Abstract
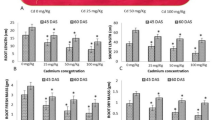
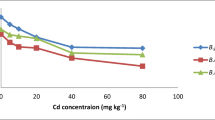
Two Brassica species Brassica juncea and Brassica carinata of the Indian mustard, were grown in an artificially Ni-contaminated soil to study the tolerance and Ni accumulation. Chelating agent, EDTA was applied at the rosette stage for enhancing the metal uptake. Nickel concentration over almost double that in control was observed in both the species with Ni contamination along with EDTA application. Specie B. juncea appeared to be slightly more tolerant and higher accumulator of Ni. In agreement with the earlier reports, the translocation of the pollutant metal to the shoot from the root seemed to be restricted in both of Brassica species at higher rate of Ni application plus EDTA. The results of the present study indicated that B. juncea has the potential to be hyperaccumulator of Ni.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, C., Deram, A., Petit, D., Brooks, R., Steward, B. and Simcock, R.: 1999, 'Induced hyperaccumulation: Metal movement and problems', Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Biogeochemistry of trace elements, Vienna, pp. 122–123.
Blaylock, M.J., Salt, D.E., Dushenkov, S., Zokharova, O., Gussman, C., Kapulnik, Y., Ensly, B.F. and Raskin, D.: 1997, 'Enhanced accumulation of Pb in mustard by soil applied chelating agents', Environ. Sci. Technol. 31, 860–865.
Brooks, R.R. and Robinson, B.H.: 1998, 'The potential use of hyperacuumulators and other plants for phytomining', in R.R. Brooks (ed.), Plants that Hyperaccumulate Heavy Metals, Wallingford, CAB International, pp. 327–365.
Clothier, B.E., Vogetor, I., Green, S.R., Dijssel, C., Robinson, B.H. and Kirkham, M.B.: 1999, Bio-availability and Flux of Copper in EDTA-Treated Soil. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Biogeochemistry of trace elements, Vienna, pp. 124–125.
Ebbs, S.D. and Kochian, L.V.: 1997, 'Toxicity of zinc and copper to Brassica species: Implications for phytoremediation', J. Environ. Qual. 26, 776–781.
Guo, Y.L., Schulz, R. and Marschner, H.: 1995, 'Genotypic differences in uptake and distribution of Cd and Ni in plants', Angew. Botanik. 69, 42–48.
Huang, J.W., Chen, J., Berti, W.R. and Cunninghum, S.D.: 1997, 'Phytoremedition of lead-contaminated soils: Role of synthetic chelates in lead phytoextraction', Environ. Sci. Technol. 31, 800–805.
Kumar, P.B.A.N., Dushenkov, V., Motto, H. and Rashkin, I.: 1995, 'Phytoextraction: The use of plants to remove heavy metals from soils', Environ. Sci. Technol. 29, 1232–1238.
Lindsay, W.L. and Norvell, W.A.: 1978, 'Development of a DTPA soil test for Zn, Fe, Mn and Cu', Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 42, 421–428.
Mitchell, R.L.: 1945, 'Cobalt and Nickel in soils and plants', Soil Sci. 60, 63–70.
Monni, S., Salemaa, M. and Uhlig, C.: 1999, 'Nickel accumulation in Empetrum nigrum', Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Biogeochemistry of trace elements, Vienna, pp. 568–569.
Petterson, O.: 1976, 'Heavy metal ion uptake in plants from nutrient solutions with metal ion, plant species and growth period variation', Plant Soil. 45, 445–459.
Richards, L.A. (ed.): 1954, 'Diagnosis and improvement of saline alkali soils', Agricultural Handbook, US Department of Agriculture 60, Washington, DC, USA.
Shallari, S., Echevarria, G. and Morel, J.L.: 1999, 'Where do plants take up their nickel from?', Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Biogeochemistry of trace elements, Vienna, pp. 526–527.
Vassil, A.D., Kapulnik, Y., Raskin, I. and Salt, E.: 1998, 'The role of EDTAin lead transport and accumulation by Indian mustard', Plant Physiol. 117, 447–453.
Wasay, S.A., Barrington, S. and Tokunaga, S.: 1998, 'Retention form of heavy metals in three polluted soils', J. Soil Contam. 7, 103–119.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panwar, B., Ahmed, K. & Mittal, S. Phytoremediation of Nickel-Contaminated Soils by Brassica Species. Environment, Development and Sustainability 4, 1–6 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016337132370
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016337132370