Abstract
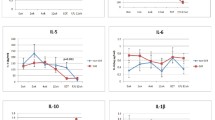
To compare virological, biochemical, and immuneresponses to human lymphoblastoid interferon(IFN-α) and human fibroblast interferon(IFN-β) in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus(HCV) infection, 120 patients were randomly assigned to threegroups (group A, 60 patients receiving IFN-α, 6million units (MU) once a day, daily for one month andthrice weekly for five months; group B, 40 patients receiving 6 MU IFN-β once a day daily fortwo months; and group C, 20 patients receiving 3 MUIFN-β twice a day (6 MU/day) daily for two months).Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels were measured byenzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Patients withsustained clearance of serum HCV RNA detected bypolymerase chain reaction (PCR) at six months after IFNtreatment were defined as having complete response to IFNtreatment. A low level of HCV RNA (≤10-4copies/50 mul, measured by competitive PCR) and HCV RNAof genotype 2a were favorable factors for a completeresponse to both IFNs. Complete response in group Atreatment was strongly associated with early HCV RNAclearance, in contrast with group B. A significantlyhigher HCV RNA negativity at the second week from start of treatment was noted in group C (80.0%),compared with groups A (41.6%) and B (27.5%). sIL-2Rlevels rose in each group during IFN administration. Ingroup C, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and IL-6 levels were remarkably elevated. These findingsindicate that timing of serum HCV RNA negativity insustained response differs between IFN-α andIFN-β administrations and that early HCV RNAclearance was induced by twice-a-day IFN-βtreatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Davis GL, Balart LA, Schiff ER, Lindsay K, Bodenheimer HC Jr, Pe rrillo RP, Carey W, Jacobson IM, Payne J, Dienstag JL, VanThie l D, Tamburro C, Lefkowitch J, Albretch J, Meschievitz C, Ortego TJ, Gibas A, Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group: Treatment of chronic hepatitis C with recombinantinterferon alpha. A multicenter randomized, controlled trial. N Engl J Med 321:1501-1506, 1989
Di Bisceglie AM, Martin P, Kassianides C, Lisker-Melman M, Murray L, Waggoner J, Goodman Z, Banks SM, Hoofnagle JH: Recombinant interferon alfa Therapy for chronic hepatitisC. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med 321:1506-1510, 1989
Hayashi J, Ohmiya M, Kishihara Y, Tani Y, Kinukawa N, Ikematsu H, Kashiwagi S: A statistical analysis of predictive factors of Response to human lymphoblastoid interferon inpatients with chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol 89:2151-2156, 1994
Furusyo N, Hayashi J, Ueno K, Sawayama Y, Kawakami Y, Kishihara Y, Kashiwagi S: Human lymphoblastoid interferon treatment for patients with hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis.Clin The r 19:1352-1367, 1997
Nishiguchi S, Kuroki T, Nakatani S, Morimoto H, Takeda T, Nakajima S, Shiomi S, Seki S, Kobayashi K, Otani S: Randomised trial of effects of interferon-alpha on incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic active hepatitis C with cirrhosis. Lancet 346:1051-1055, 1995
Hayashi J, Kishihara Y, Ueno K, Yamaji K, Kawakami Y, Furusyo N, Sawayama Y, Kashiwagi S: Age-related response to interferon alfa treatment in women vs men with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Arch Intern Med 158:177-181, 1998
Hayashi J, Kashiwagi S: Hepatitis C virus infection in theelderly. Epidemiology, prophylaxis and optimal treatment. Drugs Aging 11:296-308, 1997
Yamaji K, Hayashi J, Kawakami Y, Furusyo N, Sawayama Y, Kishihara Y, Etoh Y, Kashiwagi S: Early cle arance and re-appearance of hepatitis C virus RNA in chronic hepatitis Cpatients treated with interferon-a. J Clin Gastroente l 26:193-199, 1998
Ampurdanes S, Olmedo E, Maluenda MD, Forns X, Lopez-Labrador FX, Costa J, Sanchez-Tapias JM, de Anta MT, Rodes J: Pe rmanent response to alpha-interferon Therapy inchronic hepatitis C is preceded by rapid cle arance of HCVRNA from serum. J Hepatol 25:827-832, 1996
Karino Y, Toyota J, Sugawara M, Higashino K, Sato T, Ohmura T, Suga T, Okuuchi Y, Matsushima T: Early loss of serum hepatitis C virus RNA can predict a sustained responseto interferon Therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol 92:61-65, 1996
Sáez-Royue la F, Porres JC, Moreno A, Castillo I, Martine z G, Galiana F, Carreno V: High doses of recombinant alphainterferonor gamma-interferon for chronic hepatitis C: Arandomized, controlled trial. Hepatology 13:327-331, 1991
Ohmiya M, Hayashi J, Furusyo N, Ueno K, Kishihara Y, Nabeshima S, Kashiwagi S: Large dose natural interferon alpha treatment for patients with chronic hepatitis C. Fukuoka ActaMed 88:380-388, 1997
Re ichard O, Fobe rg U, Fryden A, Mattsson L, Norkrans G, Sonnerborg A, Wejstal R, Yun ZB, Weiland O: High sustained response rate and cle arance of viremia in chronic hepatitis Cafter treatment with interferon-alpha 2b for 60 weeks. Hepatology 19:280-285, 1994
Hayashi J, Nakashima K, Kishihara Y, Ohmiya M, Yoshimura E, Hirata M, Kashiwagi S: Improved detection of antibodies to hepatitis C virus by the second-generation assay in patients with chronic non-A, non-B liver disease. J Infect 26:287-294,1993
Hayashi J, Yoshimura E, Kishihara Y, Yamaji K, Etoh Y, Ikematsu H, Kashiwagi S: Hepatitis C virus RNA levels determined by branched DNA probe assay correlated with levelsassessed using competitive PCR. Am J Gastroenterol 91:314-318, 1996
Okamoto H, Sugiyama Y, Okada S, Kurai K, Akahane Y, Sugai Y, Tanaka T, Sato K, Tsuda F, Miyakawa Y, Mayumi Y: Typing hepatitis C virus by polymerase chain reaction with type-specific primers: Application to clinical surveys and tracing infectious sources. J Gen Virol 73:673-679, 1992
Simmonds P, Alberti A, Alter HJ, Bonino F, Bradley DW, Brechot C, Brouwer JT, Chan SW, Chayama K, Chen DS, Choo QL, Colombo M, Cuypers HTM, Date T, Dushe iko GM, Esteban JI, Fay O, Hadzyannis SJ, Han J, Hatzakis A, Holmes EC, Hotta H, Houghton M, Irwine B, Kohara M, Kolberg JA, Kuo G, Lau JYN, Lelie PN, Maertens G, McOmish F, Miyamura T, Mizokami M, Nomoto A, Prince AM, Reesink HW, Rice C, Roggendorf M, Schalm SW, Shikata T, Shimotohno K, Stuyver L, Trepo C, Weiner A, Yap PL, Urdea MS: A proposedsystem for the nomenclature of hepatitis C viral genotypes. Hepatology 19:1321-1324, 1994
Kato N, Yokosuka O, Hosoda K, Ito Y, Ohto M, Omata M:Quantification of hepatitis C virus by competitive reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction: Increase of the virus inadvanced liver disease. Hepatology 18:16-20, 1993
Snedecar GW, Cochran WG: Statistical Methods. Ames, Iowa, Iowa State University Press, 1980
Hino K, Kondo T, Yasuda K, Fukuhara A, Fujioka S, Shimoda K, Niwa H, Iino S, Suzuki H: Pharmacokinetics and biological effects of beta interferon by intravenous (iv) bolus administration in healthy volunteers as compared with iv infusion. Jpn J Clin Pharmacol The r 19:625-635, 1988
Barouki FM, Witter FR, Griffin DE, Nadler PI, Woods A, Wood DL, Lietman PS: Time course of interferon levels, antiviral state, 29, 59-oligoadenylate synthetase and side effects in healthy men. J Interferon Res 7:29-39, 1987
Villa E, Trande P, Grottola A, Buttafoco P, Rebecchi AM, Stroffolini T, Callea F, Merighi A, Camellini L, Zoboli P, Cosenza R, Miglioli L, Loria P, Iori R, Carulli N, Manenti F:Alpha but not beta interferon is useful in chronic active hepatitis due to hepatitis C virus: A prospective, double-blind,randomized study. Dig Dis Sci 41:1241-1247, 1996
Pre z R, Pravia R, Artimez ML, Giganto F, Rodriguez M, Lombrana JL, Rodrigo L: Clinical efficacy of intramuscular human interferon-beta vs interferon-alpha 2b for the Treatment of chronic hepatitis C. J Viral Hepatitis 2:103-106, 1995
Saitoh H, Naitoh S, Okamoto H, Akahane Y: Prompt decrease Of circulating hepatitis C virus in patients with chronic hepatitis C after treatment with interferon. J Interferon Res 14:239-244,1994
Rubin LA, Kurman CC, Fritz ME, Biddison WE, Boutin B, Yarchoan R, Nelson DL: Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J Immunol 135:3172-3177, 1985
Hayashi J, Kishihara Y, Yamaji K, Yoshimura E, Ohmiya M, Tani Y, Ikematsu H, Kashiwagi S: Serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptors and effects of interferon-alpha for patients with chronic hepatitis C virus. Dig Dis Sci 40:1837-1841,1995
Castell JV, Gomez-Lechon MJ, David M, Hirano T, Kishimoto T, Heinrich PC: Recombinant human interleukin-6 (IL-6/BSF-2/HSF) regulates the synthesis of acute phase proteins in human hepatocytes. FEBS 232:347-350, 1988
Kakumu S, Fukatsu A, Shinagawa T, Kurokawa S, Kusakabe A: Localisation of intrahepatic interleukin 6 in patients with acute and chronic liver disease. J Clin Pathol 45:408-411, 1992
Hashimoto H, Shibukawa N, Kojima Y: The mode of production of endotoxin-induced interferon in rabbit lymphoid cell cultures. II. Priming effect of interferon on apparently noninducible cells. MicrobiloImmunol 23:1033-1036, 1979
Satoh M, Shimada Y, Inagawa H, Minagawa H, Kajikawa T, Oshima H, Abe S, Yamazaki M, Mizuno D: Priming effect of interferons and interleukin 2 on endogenous production of tumor necrosis factor in mice. Jpn J Cancer Res 77:342-344,1986
Di Bisceglie AM, Conjeevaram HS, Fried MW, Sallie R, Park Y, Yurdaydin C, Swain M, Kleiner DE, Mahaney K, Hoofnagle JH: Ribavirin as Therapy for chronic hepatitis C. A randomized,double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 123:897-903, 1995
Puoti C, Magrini A, Filippi T, Annovazzi G, Pannullo A:Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on serum liver enzymes in patients with hepatitis C virus-related chronic liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:151-154, 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furusyo, N., Hayashi, J., Ohmiya, M. et al. Differences Between Interferon-α and-β Treatment for Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Dig Dis Sci 44, 608–617 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026625928117
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026625928117