Abstract
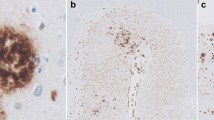
Amyloid β-protein (Aβ) deposits in the cerebral cortices of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) were investigated immunohistochemically to determine their carboxy terminal sequences. Antibodies specific for Aβ terminating at residue valine40 (Aβ40) and at residues alanine42/threonine43 (Aβ42) were used. Virtually all parenchymal Aβ deposits were positive for Aβ42. Many of these deposits were also partially or completely labeled for Aβ40. The degree of Aβ40 labeling varied from area to area within a given brain and from AD case to AD case. In contrast to parenchymal deposits, Aβ40 labeled essentially all the vascular deposits which constitute amyloid angiopathy (AA), with Aβ42 occurring variably in some of these deposits. Occasional AA was found, however, in which Aβ42 predominated or was exclusively deposited. Such a diversity of Aβ species, both in brain parenchyma and in AA, suggests that multiple C-terminal processing mechanisms occur in the cell types responsible for these deposits.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Selkoe, D. J. 1994. Normal and abnormal biology of the β-amyloid precursor protein. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 17:489–517.
Mori, H., Takio, K., Ogawara, M., and Selkoe, D. J. 1992. Mass spectrometry of purified amyloid β protein in Alzheimer's disease. J. Biol. Chem. 267:17082–17086.
Roher, A. E., Lowenson, J. D., Clarke, S., Woods, A. S., Cotter, R. J., Gowing, E., and Ball, M. J. 1993. β-Amyloid–(1–42) is a major component of cerebrovascular amyloid deposits: Implications for the pathology of Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:10836–10840.
Näslund, J., Schierhorn, A., Hellman, U., Lannfelt, L., and Roses, A. D. 1994. Relative abundance of Alzheimer Aβ amyloid peptide variants in Alzheimer disease and normal aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:8378–8382.
Greenberg, B. D. 1995. The COOH-terminus of the Alzheimer amyloid Aβ peptide: differences in length influence the process of amyloid deposition in Alzheimer brain, and tell us something about relationships among parents. Amyloid: Int. J. Exp. Clin. Invest. 2:195–203.
Iwatsubo, T., Mann, D. M. A., Odaka, A., Suzuki, N., Ihara, Y. 1995. Amyloid β protein (Aβ) deposition: Aβ42(43) precedes Aβ40 in Down syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 37:294–299.
Iwatsubo, T., Odaka, A., Suzuki, N., Mizusawa, H., Nukina, N., Ihara, Y. 1994. Visualization of Aβ42(43) and Aβ40 in senile plaques with end-specific Aβ monoclonals: evidence that an initially deposited species is Aβ42(43). Neuron 13:45–53.
Savage, M. J., Kawooya, J. K., Pinsker, L. R., Emmons, T. L., Mistretta, S., Siman, R., and Greenberg, B. D. 1995. Elevated Aβ levels in Alzheimer's disease brain are associated with selective accumulation of Aβ(42) in parenchymal amyloid plaques and both Aβ(40) and Aβ(42) in cerebrovascular deposits. Amyloid: Int. J. Exp. Clin. Invest. 2:234–240.
Tamaoka, A., Sawamura, N., Odaka, A., Suzuki, N., Mizusawa, H., Shoji, S., and Mori, H. 1995. Amyloid β-protein 1–42/43 (Aβ1–42/43) in cerebellar diffuse plaques: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunocytochemical study. Brain Res. 679:151–156.
Yamaguchi, H., Sugihara, S., Ishiguro, K., Takashima, A., and Hirai, S. 1995. Immunohistochemical analysis of COOH-termini of amyloid β protein (Aβ) using end-specific antisera for Aβ40 and Aβ42 in Alzheimer's disease and normal aging. Amyloid: Int. J. Exp. Clin. Invest. 2:7–16.
Lemere, C. A., Blusztajn, J. K., Yamaguchi, H., Wisniewski, T., Saido, T. C., and Selkoe, D. J. 1996. Sequence of deposition of heterogeneous amyloid β-peptides and APO-E in Down syndrome: implications for initial events in amyloid plaque formation. Neurobiol. Disease 3:16–32.
Akiyama, H., and McGeer, P. L. 1990. Brain microglia constitutively express β-2 integrins. J. Neuroimmunol. 30:81–93.
Gearing, M., Schneider, J. A., Robbins, R. S., Hollister, R. D., Mori, H., Games, D., Hyman, B. T., and Mirra, S. S. 1995. Regional variation in the distribution of apolipoprotein E and Aβ in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 54:833–841.
Gearing, M., Tigges, J., Mori, H., and Mirra, S. S. 1997. Aβ40 is a major form of β-amyloid in nonhuman primates. Neurobiol of Aging (in press).
Yamaguchi, H., Nakazato, Y., Shoji, M., Okamoto, K., Iahara, Y., and Hirai, S. 1991. Secondary deposition of β-amyloid within extracellular neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer-type dementia. Am. J. Pathol. 138:699–705.
Schwab, C., Steele, J. C., Akiyama, H., and McGeer, P. L. 1996. Distinct distribution of apolipoprotein E and beta-amyloid immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of parkinson dementia complex of Guam. Acta Neuropathol. 92:378–385.
Fukumoto, H., Asami-Okada, A., Suzuki, N., Shimada, H., Ihara, Y., and Iwatsubo, T. 1996. Amyloid β-protein deposition in normal aging has the same characteristics as that in Alzheimer's disease. Am. J. Pathol. 148:259–265.
Jarrett, J. T., Berger, E. P., and Lansbury, Jr. P. T. 1993. The carboxy terminus of the β amyloid protein is critical for the seeding of amyloid formation: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Biochem. 32:4693–4697.
Jarrett, J. T., and Lansbury, Jr. P. T. 1993. Seeding “one-dimensional crystallization” of amyloid: a pathogenic mechanism in Alzheimer's disease and scrapie? Cell 73:1055–1058.
Maggio, J. E., Stimson, E. R., Ghilardi, J. R., Allen, C. J., Dahl, C. E., Whitcomb, D. C., Vigna, S. R., Vinters, H. V., Labenski, M. E., and Mantyg, P. W. 1992. Reversible in vitro growth of Alzheimer disease β-amyloid plaques by deposition of labeled amyloid peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 5462–5466.
Prior, R., D'Urso, D., Frank, R., Prikulis, I., Cleven, S., Ihl, R., and Pavlakovic, G. 1996. Selective binding of soluble Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 to a subset of senile plaques. Am. J. Pathol. 148:1749–1756.
Gowing, E. Roher, A. E., Woods, A. S., Cotter, R. J., Chaney, M., and Little, S. P. 1994. Chemical characterization of Aβ 17–42 peptide, a component of diffuse amyloid deposits of Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 269:10987–10990.
Gravina, S. A., Ho, L., Eckman, C. B., Long, K. E., Otovos, Jr. L., and Younkin, L. 1995. Amyloid β protein (Aβ) in Alzheimer's disease brain. J. Biol. Chem. 270:7013–7016.
Perry, G., Cras, P., Siedlak, S. L., Tabaton, M., and Kawai, M. 1992. β-Protein immunoreactivity is found in the majority of neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease. Am. J. Pathol. 140: 283–290.
Cummings, B. J., Satou, T., Head, E., Milgram, N. W., Cole, G. M., Savage, M. J., Podlisny, M. B., Selkoe, D. J., Siman, R., Greenberg, B. D., and Cotman, C. W. 1996. Diffuse plaques contain C-terminal Aβ42 and not Aβ40: Evidence from cats and dogs. Neurobiol. Aging 17:653–659.
Giaccone, G., Pedrotti, B., Migheli, A., Verga, L., Perez, J., Racagni, G., Smith, M. A., Perry, G., De Gioia, L., Selvaggini, C., Salmona, M., Ghiso, J., Frangione, B., Islam, K., Bugiani, O., and Tagliavini, F. 1996. βAPP and tau interaction. A possible link between amyloid and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Am. J. Pathol. 148:79–87.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akiyama, H., Mori, H., Sahara, N. et al. Variable Deposition of Amyloid β-Protein (Aβ) with the Carboxy-Terminus that Ends at Residue Valine40 (Aβ40) in the Cerebral Cortex of Patients with Alzheimer's Disease: A Double-Labeling Immunohistochemical Study with Antibodies Specific for Aβ40 and the Aβ that Ends at Residues Alanine42/Threonine43 (Aβ42). Neurochem Res 22, 1499–1506 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021910729963
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021910729963