Abstract
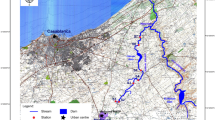
Longitudinal changes in benthic organic matter (BOM), physicochemical variables and macroinvertebrate community structure and functional organization were examined at six sites in the plains section of the Cache la Poudre River, north central Colorado, U.S.A., along a gradient affected by urbanization and agricultural activities. A corer (314 cm{2}) was used to collect BOM and macroinvertebrates and a defined area (11.4 cm{2}) of epilithon from cobble-sized rocks was removed to measure chlorophyll a and periphytic biomass monthly from September, 1993 to August, 1994. BOM dynamics in the stream reach was a consequence of the hydrological flow regime, water chemistry and the growth patterns of macrophytes. The total BOM standing stocks attained maxima at sites 3 and 4 which were primarily impacted by agricultural activities. The concentrations of periphyton chlorophyll a at downstream reaches were two to six times higher that at the upstream reference site. The results from redundancy analysis (RDA) indicated that macroinvertebrate assemblages exhibited the strongest relationship with the distribution and abundance of aquatic vascular plants. The aquatic vascular plants supported a significantly higher diversity of macroinvertebrates. The major roles of aquatic vascular plants were to trap fine particulate organic matter and serve as spatial habitat structure for benthic macroinvertebrates. The spatial variations in the functional organization of macroinvertebrate communities reflected the alterations of physicochemical characteristics and food resource availability in the stream ecosystem. Collector-gatherers formed the dominant group at site 2 which were impacted by the effluents from wastewater treatment facilities. Conversely, the densities of scrapers and shredders were much reduced at the sampling site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association, 1989. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C.
Anderson, N. H. & J. R. Sedell, 1979. Detritus processing by macroinvertebrates in stream ecosystems. Annual Review of Entomology 24: 351-377.
Angradi, T. R., 1991. Transport of coarse particulate organic matter in an Idaho river, U.S.A. Hydrobiologia 211: 171-183.
Benke, A. C., G. E. Willeke, F. K. Parrish & D. L. Stites, 1981. Effects of urbanization on stream ecosystems. Completion report project number A-055-GA, Office of Water Research and Technology, U.S. Department of the Interior.
Barmuta, L. A., 1988. Benthic organic matter and macroinvertebrate functional feeding groups in a forested upland stream in temperate Victoria. Verh. int. Ver. Theor. Ang. Limnol. 23: 1394-1398.
Boulton, A. J. & P. S. Lake, 1992. Benthic organic matter and detritivorous macroinvertebrates in two intermittent streams in south-eastern Australia. Hydrobiologia 241: 107-118.
Britton, D. L., 1990. Fire and the dynamics of allochthonous detritus in a South African mountain stream. Freshwat. Biol. 24: 347-360.
Cody, R. P. & J. K. Smith, 1997. Applied statistics and the SAS programming language. 4th ed. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: 150-174.
Corkum, L. D., 1992. Relationships between density of macroinvertebrates and detritus in rivers. Arch. Hydrobiol. 125: 149-166.
Cummins, K.W., 1974. Structure and function of stream ecosystem. BioScience 24: 631-641.
Cummins, K.W., 1975. Macroinvertebrates. In Whitton, B. A. (ed.), River Ecology. Blackwell, Oxford: 170-198.
Cummins, K. W., J. R. Sedell, F. J. Swanson, G. W. Minshall, S. G. Fisher, C. E. Cushing, R. C. Petersen & R. L. Vannote, 1983. Organic matter budgets for stream ecosystems: problems in their evaluation. In Barnes, J. R. & G. W. Minshall (eds), Stream Ecology. Plenum Press, New York: 299-353.
Delong, M. D. & M. A. Brusven, 1992. Patterns of periphyton chlorophyll a in an agricultural nonpoint source impacted stream. Wat. Res. Bull. 28: 731-741.
Delong, M. D. & M. A. Brusven, 1993. Storage and decomposition of particulate organic matter along the longitudinal gradient of an agriculturally-impacted stream. Hydrobiologia 262: 77-88.
Delong, M. D. & M. A. Brusven, 1994. Allochthonous input of organic matter from different riparian habitats of an agriculturally impacted stream. Envir. Man. 18: 59-71.
Delong, M. D. & M. A. Brusven, 1998. Macroinvertebrate community structure along the longtiduinal gradient of an agriculturally impacted stream. Envir. Man. 22: 445-457.
Dennehy, K. F., D. W. Litke, P. B. McMahon, J. S. Heiny & C. M. Tate, 1995. Water-quality assessment of the South Platte River Basin, Colorado, Nebraska, and Wyoming-Analysis of available nutrient, suspended-sediment, and pesticide data, water years 1980-1992. U.S. Geological Survey, Wat. Res. Investigations Report 94-4095.
Dennehy, K. F., D. W. Like, C. M. Tate & H. S. Heiny, 1993. South Platte River Basin-Colorado, Nebraska, and Wyoming. Wat. Res. Bull. 28: 647-683.
Drake, J. A., 1984. Species aggregation: the influence of detritus in a benthic invertebrate community. Hydrobiologia 112: 109-115.
Dudley, T. L., S. D. Cooper & N. Hemphill, 1986. Effects of macroalgae on stream invertebrate community. J. N. am. Benthol. Soc. 5: 93-106.
Egglishaw, H. J., 1968. The quantitative relationship between bottom fauna and plant detritus in streams of different calcium concentrations. J. appl. Ecol. 5: 731-740.
Fox, A. M., 1992. Macrophytes. In Calow, P. & G. E. Petts (eds), The Rivers Handbook - Hydrological and Ecological Principles. Volume 1. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford: 216-233.
Gollady, S. W., J. R. Webster & E. F. Benfield, 1989. Changes in stream benthic organic matter following watershed disturbance. Holarct. Ecol. 12: 96-105.
Gregg, W. W. & F. L. Rose, 1982. The effects of aquatic macrophytes on the stream micro-environment. Aquat. Bot. 14: 309-324.
Gregg, W. W. & F. L. Rose, 1985. Influences of aquatic macrophytes on invertebrate community structure, guild structure and microdistribution in streams. Hydrobiologia 128: 45-56.
Hawkins, C. P. & J. R. Sedell, 1981. Longitudinal and seasonal changes in functional organization of macroinvertebrate communities in four Oregon streams. Ecology 62: 387-397.
Hill, B. H. & J. R. Webster, 1983. Aquatic macrophyte contribution to the New River organic matter budget. In Fontain, T. D. III & S. M. Bartell (eds), Dynamics of Lotic Ecosystems. Ann Arbor Science Publishers, Ann Arbor, Michigan: 273-282.
Huck, S.W. & W. H. Cormier, 1996. Reading statistics and research. 2nd edn. Harper Collins College Publishers, New York.
Iversen, T. M., J. Thorup, T. Hansen, L. Lodal & J. Olsen, 1985. Quantitative estimates and community structure of invertebrates in a macrophyte rich stream. Arch. Hydrobiol. 102: 291-301.
Jones, R. C. & C. C. Clark, 1987. Impact of watershed urbanization on stream insect communities. Wat. Res. Bull. 23: 1047-1055.
Kerans, B. L. & J. R. Karr, 1994. A benthic index of biotic integrity (B-IBI) for rivers of the Tennessee Valley. Ecol. Appl. 4: 768-785.
Koetsier, P., G. W. Minshall & C. T. Robinson, 1996. Benthos and macroinvertebrate drift in six streams differing in alkalinity. Hydrobiologia 317: 41-49.
Lamberti, G. A. & J. W. Moore, 1984. Aquatic insects as primary consumers. In Resh, V. H. & D. M. Rosenberg (eds), The Ecology of Aquatic Insects. Praeger Publishers, New York: 164-195.
Ludwig, J. A. & J. F. Reynolds, 1988. Statistical ecology: a primer on methods and computing. John Wiley & Sons, New York: 85-103.
Malmqvist, B., L. M. Nilsson & B. S. Svensson, 1978. Dynamics of detritus in a small stream in southern Sweden and its influence on the distribution of the bottom animal communities. Oikos 31: 3-16.
Maridet, L., J. G. Wasson, M. Philippe & C. Amoros, 1995. Benthic organic matter dynamics in three streams: Riparian vegetation or bed morphology control? Arch. Hydrobiol. 132: 415-425.
Merritt, R. W. & K. W. Cummins, 1996. An introduction to the aquatic insects of North America. 3rd edn. Kendall/Hunt, Dubuque, Iowa.
Minshall, G. W., J. T. Brock & T. W. LaPoint, 1982. Characterization and dynamics of benthic organic matter and invertebrate functional feeding group relationships in the Upper Salmon River, Idaho (U.S.A.). Int. Rev. ges. Hydrobiol. 67: 793-820.
Minshall, G. W. & J. N. Minshall, 1977. Microdistribution of benthic invertebrates in a Rocky Mountain (USA) stream. Hydrobiologia 55: 231-249.
Naiman, R. J., J. M. Melillo, M. A. Lock, T. E. Ford & S. E. Reice, 1987. Longitudinal patterns of ecosystem processes and community structure in a subarctic river continuum. Ecology 68: 1139-1156.
Naiman, R. J. & J. R. Sedell, 1979. Benthic organic matter as a function of stream order in Oregon. Arch. Hydrobiol. 87: 404-422.
Olive, J. H., J. L. J ackson, J. Bass, L. Holland & T. Savisky, 1988. Benthic macroinvertebrates as indexes of water quality in the upper Cuyahoga River. Ohio J. Sci. 88: 91-98.
Plafkin, J. L., M. T. Barbour, K. D. Porter, S. K. Gross & R. M. Hughes, 1989. Rapid bioassessment protocols for use in streams and rivers: benthic macroinvertebrates and fish. Assessment and Water Protection Division, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Report 444/4-89-001.
Rabeni, C. F., S. P. Davies & K. E. Gibbs, 1985. Benthic invertebrate response to pollution abatement: Structural changes and functional implications. Wat. Res. Bull. 21: 489-497.
Sculthorpe, C. D, 1967. The Biology of Aquatic Vascular Plants. Edward Arnold, London.
Thorp, J. H. & A. P. Covich, 1991. Ecology and classification of North American freshwater invertebrates. Academic Press, San Diego, California.
Shieh, S.-H., 1998. Macroinvertebrate community structure, functional organization, production and energy flow in a Colorado plains stream. Ph. D. thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado.
Shieh, S.-H, B. C. Kondratieff, J. V. Ward & D. A. Rice, 1999. The relationship of macroinvertebrate assemblages to water chemistry in a polluted Colorado plains stream. Arch. Hydrobiol. 145: 405-432.
Short, R. A. & J. V. Ward, 1981. Benthic detritus dynamics in a mountain stream. Holarctic Ecol. 4: 32-35.
Ter Braak, C. J. F., 1988. CANOCO-a FORTRAN program for canonical correspondence analysis, principal components analysis and redundancy analysis (version 3.12). Agricultural Mathematics Group, Box 100, 6700 AC Wageningen, The Netherlands.
Ter Braak, C. J. F., 1990. Update notes: CANOCO, Version 3.10. Agricultural Mathematics Group, Wageningen, The Netherlands.
Ter Braak, C. J. F., 1995. Ordination.In Jongman, R. H. G., C. J. F. Ter Braak & O. F. R. Van Tnogeren (eds), Data Analysis in Community and Landscape Ecology. Cambridge University Press: 91-173.
Thorp, J. H. & A. P. Covich, 1991. Ecology and classification of North American freshwater invertebrates. Academic Press, San Diego, California.
Tuchman, N. C. & R. H. King, 1993. Changes in mechanisms of summer detritus processing between wooded and agricultural sites in a Michigan headwater stream. Hydrobiologia 268: 115-127.
Vannote, R. L., G. W. Minshall, K. W. Cummins, J. R. Sedell & C. E. Cushing, 1980. The river continuum concept. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 37: 130-137.
Voelz, N. J. & J. V. Ward, 1990. Macroinvertebrate responses along a complex regulated stream environmental gradient. Regulated Rivers: Res. Man. 5: 365-374.
Voelz, N. J. & J. V. Ward, 1991. Biotic responses along the recovery gradient of a regulated stream. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 48: 2477-2490.
Ward, J. V. & B. C. Kondratieff, 1992. An Illustrated Guide to the Mountain Stream Insects of Colorado. The University Press of Colorado, Niwot, Colorado.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shieh, SH., Kondratieff, B. & Ward, J. Longitudinal changes in benthic organic matter and macroinvertebrates in a polluted Colorado plains stream. Hydrobiologia 411, 191–209 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003835929331
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003835929331