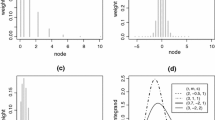
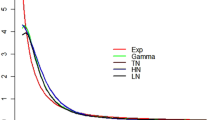
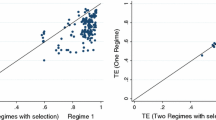
Abstract
In this paper we describe the use of modern numerical integration methods for making posterior inferences in composed error stochastic frontier models for panel data or individual cross- sections. Two Monte Carlo methods have been used in practical applications. We survey these two methods in some detail and argue that Gibbs sampling methods can greatly reduce the computational difficulties involved in analyzing such models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aigner, D., C. A. K. Lovell, and P. Schmidt. (1977). “Formulation and Estimation of Stochastic Frontier Productions Function Models.” Journal of Econometrics 6, 21–37.
Bauer, P.W. (1990). “Recent Developments in the Econometric Estimation of Frontiers.” Journal of Econometrics 46, 39–56.
van den Broeck, J., G. Koop, J. Osiewalski, and M. Steel. (1994). “Stochastic Frontier Models: A Bayesian Perspective.” Journal of Econometrics 61, 273–303.
Carlin, B., N. Polson, and D. Stoffer. (1992). “A Monte Carlo Approach to Nonnormal and Nonlinear State-Space Modelling.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 87, 493–500.
Casella, G., and E. George. (1992). “Explaining the Gibbs Sampler.” The American Statistician 46, 167–174.
Chib, S. (1995). “Marginal Likelihood from the Gibbs Output.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 90, 1313–1321.
Devroye, L. (1986). Non-Uniform Random Variate Generation. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Fernández, C., J. Osiewalski, and M. F. J. Steel. (1997). “On the Use of Panel Data in Stochastic Frontier Models with Improper Priors.” Journal of Econometrics 79, 169–193.
Gelfand, A. E., and D. K. Dey. (1994). “Bayesian Model Choice: Asymptotics and Exact Calculations.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Ser. B 56, 501–514.
Gelfand, A. E., and A. F. M. Smith. (1990). “Sampling-Based Approaches to Calculating Marginal Densities.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 85, 398–409.
Gelman, A., and D. Rubin. (1992). “A Single Series from the Gibbs Sampler Provides a False Sense of Security.” In J. M. Bernardo, J. O. Berger, A. P. Dawid, and A. F. M. Smith (eds.), Bayesian Statistics 4. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Geweke, J. (1989). “Bayesian Inference in Econometric Models Using Monte Carlo Integration.” Econometrica 57, 1317–1339.
Geweke, J. (1991). “Efficient Simulation from the Multivariate Normal and Student-t Distributions Subject to Linear Constraints.” In E. M. Keramidas and S. M. Kaufman (eds.), Computing Science and Statistics: Proceedings of the 23rd Symposium on the Interface. Interface Foundation of North America.
Geweke, J. (1992). “Evaluating the Accuracy of Sampling-Based Approaches to the Calculation of Posterior Moments.” In J. M. Bernardo, J. O. Berger, A. P. Dawid, and A. F. M. Smith (eds.), Bayesian Statistics 4. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Geweke, J. (1995). “Posterior Simulators in Econometrics.” Working paper 555. Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis.
Greene,W. H. (1990). “A Gamma-Distributed Stochastic Frontier Model.” Journal of Econometrics 46, 141–163.
Hills, S. E., and A. F. M. Smith. (1992). “Parameterization Issues in Bayesian Inference.” In J. M. Bernardo, J. O. Berger, A. P. Dawid, and A. F. M. Smith (eds.), Bayesian Statistics 4. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Koop, G., J. Osiewalski, and M. F. J. Steel. (1994). “Bayesian Efficiency Analysis with a Flexible Form: The AIM Cost Function.” Journal of Business and Economic Statistics 12, 339–346.
Koop, G., J. Osiewalski, and M. F. J. Steel. (1997a). “The Components of Output Growth: A Stochastic Frontier Analysis.” Manuscript.
Koop, G., J. Osiewalski, and M. F. J. Steel. (1997b). “Modeling the Sources of Output Growth in a Panel of Countries.” Manuscript.
Koop, G., J. Osiewalski, and M. F. J. Steel. (1997c). “Bayesian Efficiency Analysis through Individual Effects: Hospital Cost Frontiers.” Journal of Econometrics 76, 77–105.
Koop, G., M. F. J. Steel, and J. Osiewalski. (1995). “Posterior Analysis of Stochastic Frontier Models Using Gibbs Sampling.” Computational Statistics 10, 353–373.
Kumbhakar, S. C. (1997). “Modeling Allocative Inefficiency in a Translog Cost Function and Cost Share Equations: An Exact Relationship.” Journal of Econometrics 76, 351–356.
Ley, E., and M. F. J. Steel. (1992). “Bayesian Econometrics: Conjugate Analysis and Rejection Sampling Using Mathematica.” In H. Varian (ed.), Economic and Financial Modeling Using Mathematica, Chapter 15. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Meeusen, W., and J. van den Broeck. (1977). “Efficiency Estimation from Cobb-Douglas Production Functions with Composed Error.” International Economic Review 8, 435–444.
Naylor, J. C., and A. F. M. Smith. (1982). “Applications of a Method for the Efficient Computation of Posterior Distributions.” Applied Statistics 31, 214–225.
Newton, M., and A. Raftery. (1994). “Approximate Bayesian Inference by the Weighted Likelihood Bootstrap.” With discussion. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B 56, 3–48.
O'Hagan, A. (1994). Bayesian Inference. London: Edward Arnold.
Pitt, M. M., and L. F. Lee. (1981). “The Measurement and Sources of Technical Inefficiency in the Indonesian Weaving Industry.” Journal of Development Economics 9, 43–64.
Raftery, A., and S. Lewis. (1992). “How Many Iterations in the Gibbs Sampler?” In J. M. Bernardo, J. O. Berger, A. P. Dawid, and A. F. M. Smith (eds.), Bayesian Statistics 4. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Ripley, B. D. (1987). Stochastic Simulation. New York: Wiley.
Ritter, C. (1993). “The Normal-Gamma Frontier Model under a Common Vague Prior Does not Produce a Proper Posterior.” Manuscript.
Ritter, C., and L. Simar. (1997). “Pitfalls of Normal-Gamma Stochastic Frontier Models.” Journal of Productivity Analysis 8, 167–182.
Ritter, C., and M. A. Tanner. (1992). “Facilitating the Gibbs Sampler: The Gibbs Stopper and the Griddy-Gibbs Sampler.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 87, 861–868.
Schmidt, P., and R. C. Sickles. (1984). “Production Frontiers and Panel Data.” Journal of Business and Economic Statistics 2, 367–374.
Smith, A. F. M., and A. E. Gelfand. (1992). “Bayesian Statistics without Tears: A Sampling-Resampling Perspective.” The American Statistician 46, 84–88.
Tanner, M. A. (1991). Tools for Statistical Inference. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Tanner, M. A., and W. H. Wong. (1987). “The Calculation of Posterior Distributions by Data Augmentation.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 82, 528–540.
Tierney, L. (1994). “Markov Chains for Exploring Posterior Distributions.” With discussion. Annals of Statistics 22, 1701–1762.
Tierney, L., and J. B. Kadane. (1986). “Accurate Approximations for Posterior Moments and Marginal Densities.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 81, 82–86.
Zeger, S., and M. Karim. (1991). “Generalized Linear Models with Random Effects: A Gibbs Sampling Approach.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 86, 79–86.
Zellner, A., and C. Min. (1995). “Gibbs Sampler Convergence Criteria.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 90, 921–927.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osiewalski, J., Steel, M.F.J. Numerical Tools for the Bayesian Analysis of Stochastic Frontier Models. Journal of Productivity Analysis 10, 103–117 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018302600587
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018302600587