Abstract
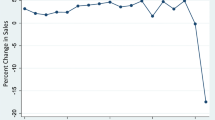
Incentive regulation in the form of price caps was adopted for interstate access service in 1991 as a way to provide local exchange carriers with an incentive to improve their productive efficiency. An issue that has arisen with the adoption of price cap regulation is whether deterioration in service quality for interstate access service has been an unintended consequence. The analysis in this paper uses several different measures of service quality, including the average installation interval, the percent of commitments met, total trouble reports, and the average repair interval for both switched access service and special access service, to investigate empirically whether there has been a decline in service quality between 1991 and 2000. The results are conclusive. Overall service quality has fallen. To rectify the situation, a proposal is offered to adjust the price cap index to penalize LECs who fail to provide an acceptable level of aggregate service quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel, J. (2000). The Performance of the State Telecommunications Industry under Price Cap Regulation: An Assessment of the Empirical Evidence, Columbus, OH: National Regulatory Research Institute.
Abramovitz, M. (1956). Resource and Output Trends in the United States since 1870, New York: National Bureau of Economic Research.
Averch, H. & Johnson, L. (1962). "Behavior of the Firm Under Regulatory Constraint." American Economic Review. 52, 1052-1069.
Banerjee, A. (2001). Does Incentive Regulation "Cause" Degradation of Retail Telephone Service Quality? New York: National Economic Research Associates.
Baron, D. (1991) "Information, Incentives, and Commitment in Regulatory Mechanisms: Regulatory Innovation in Telecommunications." In M. Einhorn (ed.), Price Caps and Incentive Regulation in Telecommunications, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston.
Bernstein, J. & Sappington, D. (1999) "Setting the X Factor in Price-Cap Regulation Plans." Journal of Regulatory Economics. 16, 5-25.
Brennan, T. (1989). "Regulating by Capping Prices." Journal of Regulatory Economics.1,133-147.
Cabral, L. & Riordan, M. (1989). "Incentives for Cost Reduction under Price Cap Regulation." Journal of Regu-latory Economics.1,26-42.
Chamberlin, E. (1948). The Theory of Monopolistic Competition, Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Cochrane, D. & Orcutt, G. (1949). "Application of Least Squares Regressions to Relationships Containing Auto-correlated Error Terms." Journal of the American Statistical Association. 44, 32-61.
Davidson, R. & MacKinnon, J. (1993). Estimation and Inference in Econometrics, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Ergas, H. & Small, J. (2001). Price Caps and Rate-of-Return Regulation, Kingston, Ontario: Network Economics Consulting Group.
Federal Communications Commission (2001). Trends in Telephone Service, Washington, DC: Industry Analysis Division.
Kahn, A. (1970). The Economics of Regulation, New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Khilstron, R. & Levhari, D. (1977). "Quality, Regulation, and Efficiency." Kyklos. 30, 214-234.
Kridel, D., Sappington, D., & Weisman, D. (1996). "The Effects of Incentive Regulation in the Telecommunications Industry: A Survey." Journal of Regulatory Economics.9, 269-306.
Laffont, J. & Tirole, J. (2000). Competition in Telecommunications, Cambridge: The MIT Press.
Levhari, D. & Peles, Y. (1973). "Market Structure, Quality, and Durability." Bell Journal of Economics and Management Science.4, 235-248.
Littlechild, S. (1983). Regulation of British Telecom's Profitability, Report to the Secretary of State, Department of Industry, London.
Martin, S. (1993). Advanced Industrial Economics, Cambridge: Blackwell Publishers.
Minnesota Public Utilities Commission (2002). Qwest Service Quality Standards, Staff Briefing Paper, Minneapolis, MN, February 5.
Mitchell, B. & Vogelsang, I. (1991). Telecommunications Pricing: Theory and Practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Noam, E. (1991). "The Quality of Regulation in Regulating Quality." In M. Einhorn (ed.), Price Caps and Incentive Regulation in Telecommunications, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston.
Norsworthy, J. & Tsai, D. (1999). "The Role of Service Quality and Capital Technology in Telecommunications Regulation." Information Economics and Policy. 11, 127-145.
Panzan, J. (1975). "Regulation, Service Quality, and Market Performance." Research Center in Economic Growth, Stanford University, Palo Alto.
Roycroft, T. & Garcia-Murrilo, M. (2000). "Trouble Reports as an Indicator of Service Quality: The Influence of Competition, Technology, and Regulation." Telecommunications Policy. 24, 947-967.
Sappington, D. (1980). "Strategic Firm Behavior under a Dynamic Regulatory Adjustment Process." The Bell Journal of Economics. 11, 360-372.
Schmalensee, R. (1970). "Regulation and the Durability of Goods." Bell Journal of Economics and Management Science.1,54-64.
Sherman, R. (1985). "The Averch and Johnson Analysis of Public Utility Regulation Twenty Years Later." Review of Industrial Organization.2, 178-193.
Sherman, R. (1992). "Capital Waste in the Rate-of-Return Regulated Firm." Journal of Regulatory Economics.4, 197-204.
Spence, M. (1975), "Monopoly, Quality, and Regulation." Bell Journal of Economics.6,417-429.
Taylor, L. (1994). Telecommunications Demand in Theory and Practice, Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Uri, N. (2000), "Measuring Productivity Change in Telecommunications." Telecommunications Policy. 24, 439-452.
Uri, N. (2001a). "The Effect of Incentive Regulation on Productive Efficiency in Telecommunications." Journal of Policy Modeling. 23, 825-846.
Uri, N. (2001b). "Monopoly Power and the Problem of CLEC Access Charges." Telecommunications Policy. 25, 611-623.
Uri, N. & Setzer, F. (2003). "Assessing the Performance of the Price Cap Plan for Local Exchange Carriers in the United States." European Journal of Law and Economics. 15, 263-276.
Vogelsang, I. (1988). "Price-Cap Regulation of Telecommunications Services: A Long-Run Approach." In M. Crew (ed.), Deregulation and Diversification of Utilities, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Vogelsang, I. (1991). "A Non-Bayesian Incentive Mechanism Using Two-Part Tariffs." In M. Einhorn (ed.), Price Caps and Incentive Regulation in Telecommunications, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston.
Weisman, D. (2002). "Price Regulation and Quality." Unpublished manuscript, Department of Economics, Kansas State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uri, N.D. Service Quality Effects of Incentive Regulation on Access Service in Telecommunications in the United States. European Journal of Law and Economics 16, 369–390 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025319025855
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025319025855