Abstract
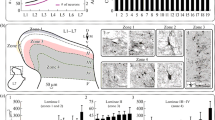
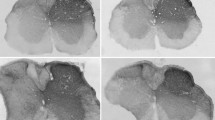
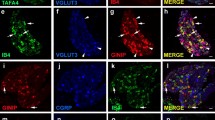
We have investigated the presence of three neurochemical markers, glutamate, calbindin-D28k, and nitric oxide synthase, in spinal neurones that transmit chemical noxious inputs from both the skin and the viscera, by combining retrograde labelling with the fluorescent tracer Fluorogold with dual labelling immunohistochemistry. Neurones projecting to the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) that expressed Fos protein in response to cutaneous or visceral noxious stimulation were concentrated in lamina I of the cervical and lumbosacral segments, respectively. Although both labelled neuronal populations were numerous, the spino-solitary cells that transmit visceral nociceptive input predominated over those transmitting cutaneous nociceptive input. Calbindin-D28k-immunoreactivity was observed in neurones of three morphological types (fusiform, flattened, and pyramidal) projecting to the NTS that were activated by somatic or visceral nociceptive neurones. Nitric oxide synthase and glutamate immunoreactivities were present only in viscerally activated nociceptive neurones projecting to the NTS. Glutamate-immunopositive NTS-projecting cells were exclusively of the flattened type, and the nitric oxide synthase-immunolabelled NTS-projecting cells comprised 75% fusiform cells and 25% flattened cells. These data suggest that the involvement of excitatory spinal lamina I projection neurones in the transmission of peripheral chemical nociceptive inputs to the NTS may be restricted to information of visceral origin.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abram, S.E., Kostreva, D.R., Hopp, F.A., and Kampine, J.P. (1983). Cardiovascular responses to noxious radiant heat in anesthetized cats. Am. J. Physiol. 245:R576–R580.
Agarwal, S.K. and Calaresu, F.R. (1990). Reciprocal connections between nucleus tractus solitarii and rostral ventrolateral medulla. Brain Res. 523:305–308.
Alam, M. and Smirk, F.H. (1938). Observations in man concerning the effects of different types of sensory stimulation upon blood pressure. Clin. Sci. 3:253–258.
Apkarian, A.V., Jyvasjarvi, E., Kniffki, K.D., Mengel, M.K., and Stiefenhofer, A. (1989). Activation of carotid sinus baroreceptors reduces pain sensations evoked by electrical and cold stimulation of human teeth. Proc. Finn. Dental Soc. 85:409–413.
Bandler, R. and Tork, I. (1987). Midbrain periaqueductal grey region in the cat has afferent and efferent connections with solitary tract nuclei. Neurosci. Lett. 74:1–6.
Baringa, M. (1991). Is nitric oxide the “retrograde messenger”? Science 254:1296–1297.
Barraco, I.R.A. (ed.) (1994). Nucleus of the Solitary Tract, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Batten, T.F.C., Atkinson, L., and Deuchars, J. (2000). Nitric oxide systems in the medulla oblongata and their involvement in autonomic control. In (H.W.M. Steinbusch and J. De Vente, eds.), Functional Neuroanatomy of the Nitric Oxide System, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 177–213.
Behbehani, M.M. (1995). Functional characteristics of the midbrain periaqueductal gray. Prog. Neurobiol. 46:575–605.
Bullitt, E. (1990). Expression of c-fos-like protein as a marker for neuronal activity following noxious stimulation in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 296:517–530.
Celio, M.R. (1990). Calbindin D-28k and parvalbumin in the rat nervous system. Neuroscience 35:375–475.
De Pommery, J., Roudier, F., and Menétrey, D. (1984). Postsynaptic fibers reaching the dorsal column nuclei in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 50:319–323.
DeLeo, J.A., Coombs, D.W., and McCarthy, L.E. (1991). Differencial c-fos-like protein expression in mechanically versus chemically induced visceral nociception. Mol. Brain Res. 11:167–170.
Donovick, P.J. (1974). A metachromatic stain for neuronal tissue. Stain Tech. 49:49–51.
Dragunow, M. and Faull, R. (1989). The use of c-fos as a metabolic marker in neuronal pathway tracing. J. Neurosci. Methods 29:261–265.
Esteves, F., Lima, D., and Coimbra, A. (1993). Structural types of spinal cord marginal (lamina I) neurons projecting to the nucleus of the tractus solitarius in the rat. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 10:203–216.
Gamboa-Esteves, F.O., Kaye, J.C., McWilliam, P.N., and Batten, T.F.C. (2001). Immunohistochemical profiles of spinal lamina I neurones retrogradely labelled from the nucleus tractus solitarii in rat suggest excitatory projections. Neuroscience 104:523–538.
Giesler, G.J., Nahin, R.L., and Madsen, A.M. (1984). Postsynaptic dorsal column pathway of the rat. I. Anatomical studies. J. Neurophysiol. 51:260–275.
Harris, A.J. (1998). Using c-fos as a neuronal marker in pain. Brain Res. Bull. 45:1–8.
Helmchen, C., Fu, Q.-G., and Sandkühler, J. (1995). Inhibition of spinal nociceptive neurons by microinjections of somatostatin into the nucleus raphe magnus and the midbrain periaqueductal gray of the anesthetized cat. Neurosci. Lett. 187:137–141.
Herbert, H. and Saper, C.B. (1992). Organization of medullary adrenergic and noradrenergic projections to the periaqueductal gray matter in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 315:34–52.
Janig, W., Khasar, S.G., Levine, J.D., and Miao, F.J. (2000). The role of vagal visceral afferents in the control of nociception. Prog. Brain Res. 122:273–287.
Krukoff, T.L. (1999). Central actions of nitric oxide in regulation of autonomic functions. Brain Res. Rev. 30:52–65.
Lima, D. and Coimbra, A. (1983). The neuronal population of the marginal zone (lamina I) of the spinal cord. A study based on reconstructions of serially sectioned cells. Anat. Embryol. 167:273–288.
Lima, D. and Coimbra, A. (1986). A Golgi study of the neuronal population of the marginal zone (lamina I) of the rat spinal cord. J. Comp. Neurol. 244:53–71.
Lima, D. and Coimbra, A. (1990). Structural types of marginal (lamina I) neurons projecting to the dorsal reticular nucleus of the medulla oblongata. Neuroscience 34:591–606.
Lima, D., Avelino, A., and Coimbra, A. (1990). C-fos activation of marginal zone neurons projecting to the mesencephalon after noxious cutaneous and visceral stimulation: Evidence for the involvement of fusiform neurons in visceral pain processing. Eur. J. Neurosci. 3(Suppl.):287.
Lima, D., Avelino, A., and Coimbra, A. (1992). Differential participation of marginal cells in the transmission of nociceptive input to the thalamus and mesencephalon. Eur. J. Neurosci. 5(Suppl.):92.
Lima, D., Avelino, A., and Coimbra, A. (1993). Differential activation of c-fos in spinal neurons by distinct classes of noxious stimuli. NeuroReport 4:747–750.
Lima, D., Esteves, F., and Coimbra, A. (1994). C-fos activation by noxious input of spinal neurons projecting to the nucleus of the tractus solitarius in the rat. In (G. Gebhart, D.L. Hammond, and T.S. Jensen, eds.), Proceedings of the 7th World Congress on Pain, Progress in Pain Research and Management, IASP Press, Seattle, Washington, pp. 423–434.
Lima, D. and Avelino, A. (1994). Spinal c-fos expression is differentially induced by brief or persistent noxious stimulation. NeuroReport 5:1853–1856.
Lima, D. (1996). Endogenous pain modulatory system in the light of the gate control theory. Pain Forum 5:31–39.
Lima, D. (1997). Functional anatomy of spinofugal nociceptive pathways. Pain Rev. 4:1–19.
Loewy, A.D. and Burton, H. (1978). Nuclei of the solitary tract: Efferent projections to the lower brain stem and spinal cord of the cat. J. Comp. Neurol. 181:421–450.
Loewy, A.D. (1990). Central autonomic pathways. In (A.D. Loewy and K.M. Spyer, eds.), Central Regulation of Autonomic Functions, Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 88–103.
Lovick, T.A. (1991). Central nervous system integration of pain control and autonomic function. News Physiol. Sci. 6:82–86.
Maixner, W. (1989). Autonomic and somatosensory interactions: Physiological and pathophysiological implications. Proc. Finn. Dental Soc. 85:395–407.
Maixner, W., Gracely, R.H., Zuniga, J.R., Humphrey, C.B., and Bloodworth, G.R. (1990). Cardiovascular and sensory responses to forearm ischemia and dynamic hand exercise. Am. J. Physiol. 259:R1156–R1163.
Malmberg, A.B. and Yaksh, T.L. (1993). Spinal nitric oxide synthesis inhibition blocks NMDA-induced thermal hyperalgesia and produces antinociception in the formalin test in rats. Pain 54:291–300.
Mattson, M.P., Rychlik, B., Chu, C., and Christakos, S. (1991). Evidence for calcium-reducing and excito-protective roles for the calcium-binding protein calbindin-D28k in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuron 6:41–51.
McMahon, S.E., McWilliam, P.N., Robertson, J., and Kaye, J.C. (1992). Inhibition of carotid sinus baroreceptor neurones in the nucleus tractus solitarius of the anaesthetized cat by electrical stimulation of hindlimb afferent fibres. J. Physiol. 452:224.
Meller, S.T. and Gebhart, G.F. (1993). Nitric oxide (NO) and nociceptive processing in the spinal cord. Pain 52:127–136.
Menétrey, D. and Basbaum, A.I. (1987). Spinal and trigeminal projections to the nucleus of the solitary tract: A possible substrate for somatovisceral and viscerovisceral reflex activation. J. Comp. Neurol. 255:439–450.
Menétrey, D., Gannon, A., Levine, J.D., and Basbaum, A.I. (1989). Expression of c-fos protein in interneurons and projection neurons of the rat spinal cord in response to noxious somatic, articular, and visceral stimulation. J. Comp. Neurol. 285:177–195.
Menétrey, D., de Pommery, J., Thomasset, M., and Baimbridge, K.G. (1992). Calbindin-D28K (CaBP28k)-like immunoreactivity in ascending projections. II. Spinal projections to brain stem and mesencephalic areas. Eur. J. Neurosci. 4:70–76.
Mtui, E.P., Anwar, M., Gomez, R., Reis, D.J., and Ruggiero, D.A. (1993). Projections from the nucleus tractus solitarii to the spinal cord. J. Comp. Neurol. 337:231–252.
Paxinos, G. and Watson, C. (1997). The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 3rd edn., Academic Press, San Diego, California.
Randich, A. and Maixner, W. (1986). The role of sinoaortic and cardiopulmonary baroreceptor reflex arcs in nociception and stress-induced analgesia. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 467:385–401.
Randich, A. and Meller, S.T. (1994). Role of the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) in pain control. In (I.R.A. Barraco, ed.), Nucleus of the Solitary Tract, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 407–417.
Sancesario, G., Morello, M., Reiner, A., Giacomini, P., Massa, R., Schoen, S., and Bernadi, G. (2000). Nitrergic neurons make synapses on dual-input dendritic spines of neurons in the cerebral cortex and the straitum of the rat: Implication for a postsynaptic action of nitric oxide. Neuroscience 99:627–642.
Sheps, D.S., Bragdon, E.E., Gray, T.F., Ballenger, M., Usedom, J.E., and Maixner, W. (1992). Relation between systemic hypertension and pain perception. Am. J. Cardiol. 70:3F–5F.
Sim, L.J. and Joseph, S.A. (1994). Efferent of the opiocortin-containing region of the commissural nucleus tractus solitarius. Peptides 15:169–174.
Tavares, I. and Lima, D. (1994). Descending projections from the caudal medulla oblongata to the superficial or deep dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. Exp. Brain Res. 99:455–463.
Torvik, A. (1956). Afferent connections to the sensory trigeminal nuclei, the nucleus of the solitary tract and adjacent structures. J. Comp. Neurol. 106:51–141.
Van Bockstaele, E.J. and Aston-Jones, G. (1995). Integration in the ventral medulla and coordination of sympathetic, pain and arousal functions. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 17:153–165.
Wilson, L.B. and Hand, G.A. (1997). The pressor reflex evoked by static contraction: Neurochemistry at the site of the first synapse. Brain Res. Rev. 23:196–209.
Yamamoto, T., Carr, P.A., Baimbridge, K.G., and Nagy, J.I. (1989). Parvalbumin-and calbindin D28kimmunoreactive neurons in the superficial layers of the spinal cord dorsal horn of rat. Brain Res. Bull. 23:493–508.
Zamir, N. and Maixner,W. (1986). The relationship between cardiovascular and pain regulatory systems. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 467:371–384.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gamboa-Esteves, F.O., Lima, D. & Batten, T.F. Neurochemistry of Superficial Spinal Neurones Projecting to Nucleus of the Solitary Tract that Express c-fos on Chemical Somatic and Visceral Nociceptive Input in the Rat. Metab Brain Dis 16, 151–164 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012536910214
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012536910214