in an alfalfa-bromegrass sward. Agron. J. 88, 834–843.
Waters R A S 1951 Earthworms and the fertility of pasture. Proc. N. Z. Grassl. Assoc. 13, 168–175.
Weaver R W and Frederick L R 1982 Rhizobium. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd ed. Ed. A L Page. pp. 1043–1070. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America, Madison.
Willey R W 1979 Intercropping-its importance and research needs [review]. Field Crop Abstr. 32, 1–10 and 73–85.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, O., Curry, J.P. Effects of earthworms on biomass production, nitrogen allocation and nitrogen transfer in wheat-clover intercropping model systems. Plant and Soil 214, 187–198 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004723914623
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004723914623