Abstract
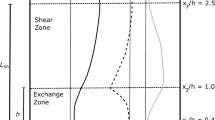
Simultaneous triaxial sonic anemometer velocity measurements vertically arrayed at six levels within and above a uniform pine forest were used to examine two parameterization schemes for the triple-velocity correlation tensor employed in higher-order closure models. These parameterizations are the gradient-diffusion approximation typically used in second-order closure models, and the full budget for the triple-velocity correlation tensor typically employed in third-order closure models. Both second- and third-order closure models failed to reproduce the measured profiles of the triple-velocity correlation within and above the canopy. However, the Reynolds stress tensor profiles (including velocity variances) deviated greatly from the measurements only within the lower levels of the canopy. It is shown that the Reynolds stresses are most sensitive to the parameterization of the triple-velocity correlation in these lower canopy regions where local turbulent production is negligible and turbulence is mainly sustained by the flux transport term. The failure of the third-order closure model to reproduce the measured third moments in the upper layers of the canopy-top contradicts conclusions from a previous study over shorter vegetation but agrees with another study for a deciduous forest. Whether the third-order closure model failure is due to the zero-fourth-cumulant closure approximation is therefore considered. Comparisons between measured and predicted quadruple velocity correlations suggest that the zero-fourth-cumulant approximation is valid close to the canopy-atmosphere in agreement with recent experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
André, J. C., Lacarrere, P., and Traore, K.: 1981, 'Pressure Effects on Triple Correlations in Turbulent Convective Flows’, in Turbulent Shear Flows III, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 243-252.
Albini, F. A.: 1981, 'A Phenomenological Model for Wind Speed and Shear Stress Profiles in Vegetation Cover Layers’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 20, 1325-1335.
Antonia, R. A. and Luxton, R.E.: 1974, 'Characteristics of Turbulence within an Internal Boundary Layer’, Adv. Geophys. 18A, 263-285.
Baldocchi, D.: 1989, 'Turbulent Transfer in a Deciduous Forest’, Tree Phys. 5, 357-377.
Baldocchi, D.: 1992, 'A Lagrangian Random Walk Model for Simulation Water Vapor, CO2 and Sensible Heat Densities and Scalar Profiles over and within a Soybean Canopy, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 61, 113-144.
Brodkey, R. S.: 1967, The Phenomena of Fluid Motions, Dover Publications, 737 pp.
Cionco, R. M.: 1965, 'A Mathematical Model for Air Flow in Vegetative Canopy’, J Appl. Meteorol. 4, 517-522.
Cionco, R. M.: 1972, 'A Wind Profile Index for Canopy Flow’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 3, 255-263.
Cowan, I. R.: 1968, 'Mass, Heat, and Momentum Exchange between Stands of Plants and their Atmospheric Environment’, Quart J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 94, 318-332.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1978, 'Closure of Second and Third Moment Rate Equations for Diffusion in Homogeneous Turbulence’, Phys. Fluids 21, 525-530.
Donaldson, C. Du P.: 1973, 'Construction of a Dynamic Model for the Production of Atmospheric Turbulence and the Dispersion of Atmospheric Pollutants’, in Workshop on Micrometeorology, Amer. Meteorol. Soc., pp. 313-392.
Ellsworth, D., Oren, R., Huang, C., Phillips, N., and Hendrey, G. R.: 1995, 'Leaf and Canopy Responses to Elevated CO2 in a Pine Forest under Free Air CO2 Enrichment’, Oecologia 104, 139-146.
Gardiner, C. W.: 1983, Handbook of Stochastic Methods for Physics, Chemistry, and the Natural Sciences, Springer-Verlag, 442 pp.
Hanjalic, K. and Launder, B. E.: 1972, 'A Reynold Stress Model for Turbulence and its Application to Thin Shear Flows’, J. Fluid Mech. 52, 609-638.
Halidin, S. and Lindroth, A.: 1986, 'Pine Forest Microclimate Simulation Using Different Diffusivities’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 35, 103-123.
Kaimal, J. C. and Finnigan, J.J.: 1994, Atmospheric Boundary Layer Flows: Their Structure and Measurement, Oxford Press, 289 pp.
Katul, G. G., Oren, R., Ellsworth, D., Hsieh, C. I., Phillips, N., and Lewin, K.: 1997a, 'A Lagrangian Dispersion Model for Predicting CO2 Sources, Sinks, and Fluxes in a Uniform Loblolly Pine (Pinus taedaL.) Stand’, J. Geophys. Res. 102, 9309-9321.
Katul, G. G., Hsieh, C. I., Kuhn, G., Ellsworth, D., and Nie, D.: 1997b, 'Turbulent Eddy Motion at the Forest-Atmosphere Interface’,J. Geophys Res. 102,13,409-13,421.
Kondo, J. and Akashi, S.: 1976,'Numerical Studies on the Two-Dimensional Flow in Horizontally Homogeneous Canopy Layers’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 10, 255-272.
Launder, B. E.: 1996, 'An Introduction to Single-Point Closure Methodology’, in T. B. Gatski, M. Y. Hussaini, and J. L. Lumley (eds.), Simulation and Modeling of Turbulent Flows, ICASE/LaRC Series in Computational Science and Engineering, Oxford University Press, 314 pp.
Launder, B. E., Reece, G. J., and Rodi, W.: 1975, 'Progress in the Development of a Reynold-Stress Turbulence Closure’, J. Fluid Mech. 68, 537-566.
Leclerc, M. Y., Thurtell, G. W., and Kidd, G. E.: 1988,'Measurements and Langevin Tracer Concentration Fields Downwind from a Circular Source Inside an Alfalfa Canopy’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 43, 287-308.
Lewellen, W. S., Teske, M. E., and Sheng, Y. P.: 1980, 'Micrometeorological Applications of a Second Order Closure Model of Turbulent Transport, in L. J. S. Bradbury, F. Durst, B. E. Launder, F. W. Schmidt, and J. H. Whitelaw (eds.), Turbulent Shear Flows II, Springer-Verlag, pp. 366-378.
Li, Z. J., Miller, D. R., and Lin, J. D.: 1985, 'A First-Order Closure Scheme to Describe Counter-Gradient Momentum Transport in Plant Canopies’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 33, 77-83.
Lumley, J. L.: 1978, 'Computational Modelling of Turbulent Flows’, Adv. Appl. Mech. 18, 123.
Maitani, T.: 1978, 'On the Downward Transport of Turbulent Kinetic Energy in the Surface Layer over Plant Canopies’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 14, 571-584.
Massman, W.: 1987, 'A Comparative Study of Some Mathematical Models of the Mean Wind Structure and Aerodynamic Drag of Plant Canopies’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 40, 179-197.
Massman, W.: 1997, 'An Analytical One-Dimensional Model of Momentum Transfer by Vegetation of Arbitrary Structure’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 83, 407-421.
Mellor, G.: 1973, 'Analytic Prediction of the Properties of Stratified Planetary Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 30, 1061-1069.
Meyers, T. and Paw U, K. T.: 1986, 'Testing of a Higher-Order Closure Model for Modeling Airflow within and above Plant Canopies’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 37, 297-311.
Meyers, T. and Baldocchi, D. D.: 1991, 'The Budgets of Turbulent Kinetic Energy and Reynolds Stress within and above Deciduous Forest’, Agric. For. Meteorol. 53, 207-222.
Monin, A. S. and Yaglom, A. M.: 1971, Statistical Fluid Mechanics, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 769 pp.
Monin, A. S. and Yaglom, A. M.: 1975, Statistical Fluid Mechanics, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 874 pp.
Mulhearn, P. J. and Finnigan, J. J.: 1978, 'Turbulent Flow over a Very Rough Random Surface’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 15, 109-132.
Nagano, Y. and Tagawa, M.: 1990: 'A Structural Turbulence Model for Triple Products of Velocity and Scalar’, J. Fluid Mech. 196, 157-185.
Nagano, Y. and Tagawa, M.: 1996, 'Coherent Motion and Their Role in Transport Processes in a Wall Turbulent Shear Flow’, in C. J. Chen, C. Shih, J. Lienau, and J. Kung (eds.), Flow and Modeling of Turbulent Measurements VI, Balkema, Rotterdam, pp. 17-28.
Nakagawa, H. and Nezu, I.: 1977, 'Prediction of the Contributions to the Reynolds Stress from Bursting Events in Open Channel Flows’, J. Fluid Mech. 80, 99-128.
Press, W. H., Teukolsky, S. A., Vetterling, W. T., and Flannery, B. P.: 1992, Numerical Recipes in Fortran, 2nd edn, Cambridge University Press, 963 pp.
Raupach, M. R.: 1994, 'Simplified Expressions for Vegetation Roughness Length and Zero-Plane Displacement as Functions of Canopy Height and Area Index’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 71, 211-216.
Raupach, M. R.: 1981, 'Conditional Statistics of Reynolds Stress in Rough-Wall and Smooth-Wall Turbulent Boundary Layers’, J. Fluid Mech. 108, 363-382.
Raupach, M. R. and Thom, A. S.: 1981, 'Turbulence in and above Plant Canopies’, Ann. Rev. Fluid. Mech,13, 97-129.
Raupach, M. R. and Shaw, R. H.: 1982, 'Averaging Procedures for Flow within Vegetation Canopies’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 22, 79-90.
Raupach, M. R., Antonia, R. A., and Rajagopalan, S.: 1991, 'Rough-Wall Turbulent Boundary Layers’, Appl. Mech. Rev. 44, 1-25.
Raupach, M. R., Denmead, O. T., and Dunin, F. X.: 1992, 'Challanges in Linking Atmospheric CO2 Concentrations to Fluxes at Local and Regional Scales’, Aust. J. Bot. 40, 697-716.
Raupach, M. R.: 1988, 'Canopy Transport Processes’, in W. L. Steffen and O. T. Denmead (eds.), Flow and Transport in the Natural Environment, Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 95-127.
Sawford, B. L.: 1986: 'Generalized Random Forcing in Random-Walk Turbulent Dispersion Models’, Phys. Fluids 29, 3582-3583.
Sawford, B. L. and Guest, F. M.: 1987, 'Lagrangian Stochastic Analysis of Flux-Gradient Relationship in the Convective Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 44, 1152-1165.
Sellers, P. J., Mintz, Y., Sud, Y., and Dalcher, A.: 1985, 'A Simple Biosphere Model (SiB) for Use within General Circulation Models’, J. Atmos. Sci., 43, 505-531.
Shaw, R. H., 1977, 'Secondary Wind Speed Maxima Inside Plant Canopies’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 16, 514-521.
Shaw, R. H., den Hartog, G., King, K. M., and Thurtell, G. W.: 1974, 'Measurements of Mean Wind Flow and Three-Dimensional Turbulence Intensity within a Mature Corn Canopy’, Agric. For. Meteorol. 13, 419-425.
Shaw, R. H., Tavangar, J., and Ward, D.: 1983, 'Structure of the Reynolds Stress in a Canopy Layer’, J. Clim. Appl. Meteor. 22, 1922-1931.
Shaw, R. H. and Seginer, I.: 1987, 'Calculation of Velocity Skewness in Real and Artificial Canopies’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 39, 315-332.
Schumann, U.: 1977, 'Realizability of Reynolds Stress Turbulence Models’, Phys. Fluids 20, 721-726.
Sreenivasan, K. R., Tavoularis, S., and Corrsin, S.: 1982, 'A Test of Gradient Transport and its Generalization’, in L. J. S. Bradbury, F. Durst, B. E. Launder, F.W. Schmidt, and J. H. Whitelaw (eds.), Turbulent Shear Flow III, Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 96-112.
Taconet, O., Bernard, R., and Vidal-Madjas, D.: 1986, 'Evapotranspiration over an Agricultural Region Using a Surface Flux/Temperature Model Based on NOAA-AVHRR Data’, J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 25, 284-307.
Thom, A S.: 1971, 'Momentum Absorption by Vegetation’, Quart J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 97, 414-428.
Wilson, J. D.: 1988, 'A Second Order Closure Model for Flow through Vegetation’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 42, 371-392.
Wilson, J. D.: 1989, 'Turbulent Transport within the Plant Canopy’, in Estimation of Areal Evapotranspiration, IAHS Publ., No. 177, pp. 43-80.
Wilson, N. R. and Shaw, R. H.: 1977, 'A Higher Order Closure Model for Canopy Flow’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 16, 1198-1205.
Wyngaard, J. C. and Sundararajan, A.: 1977, 'The Temperature Skewness Budget in the Lower Atmosphere and its Implications to Modeling’, in F. Durst, B. E. Launder, F. W. Schmidt, and J. H. Whitelaw (eds.), Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 319-326.
Zeman, O. and Tennekes, H.: 1975, 'A Self Contained Model for the Pressure Terms in the Turbulent Stress Equation of the Neutral Atmospheric Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 32, 1808-1813.
Zeman, O. and Lumley, J. L.: 1976, 'Modeling Buoyancy Driven Mixed Layers’, J. Atmos. Sci. 33, 1974-1988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katul, G., Albertson, J. An Investigation of Higher-Order Closure Models for a Forested Canopy. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 89, 47–74 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001509106381
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1001509106381