Abstract
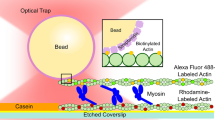
Numerous biological processes, including muscular contraction, depend upon the mechanical properties of actin filaments. One such property is resistance to bending (flexural rigidity, EI). To estimate EI, we attached the ends of fluorescently labelled actin filaments to two microsphere‘handles’ captured in independent laser traps. The positions of the traps were manipulated to apply a range of tensions (0--8 pN)to the filaments via the microsphere handles. With increasing filament tension, the displacement of the microspheres was inconsistent with a microsphere-filament system that is rigid. We maintain that this inconsistency is due to the microspheres rotating in the trap and the filaments bending near their attachments to accommodate this rotation. Fitting the experimental data to a simple model of this phenomena, we estimate actin's EI to be ×15 × 103 pN nm2, a value within the range of previously reported results, albeit using a novel method. These results both: support the idea that actin filaments are more compliant than historically assumed; and, indicate that without appropriately pretensioning the actin filament in similar laser traps, measurements of unitary molecular events (e.g. myosin displacement) may be significantly underestimated
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASHKIN, A. (1992) Forces of a single-beam gradient laser trap on a dielectric sphere in the ray optics regime. Biophys. J. 61, 569–82.
BLOCK, S. M. (1995) One small step for myosin. Nature 378, 132–3.
BREMER, A. & AEBI, U. (1992) The structure of the f-actin filament and the actin molecule. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 4, 20–6.
CHU, S. (1991) Laser manipulation of atoms and particles. Science 253, 861–6.
EGELMAN, E. H. (1985) The structure of f-actin. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 6, 129–51.
FEYNMAN, R. P., LEIGHTON, R. B. & SANDS, M. L. (1964) The Feynman Lectures on Physics, Vol. 2.Reading: Addison-Wesley.
FINER, J. T., SIMMONS, R. M. & SPUDICH, J. A. (1994) Single myosin molecule mechanics: piconewton forces and nanometre steps. Nature 368, 113–19.
FINER, J. T., MEHTA, A. D. & SPUDICH, J. A. (1995) Characterization of single actin-myosin interactions. Biophys. J. 68, 291s–7s.
FORD, L. E., HUXLEY, A. F. & SIMMONS, R. M. (1981) The relation between stiffness and filament overlap in stimulated frog muscle fibres. J. Physiol. 311, 219–49.
FRISCH-FAY, R. (1962) Flexible Bars. Washington: Butterworths.
GITTES, F., MICKEY, B., NETTLETON, J. & HOWARD, J. (1993) Flexural rigidity of microtubules and actin filaments measured from thermal fluctuations in shape. J. Cell Biol. 120(4), 923–34.
GOLDMAN, Y. E. & HUXLEY, A. F. (1994) Actin compliance: are you pulling my chain? Biophys. J. 67, 2131–6.
HARRIS, R. A. & HEARST, J. E. (1965) On polymer dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 44(7), 2595–602.
HIGUCHI, H., YANAGIDA, T. & GOLDMAN, Y. E. (1995) Compliance of thin filaments in skinned fibers of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biophys. J. 69, 1000–10.
HUXLEY, H. E., STEWART, A., SOSA, H. & IRVING, T. (1994) X-ray diffraction measurements of the extensibility of actin and myosin filaments in contracting muscle. Biophys. J. 67, 2411–21.
ISAMBERT, H., VENIER, P., MAGGS, A. C., FATTOUM, A., KASSAB, R., PANTALONI, D. & CARLIER, M. (1995) Flexibility of actin filaments derived from thermal fluctuations. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 11437–44.
KABSCH, W. & VANDEKERCKHOVE, J. (1992) Structure and function of actin. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 21, 49–76.
KAS, J., STREY, H., BARMANN, M. & SACKMANN, E. (1993) Direct measurement of the wave-vector-dependent bending stiffness of freely flickering actin filaments. Europhys. Lett. 21(8), 865–70.
KISHINO, A. & YANAGIDA, T. (1988) Force measurements by micromanipulation of a single actin filament by glass needles. Nature 334, 74–7.
KOJIMA, H., ISHIJIMA, A. & YANAGIDA, T. (1994) Direct measurements of stiffness of single actin filaments with and without tropomyosin by in vitronanomanipulation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 12962–6.
LANDAU, L. D. & LIFSHITZ, E. M. (1958) Statistical Physics. London: Pergamon Press Ltd.
MARGOSSIAN, S. S. & LOWEY, S. (1982) Preparation of myosin and its subfragments from rabbit skeletal muscle. In Methods Enzymol, Vol. 85. Structural and Contractile Proteins. (edited by FREDERIKSEN, D. W. & CUNNINGHAM, L. W.) New York: Academic Press.
MIYATA, H., HAKOZAKI, H., YOSHIKAWA, H., SUZUKI, N., KINOSITA, K., NISHIZAKA, T. & ISHIWATA, S. (1994) Stepwise motion of an actin filament over a small number of heavy meromyosin molecules is revealed in an in vitro motility assay. J. Biochem. 115, 644–7.
MOLLOY, J. E., BURNS, J. E., KENDRICK-JONES, J., TREGEAR, R. T. & WHITE, D. C. S. (1995) Movement and Force produced by a single myosin head. Nature 378, 209–12.
NAGASHIMA, H. & ASAKURA, S. (1980) Dark-field light microscopic study of the flexibility of f-actin complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 136, 169–82.
NISHIZAKA, T., MIYATA, H., YOSHIKAWA, H., ISHIWATA, S. & KINOSITA, K. (1995) Unbinding force of a single motor molecule of muscle measured using optical tweezers. Nature 377, 251–4.
OOSAWA, F. (1977) Actin-actin bond strength and the conformational change of f-actin. Biorheology 14, 11–19.
PARDEE, J. D. & SPUDICH, J. A. (1982) Purification of muscle actin. In Methods Enzymol, Vol. 85. Structural and Contractile Proteins. (edited by FREDERIKSEN, D. W. & CUNNINGHAM, L. W.) New York: Academic Press.
SVOBODA, K. & BLOCK, S. M. (1994) Biological applications of optical forces. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 23, 247–85.
SVOBODA, K., SCHMIDT, C. F., SCHNAPP, B. J. & BLOCK, S. M. (1993) Direct observation of kinesin stepping by optical trapping interferometry. Nature 365, 721–7.
VANBUREN, P., WORK, S. S. & WARSHAW, D. M. (1994) Enhanced force generation by smooth muscle myosin in vitro. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 202–5.
VANBUREN, P. GUILFORD, W. H., KENNEDY, G., WU, J. & WARSHAW, D. M. (1995) Smooth muscle myosin: a high force-generating molecular motor. Biophys. J. 68, 256s–9s.
WAKABAYASHI, K., SUGIMOTO, Y., TANAKA, H., UENO, Y., TAKEZAWA, Y. & AMEMIYA, Y. (1994) X-ray diffraction evidence for the extensibility of actin and myosin filaments during muscle contraction. Biophys. J. 67, 2422–35.
WARSHAW, D. M., DEROSIERS, J. M., WORK, S. S. & TRYBUS, K. M. (1990) Smooth muscle myosin cross-bridge interactions modulate actin filament sliding velocity in vitro. J. Cell Biol. 111, 453–63.
YANAGIDA, T., NAKASE, M., NISHIYAMA, K. & OOSAWA, F. (1984) Direct observation of motion of single F-actin filaments in the presence of myosin. Nature 307, 58–60.
YIN, H., WANG, M. D., SVOBODA, K., LANDICK, R., BLOCK, S. M. & GELLES, J. (1995) Transcription against an applied force. Science 270, 1653–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DUPUIS, D.E., GUILFORD, W.H., WU, J. et al. Actin filament mechanics in the laser trap. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 18, 17–30 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018672631256
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018672631256