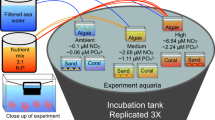
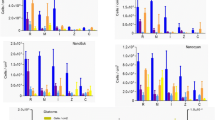
Abstract
Colonization of surfaces in marine benthic environments is often one of the most significant moments in the life history of benthic organisms, representing, for example, a change from a planktonic to a benthic existence, a shift from a mobile to a sessile life form, or the initiation of pathogenesis. Many of the surfaces that are colonized are, in fact, other marine organisms, and in a general sense there is widespread evidence that specific chemical cues derived from marine organisms affect colonization by both marine prokaryotes and eukaryotes. However, detailed information for any one system on the nature of such cues, their distribution in situ, and their effects on the demography of colonizers is rare. Here, we selectively review the literature on chemical cues for colonization in the sea, focussing on contrasts between positive (inducers) and negative (inhibitors, deterrents) cues and on prokaryote/eukaryote interactions. We also consider whether generalized life history or natural history characteristics of colonizers (i.e., the mobility of a propagule, the extent to which a species is a habitat generalist or specialist, etc.) affect their response to chemical cues, and we touch briefly on some recent highlights relevant to the critical interplay between hydrodynamics and chemistry. A number of important methodological concerns are now being addressed through the introduction of field assays and analyses for chemical cues, and through molecular techniques for the characterization of microbial biofilms. These developments are encouraging, as is the increasingly multidisciplinary and cross-taxonomic approach to research in this area.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Amsler, C. D. and Iken, K. 2001. Chemokinesis and chemotaxis in marine bacteria and algae; pp. 413–430, in J. B. McClintock and B. J. Baker (eds.). Marine Chemical Ecology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Armstrong, E., Yan, L. M., Boyd, K. G., Wright, P. C., and Burgess, J. G. 2001. The symbiotic role of marine microbes on living surfaces. Hydrobiologia 461:37–40.
Bauer, W. D. and Robinson, J. B. 2002. Disruption of bacterial quorum sensing by other organisms. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 13:234–237.
Blackburn, N., Fenchel, T., and Mitchell, J. 1998. Microscale nutrient patches in planktonic habitats shown by chemotactic bacteria. Science 282:2254–2256.
Bouarab, K., Kloareg, B., Potin, P., and Correa, J. A. 2001. Ecological and biochemical aspects in algal infectious diseases. Cahi. Biol. Mar. 42:91–100.
Browne, K. A. and Zimmer, R. A. 2001. Controlled field release of a waterborne chemical signal stimulates planktonic larvae to settle. Biol. Bull. 200:87–91.
Burgess, J. G., Jordan, E. M., Bregu, M., Mearns-Spragg, A., and Boyd, K. G. 1999. Microbial antagonism: a neglected avenue of natural products research. J. Biotech. 70:27–32.
Burke, R. D. 1984. Pheromonal control of metamorphosis in the sand dollar, Dendraster excentricus. Science 225:440.
Butman, C. A. 1987. Larval settlement of soft-sediment invertebrates: The spatial scales of pattern explained by active habitat selection and the emerging role of hydrodynamical processes. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 25:113–165.
Charlton, T. S., Denys, R., Netting, A., Kumar, N., Hentzer, M., Givskov, M., and Kjelleberg, S. 2000. A novel and sensitive method for the quantification of N-3-oxoacyl homoserine lactones using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: application to a model bacterial biofilm. Environ. Microbiol. 2:530–541.
Christie, G. B., Christov, V., De Nys, R., Steinberg, P. D., and Hodson, S. 1998. Antifouling polymers. International Patent Application, PCT/AU98/00509.
Clare, A. S. 1996. Marine natural product antifoulants: status and potential. Biofouling 9:211–229.
Clare, A. S. and Matsumura, K. 2000. Nature and perception of barnacle settlement pheromones. Biofouling 15:57–71.
Cottrell, M. T. and Kirchman, D. L. 2000. Community composition of marine bacterioplankton determined by 16S rRNAgene clone libraries and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl. Environ. Microb. 66:5116–5122.
Cronin, G. 2001. Chemical mediation of surface colonization, pp. 325–353, in J. B. McClintock and J. B. Baker (eds.). Marine Chemical Ecology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
DahllÖf, I. 2002. Molecular community analysis of microbial diversity. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 13:213–217.
Davies, D. G., Parsek, M. R., Pearson, J. P., Iglewski, B. H., Costerton, J.W., and Greenberg, E. P. 1998. The involvement of cell-to-cell signals in the development of a bacterial biofilm. Science 280:295–298..
De Nys, R. and Steinberg, P. D. 1999. Role of secondary metabolites from algae and seagrasses in biofouling control, pp. 223–244, in M. Fingerman, R. Nagabhushanam and M.-F. Thompson (eds.). Recent Advances in Marine Biotechnology, Vol. III. Science Publishers, Enfield, New Hampshire.
De Nys, R., Steinberg, P. D., Willemsen, P., Dworjanyn, S. A., Gabalish, C. L., and King, R. J. 1995. Broad spectrum effects of secondary metabolites from the red alga Delisea pulchra in antifouling assays. Biofouling 8:259–271.
De Nys, R., Dworjanyn, S. A., and Steinberg, P. D. 1998. A new methodology for determining surface concentrations of marine natural products on seaweeds. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 162: 79–87.
Dunny, G.M. and Winans, S.C. (eds.). 1999. Cell–cell Signaling in Bacteria.ASM Press, Washington, DC.
Dworjanyn, S.A. 2001. Chemically mediated antifouling and the cost of producing secondary metabolites in a marine alga. PhD thesis. University of New South Wales, Sydney.
Dworjanyn, S. A., De Nys, R., and Steinberg, P. D. 1999. Localisation and surface quantification of secondary metabolites in the red alga Delisea pulchra. Mar. Biol. 133:727–736.
Eberl, L., Molin, S., and Givskov, M. 1999. Surface motility in Serratia liquefaciens.J. Bacteriol. 181:1703–1712.
Faimali, M., Sepcic, K., Turk, T., and Geraci, S. 2002. Non-toxic antifouling mechanism of polymeric 3-alkylpyridinium salts from the Mediterranean sponge Reniera sarai (Pulitzer-Finali). Biofouling. In press.
Fingerman, M., Nagabhushanam, R., and Thompson, M.-F. (eds.) 1999. RecentAdvances in Marine Biotechnology, Vol. III. Science Publishers, Enfield, New Hampshire.
Fisher, R. and Bellwood, D. R. 2002. The influence of swimming speed on sustained swimming performance of late-stage reef fish larvae. Mar. Biol. 140:801–807.
Fleck, J., Fitt, W. K., and Hahn, M. G. 1999. A proline-rich peptide originating from decomposing mangrove leaves is one natural metamorphic cue of the tropical jellyfish Cassiopea xamachana. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 183:115–124.
Friedrich, A. B., Fischer, I., Proksch, P., Hacker, J., and Hentschel. 2001. Temporal variation of the microbial community associated with the mediterranean sponge Aplysina aerophoba. FEMS Microb. Ecol. 38:105–113.
Fusetani, N. 1997. Marine natural products influencing larval settlement and metamorphosis of benthic invertebrates. Curr. Org. Chem. 1:127–152.
Gil-Turnes, M. S., Hay, M. E., and Fenical, W. 1989. Symbiotic marine bacteria chemically defend crustacean embryos from a pathogenic fungus. Science 246:116–118.
Green, K. M., Russell, B. D., Clark, R. J., Jones, M. K., Garson, M. J., Skilleter, G. A., and Degnan, B. M. 2002. A sponge allelochemical induces ascidian settlement but inhibits metamorphosis. Mar. Biol. 140:355–363.
Hadfield, M. G. and Paul, V. J. 2001. Natural chemical cues for settlement and metamorphosis of marine-invertebrate larvae, pp. 431–461, in J. B. McClintock and B. J. Baker (eds.). Marine Chemical Ecology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Hellio, C., De La Broise, D., Dufosse, L., Le Gal, Y., and Bourgougnon, N. 2001. Inhibition of marine bacteria by extracts of macroalgae: potential use for environmentally friendly antifouling paints. Mar. Environ. Res. 52:231–247.
Henrikson, A. A. and Pawlik, J. R. 1995. A new antifouling assay method-results from field experiments using extracts of four marine organisms. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 194:157–165.
HolmstrÖm, C. and Kjelleberg, S. 1999. Marine Pseudoalteromonas species are associated with higher organisms and produce biologically active extracellular agents. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 30:285–293.
HolmstrÖm, C. and Kjelleberg, S. 2000. Bacterial interactions with marine fouling organisms, pp. 101–115, in L. V. Evans (ed.). Biofilms: recent advances in their study and control. Harwood Academic Publishers, Amsterdam.
HolmstrÖm, C., James, S., Egan, S., and Kjelleberg, S. 1996. Inhibition of common fouling organisms by marine bacterial isolates with special reference to the role of pigmented bacteria. Biofouling 10:251–259.
Hornsey, J. S. and Hide, D. 1974. The production of antimicrobial compounds by British marine algae. I. Antibiotic-producing marine algae. Br. Phycol. J. 9:353–361.
Jennings, J. G. and Steinberg, P. D. 1997. Phlorotannins versus other factors affecting ephiphyte abundance on the kelp Ecklonia radiata. Oecologia 109:461–473.
Jensen, P. R. and Fenical, W. 1995. The relative abundance and seawater requirements of grampositive bacteria in near-shore tropical marine samples. Microb. Ecol. 29:249–257.
Jensen, R. A. and Morse, D. E. 1990. Chemically induced metamorphosis of polychaete larvae in both the laboratory and ocean environment. J. Chem. Ecol. 16:911–930.
Jensen, R. A., Morse, D. E., Petty, R. L., and Hooker, N. 1990. Artificial induction of larval metamorphosis by free fatty acids. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 67:55–71.
Jensen, P. R., Jenkins, K. M., Porter, D., and Fenical, W. 1998. Evidence that a new antibiotic flavone glycoside chemically defends the sea grass Thalassia testudinum against zoosporic fungi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64:1490–1496.
Johnson, C. R. and Sutton, D. C. 1994. Bacteria on the surface of crustose coralline algae induce metamorphosis of the crown-of-thorns starfish Acanthaster planci. Mar. Biol. 120:305–310.
Johnson, C. R., Lewis, R. E., Nichols, D. S., and Degnan, B. M. 1997. Bacterial induction of settlement and metamorphosis in marine invertebrates. Proceedings 8th International Coral Reef Sympsium, pp. 1219–1224.
Joint, I., Callow, M. E., Callow, J. A., and Clarke, K. R. 2000. The attachment of Enteromorpha zoospores to a bacterial biofilm assemblage. Biofouling 16:151–158.
Keough, M. J. and Raimondi, P. T. 1995. Responses of settling invertebrate larvae to bioorganic films: effects of different types of films. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 185:235–352.
Kievit, T. R. and Iglewski, B. H. 2000. Bacterial quorum sensing in pathogenic relationships. Infect. Immun. 68:4839–4849.
Kirchman, D., Graham, S., Reish, D., and Mitchell, R. 1982. Lectins may mediate the settlement and metamorphosis of Janua (Dexiospira) brasiliensis Grube (Polychaeta: Spirobidae). Mar. Biol. Lett. 3:131.
Kjelleberg, S. and Steinberg, P. D. 2002. Defenses against bacterial colonization of marine plants, pp. 152–172, in S. Lindow, E. Hecht-Poinbar and V. Elliott (eds.). Phyllosphere Microbiology. American Phytopathological Society Press, St. Paul, Minnesota.
Kon-ya, K., Shimidzu, N., Miki, W., and Endo, M. 1994. Indole derivatives as potent inhibitors of larval settlement by the barnacle, Balanus amphitrite. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 58:85–93.
Krug, P. J. and Manzi, A. E. 1999. Waterborne and surface-associated carbohydrates as settlement cues for larvae of the specialist marine herbivore Alderia modesta. Biol. Bull. 197:94–103.
Krug, P. J. and Zimmer, R. K. 2000a. Larval settlement: chemical markers for tracing production, transport, and distribution of a waterborne cue. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 207:283–296. CHEMICAL CUES FOR SURFACE COLONIZATION 1949
Krug, P. J. and Zimmer, R. K. 2000b. Developmental dimorphism and expression of chemosensorymediated behavior: habitat selection by a specialist marine herbivore. J. Exp. Biol. 203:1741–1754.
Kubanek, J., Whalen, K. E., Engel, S., Kelly, S. R., Henkel, T. P., Fenical, W., and Pawlik, J. R. 2002. Multiple defensive roles for triterpene glycosides from two Caribbean sponges. Oecologia 131:125–136.
Kupper, F. C., Kloareg, B., Guern, J., and Potin, P. 2001. Oligoguluronates elicit an oxidative burst in the brown algal kelp Laminaria digitata. Plant Physiol. 125:278–291.
Lambert, W. J., Todd, C. D., and Hardege, J. D. 1997. Partial characterization and biological activity of a metamorphic inducer of the dorid nudibranch Adalaria proxima (Gastropoda: Nudibranchia). Invert. Biol. 116:71–81.
Leis, J. M. and Carson-Ewart, B. 1997. In situ swimming speeds of the late pelagic larvae of some Indo-Pacific coral reef fishes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 159:165–174.
Lynch, M. J., Swift, S., Kirke, D. F., Keevil, C. W., Dodd, C. E. R., and Williams, P. 2002. The regulation of biofilm development by quorum sensing in Aeromonas hydrophila. Environ. Microbiol. 4:18–28.
Manefield, M., De Nys, R., Kumar, N., Read, R., Givskov, M., Steinberg, P. D., and Kjelleberg, S. 1999. Evidence that halogenated furanones from Delisea pulchra inhibit acylated homoserine lactone (AHL) mediated gene expression by displacing the AHL signal from its receptor protein. Microbiology 145:283–291.
Manefield, M., Rasmussen, T. B., Henzter, M., Andersen, J. B., Steinberg, P., Kjelleberg, S., and Givskov, M. 2002. Halogenated furanones inhibit quorum sensing through accelerated LuxR turnover. Microbiology 148:1119–1127.
Maximilien, R., De Nys, R., HolmstrÖm, C., Gram, L., Kjelleberg, S., and Steinberg, P. D. 1998. Bacterial fouling is regulated by secondary metabolites from the red alga Delisea pulchra. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 15:233–246.
McClintock, J. B. and Baker, J. B. (eds). 2001. Marine Chemical Ecology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
McDougald, S. D., Rice, S. A., and Kjelleberg, S. 2001. SmcR-dependent regulation of adaptive phenotypes in Vibrio vulnificus. J. Mol. Biol. 183:758–762.
McLean, R. J. C., Whiteley, M., Stickler, D. J., and Fuqua, W.C. 1997. Evidence of autoinducer activity in naturally occurring biofilms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 154: 259–263.
Morse, A. N. C. 1992. Recruitment of marine invertebrate larvae, pp 385-403, in D. M. John, S. J. Hawkins and J. H. Price (eds.). Plant–Animal Interactions in the Marine Benthos. Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Morse, A. N. C. and Morse, D. E. 1996. Flypapers for coral and other planktonic larvae. Bioscience 46:254–262.
Morse, D. E. and Morse, A. N. C. 1991. Enzymatic characterisation of the morphogen recognised by Agaricia humilis (scleractinian coral) larvae. Biol. Bull. 181:104–122.
Mullins, T. D., Britschgi, T. B., Krest, R. L., and Giovannoni, S. J. 1995. Genetic comparisons reveal the same unknown bacterial lineages in Atlantic and Pacific bacterioplankton communities. Limnol. Oceanogr. 40:148–158.
Negri, A. P., Webster, N. S., Hill, R. T., and Heyward, A. J. 2001. Metamorphosis of broadcast spawning corals in response to bacteria isolated from crustose algae.Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 223:121–131.
Pawlik, J. R. 1990. Natural and artificial induction of metamorphosis of Phragmatopoma lapidosa californica (Polychaeta: Sabellariidae), with a critical look at the effects of bioactive compounds on marine invertebrate larvae. Bull. Mar. Sci 46:512–536.
Pawlik, J. R. and Faulkner, D. J. 1986. Specific free fatty acids induce larval settlement and metamorphosis of the reef-building tubeworm Phragmatopoma californica (Fewkes). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 102:301–310.
Raimondi, P. T. and Morse, A. N. C. 2000. The consequences of complex larval behavior in a coral. Ecology 81:3193–3211.
Rasmussen, T. B., Manefield, M., Andersen, J., Eberl, L., Anthoni, U., Christophersen, C., Steinberg, P., Kjelleberg, S., and Givskov, M. 2000. How Delisea pulchra furanones affect quorum sensing and swarming motility in Serratia liquefaciens MG1. Microbiology 146:3237–3244.
Ren, D., Sims, J. J., and Wood, T.K. 2001. Inhibition of biofilm formation and swarming of Escherichia coli by (5Z)-4-bromo-5-(bromomethylene)-3-butyl-2(5H)-furanone. Environ. Microb. 3:731–736.
Rittschof, D. 1990. Peptide-mediated behaviors in marine organisms: Evidence for a common theme. J. Chem. Ecol. 16:261–267.
Rittschof, D. 2001. Natural product antifoulants and coatings development, pp. 543–566, in J. B. McClintock and B. J. Baker (eds.). Marine Chemical Ecology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Roberts, R. 2001. A review of settlement cues for larval abalone (Haliotis spp.). J. Shellfish Res. 2:571–586.
Rodelas, B., Lithgow, J. K., Wisniewski-Dye, F., Hardman, A., Wilkinson, A., Economou, A., Williams, P., and Downie, J. A. 1999. Analysis of quorum-sensing-dependent control of rhizosphere-expressed (rhi) genes in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae. J. Bacteriol. 181:3816–3823.
Salomon, C. E., Deerinck, T., Ellisman, M. H., and Faulkner, D. J. 2001. The cellular localisation of dercitamide in the Palauan sponge Oceanapia sagittaria. Mar. Biol. 139:313–319.
Sanchez, P., Correa, J. A., and Garciareina, G. 1996. Host-specificity of Endophyton ramosum (Chlorophyta), the causative agent of green patch disease in Mazzaella laminarioides (Rhodophyta). Eur. J. Phycol. 31:173–179.
Schmitt, T. M., Hay, M. E., and Lindquist, N. 1995. Constraints on chemically mediated coevolution: multiple functions for seaweed secondary metabolites. Ecology 76: 107–123.
Slattery, M. 1997. Chemical cues in marine invertebrate larval settlement, pp. 135, in R. Nagabhushanam and J. F. Thompson (eds.). Marine Woodboring and Fouling Organisms of the Indian Ocean: A Review. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co., New Delhi
Steinberg, P. D., De Nys, R., and Kjelleberg, S. 2001. Chemical mediation of surface colonization, pp. 355–387, in J. B. McClintock and J. B. Baker (eds.). Marine Chemical Ecology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida
Szewzyk, U., HolmstrÖm, C., Wrangstadh, M., Samuelsson, M. O., Maki, J. S., and Kjelleberg, S. 1991. Relevance of the exopolysaccharide of marine Pseudomonas sp strain S9 for the attachment of Ciona intestinalis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 75:259–265.
Takahashi, Y., Itoh, K., Ishii, M., Suzuki, M., and Itabashi, Y. 2002. Induction of larval settlement and metamorphosis of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius by glycoglycerolipids from the green alga Ulvella lens. Mar. Biol. 140:763–771.
Tsukamoto, S., Kato, H., Hirota, H., and Fusetani, N. 1999. Lumichrome: a larval metamorphosisinducing substance in the ascidian Halocynthia roretzi. Eur. J. Biochem. 264: 785–789.
Unabia, C. R. C. and Hadfield, M. G. 1999. Role of bacteria in larval settlement and metamorphosis of the polychaete Hyroides elegans. Mar. Biol. 133:55–64.
Uppalapati, S. R. and Fujita, Y. 2000. Carbohydrate regulation of attachment, encystment, and appressorium formation by Pythium porphyrae (Oomycota) zoospores on Porphyra yezoensis (Rhodophyta). J. Phycol. 36:359–366.
Visick, K. L. and Ruby, E. G. 1999. The emergent properties of quorum sensing: consequences to bacteria of autoinducer signaling in their natural environment. pp. 333–352, in G. M. Dunny and S. C. Winans (eds.). Cell–Cell Signaling in Bacteria. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
Wahl, M. 1995. Bacterial epibiosis on Bahamian and Pacific ascidians. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 191:239–255. CHEMICAL CUES FOR SURFACE COLONIZATION 1951
Wahl, M. and Mark, O. 1999. The predominantly facultative nature of epibiosis: experimental and observational evidence. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 187:59–66.
Wahl, M., Jensen, P. R., and Fenical, W. 1994. Chemical control of bacterial epibiosis on ascidians. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 110:45–57.
Walker, R. P., Thompson, J. E., and Faulkner, D. J. 1985. Exudation of biologically active metabolites in the sponge Aplysina fistularis II. Chemical evidence. Mar. Biol. 88: 27–32.
Weinberger, F. and Friedlander, M. 2000a. Response of Gracilaria conferta (Rhodophyta) to oligoagars results in defense against agar-degrading epiphytes. J. Phycol. 36:1079–1086.
Weinberger, F., and Friedlander, M. 2000b. Endogenous and exogenous elicitors of a hypersensitive response in Gracilara conferta (Rhodophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 12:139–145.
Welch, J. M. and Forward, R. B. 2001. Flood tide transport of blue crab, Callinectes sapidus, postlarvae: behavioural responses to salinity and turbulence. Mar. Biol. 139:911–918.
Whitehead, N. A., Barnard, A. M., Slater, H., Simpson, N. J., and Salmond, G. P. 2001. Quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 25:365–404.
Wieczorek, S. K. and Todd, C. D. 1998. Inhibition and facilitation of settlement of epifaunal marine invertebrate larvae by microbial biofilm cues. Biofouling 12:81–118.
Williamson, J. E., De Nys, R., Kumar, N., Carson, D. G., and Steinberg, P. D. 2000. Induction of metamorphosis in the sea urchin Holopneustes purpurascens by a metabolite complex from the algal host Delisea pulchra. Biol. Bull. 198:332–345.
Winans, S. C. and Bassler, B. L. 2002. Mob psychology. J. Bacteriol. 184:873–883.
Zimmer, R. K. and Butman, C. A. 2000. Chemical signaling processes in the marine environment. Biol. Bull. 198:168–187.
Zimmer-faust, R. K. and Tamburri, M. N. 1994. Chemical identity and ecological implications of a water-borne, larval settlement cue. Limnol. Oceanogr. 39:1075–1087.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steinberg, P.D., de Nys, R. & Kjelleberg, S. Chemical Cues for Surface Colonization. J Chem Ecol 28, 1935–1951 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020789625989
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020789625989