Abstract
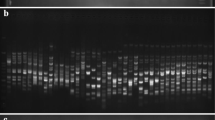
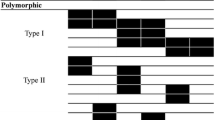
Wheat-rye translocation line (2BS/2RL) has been developed for resistance to biotype L of Hessian fly and agronomically useful traits. AFLP analysis using 64 primer pairs was conducted in order to identify 2RL-specific polymorphisms between “Coker 797” (non-2RL), near-isogenic line (NIL) carrying 2RL, and “Hamlet”. Nine primer combinations identified twelve reproducible polymorphic fragments in the NIL carrying 2RL. These twelve fragments were cloned and sequenced with an aim towards converting AFLP markers into sequence tagged sites (STS). A comparison of the 12 sequences with non-redundant accessions in the NCBI database using the BLAST search option indicated that one fragment of approximately 200 bp in length (amplified using primer combination E+AAC / M+CTA) was highly homologous with the rye-specific repetitive sequence R173-1 and Wis-2-lA, a retrotransposon-like element in wheat. Two STS primers (SJ07 and SJ09) out of twelve STS primer sets enabled the detection of polymorphisms between Coker 797 and NIL carrying 2RL. In order to verify whether the polymorphism detected by primers SJ07 and SJ09 was in fact the result of the presence of 2RL, additional plant material was examined. Amplified products of about 260 bp fragment with the SJ07 primer set were generated in rye cvs.“Chilbohomil” and “Jochunhomil”, triticale experimental line Suwon 15, and wheat experimental line K-14 (1AL/1RS & 2BS/2RL), as well as NIL carrying 2RL and Hamlet, but not in Coker 797 (non-2RL), “Keumgangmil” (non-translocation wheat), KS92WGRC17 (PI592729 /;/ 6BS/6BL-6RL), KS92WGRC19 (P1592731 /;/ 4BS/4BL-6RL), “TAM200” (1AL/1RS), and “Siouxland” (1BL/1RS). Our data suggest that primer set SJ07 amplifies a “2RL-specific” fragment of diagnostic value.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett, B.A. & K.K. Kidwell, 1998. AFLP-based genetic diversity assessment among wheatcultivars from the Pacific Northwest. Crop Sci 38: 1261–1271.
Barrett, B.A., K.K. Kidwell & P.N. Fox,1998. Comparison of AFLP and pedigree-based genetic diversity assessment methods using wheat cultivars from Pacific Northwest. Crop Sci 38: 1271–1278.
Burkhamer, R.L., S.P. Lanning, R.J. Martens, J.M. Martin & L.E. Talbert, 1998. Predicting progeny variance from parental divergence in hard red spring wheat. Crop Sci 38: 243–248.
Brunell, M.S., A.J. Lukaszewski & R. hitkus, 1999. Development of arm specific RAPD markers forrye chromosome 2R in wheat. Crop Sci 39: 1702–1706.
Cho, YG., M.W. Blair, O. Panaud & S.R. McCouch,1996. Cloning and mapping of variety-specific rice genomic DNA sequences: amplified fragment length polymorphisms (AFLP) from silverstained polyacrylamide gels. Genome 39: 373–378.
Friebe, B., J.H. Hatchett, R.G. Sears & B.S. Gill, 1990. Transfer of Hessian fly resistance from ‘Chaupon’ rye to hexaploid wheat via a 2BS/2RL wheat-rye chromosome translocation. Theor Appl Genet 79: 385–389.
Graybosch, R.A., Y.W. Seo & C.J. Peterson,1993. Detection of wheat-rye chromosomal translocation using an antisecalin monoclonal antibody. Cereal Chem 70: 458–463.
Guidet, F., P. Rogowsky, C. Taylor, W. Song & P. Langridge, 1992. Cloning andcharacterization of a new rye-specific repeated sequence. Genome 34: 81–87.
Haley, S.D., L.K. Afanador, P.N. Miklas, J.P. Stavely & J.D. Kelly, 1994. Identification of RAPD markers linked to a major rust resistance gene block in common bean. Theor Appl Genet 83: 505–512.
Hartl, L., H. Weiss, U. Stephan, F.J. Zeller & A. Jahoor,1995. Molecular identification of powdery mildew resistance genes in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 90: 601–606.
Hatchett, J.H., R.G. Sears & T.S. Cox, 1993. Inheritance of resistance to Hessian flyin rye and in wheat-rye translocation lines. Crop Sci 33: 730–734.
Iqbal, M.J. & A.L. Rayburn, 1995.Identification of the 1RS rye chromosomal segment in wheat by RAPD analysis. Theor Appl Genet 91: 1048–1053.
Jang, C.S., B.H. Hong & Y.W. Seo, 1999. Expressed sequence tags of the wheat-rye translocation line possessing2BS/2RL. Korean J Crop Sci 44: 302–307.
Kawchuk, L.M., J. Hachey & D.R. Lynch, 1998.Development of sequence characterized DNA markers links to a dominant verticillium wilt resistance gene in tomato. Genome 41: 91–95.
Knackstedt, M.A., R.G. Sears, D.E. Rogers & G.L. Lookhart, 1994. Effects of T2BS.2RLwheat-rye translocation on breadmaking quality in wheat. Crop Sci 34: 1066–1070.
Koebner, R.M.D., 1995.Generation of PCR-based markers for the detection of rye chromatin in wheat background. Theor Appl Genet 90: 740–745.
Koebner, R.M.D. & K.W. Shepherd, 1986. Controlled introgression to wheat of genes from ryechromosome arm 1RS by induction of allosyndesis. 1. Isolation of recombinants. Theor Appl Genet 73: 197–208.
Lee, J.H., R.A. Graybosch, S.M. Kaeppler & R.G. Sears, 1996. A PCR assay for detection of a 2RL.2BS wheat-ryechromosome translocation. Genome 39: 605–608.
Michelmore, R.W., I. Paran & R.V. Kesseli, 1991.Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis; A rapid method to detect markers in specific genome regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 9828–9832.
Melotto, M.,L. Afandor & J.D. Kelly, 1996. Development of a SCAR marker linked to the I gene in common bean. Genome 39: 1216–1219.
Moonen, J.H.E. & A.C. Zeven, 1984. SDS-PAGE of the highmolecular-weight subunits ofwheat glutenin and the characterization of 1R(1B) substitution and 1BL/1RS translocation lines. Euphytica 33: 3–8.
Murphy, G.J.P., H. Lucas, G. Moore & R.B. Flavell, 1992. Sequence analysis of WIS–2–1A, a retrotransposon-likeelement from wheat. Plant Mol Biol 20: 991–995.
Powell, W., M. Morgante, C. Andre, M. Hanafey, J. Vogel, S. Tingey & A. Rafalski, 1996. The utility of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP, and SSRP (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis. Mol Breed 2: 225–238.
Qu, L.-J., T.N. Foote, M.A. Roberts, T.A. Money, L. Aragon-Alcaide, J.W. Snape & G. Moore, 1998. A simple PCR-based method for scoring the ph1b deletion in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 96: 371–375.
Rogowsky, P.M., J.-Y Liu, S. Manning, C. Taylor & P. Langridge, 1992a.Structure heterogeneity in the R173 family of rye-specific repetitive. Plant Mol Biol 20: 95–102.
Rogowsky, P.M., K. W. Shepherd & P. Langridge, 1992b. Polymerase chain reaction based of rye involving repeatedDNA sequences. Genome 35: 621–626.
Russell, J.R., D.J. Fuller, M. Macaulay, B.G. Hatz, A. Jahoor, W. Powell & R. Waugh, 1997. Direct comparison of levels of genetic variation among barley accessions detected by RFLPs, AFLPs, SSRs, and RAPDs. Theor Appl Genet 95: 714–722.
Sears, R.G.,J.H. Hatchett, T.S. Cox & B.S. Gill, 1992. Registration of Hamlet, a Hessian fly resistant hard red winter wheat germplasm. Crop Sci 32: 506.
Seo, Y.W., J.W. Johnson & R.L. Janet, 1997. A molecular marker associated with the H21 Hessian flyresistance gene in wheat. Mol Breed 3: 177–181.
Seo, Y.W., R.A. Graybosoch, C.J. Peterson & D.R. Shelton, 1995. Assessment of Enzyme-linked Immuno assay of rye secalins as a tool in the prediction of 1RS wheat quality. Cereal Chem 72: 252–254.
Shan, X., T.K. Blake & L.E. Talbert, 1999. Conversion of AFLPmarkers to sequence-specific PCR markers in barley and wheat. Theor Appl Genet 98: 1072–1078.
Singh, N.K. & K.W. Shepherd, 1984. Mapping of the genes controlling the high-molecular-weight glutenin subunits of rye on the long arm of chromosome 1R. Genet Res 44: 117–123.
Vos, P., R. Hogers, M. Bleeker, M. Reijans. T. van de Lee, M. Hornes, A. Frijters, J. Pot, J. Peleman, M. Kuiper & M. Zabeau, 1995. AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23: 4407–4414.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, Y.W., Jang, C.S. & Johnson, J.W. Development of AFLP and STS markers for identifying wheat-rye translocations possessing 2RL. Euphytica 121, 279–287 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012020532485
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012020532485