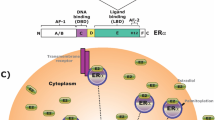
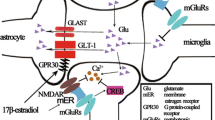
Abstract
For many molecules, which have been found first in a certain tissue and with a certain activity in the body, multiple activities have been discovered decades later. The steroidal compound estrogen (estradiol) is certainly such a molecule. What was first described as the female sex hormone is now well acknowledged as a central neuroactive and neuromodulatory molecule. One important aspect of estrogen's effects on neurons is its neuroprotective activity. Cellular and molecular studies underline powerful neuroprotective functions of estrogen which are characterized by long-term “classical” genomic effects as well as by rapid activities depending on estrogens interaction with neuronal membranes and intracellular signal transduction pathways. In addition, estrogen has been shown to bear an intrinsic antioxidant structure that lies in the phenolic moiety of the steroidal compound. This antioxidant activity of estrogen and estrogen-derivatives may provide an antioxidant “chemical shield” for neurons and may complement other neuroprotective activities of estrogen and therefore also mediate some of the beneficial effects of estrogen replacement with respect to Alzheimer's Disease. Although, investigated for decades estrogen and its receptors may still hold many surprises that remain to be identified. With the advent of novel genomic techniques, the neuronal target genes of estrogen will be identified in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AZCOITIA, I., SIERRA, A. & GARCIA-SEGURA, L. M. (1999) Neuroprotective effects of estradiol in the adult rat hippocampus: Interaction with insulin-like growth factor-I signalling. Journal of Neuroscience Research 58, 815–822.
BAULIEU, E. E. & KELLY, P. A. (1990) Hormones. From molecules to disease. New York and London: Chapman and Hall, Herman Publishers in Arts and Science.
BEDARD, P. J., LANGLELIER, P. & VILENEUVE, A. (1977) Estrogens and the extrapyramidal system. Lancet 2, 1367–1368.
BEHL, C. (1999) Alzheimer?s disease and oxidative stress: Implications for novel therapeutic approaches. Progress in Neurobiology 57, 301–323.
BEHL, C., WIDMANN, M., TRAPP, T. & HOLSBOER, F. (1995) 17-Beta estradiol protects neurons from oxidative stress-induced cell death in vitro. Biochemical Biophysical Research Communications 216, 473–482.
BEHL, C. et al. (1997) Neuroprotection against oxidative stress by estrogens-structure-activity relationship. Molecular Pharmacology 51, 535–541.
BICKNELL, R. J. (1998) Sex-steroid actions on neurotransmission. Current Opinion in Neurology 11, 667–671.
BODINE, P. V. N., HARRIS, H. A. & KOMM, B. S. (1999) Suppression of ligand-dependent estrogen receptor activity by bone-resorbing cytokines in human osteoblasts. Endocrinology 140, 2439–2451.
FILLIT, H. (1994) Estrogens in the pathogenesis and treatment of Alzheimer?s disease in postmenopausal women. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 743, 233–238, (Discussion, pp. 238–239).
GALIEN, R. & GARCIA, T. (1997) Estrogen receptor impairs interleukin-6 expression by preventing protein binding on the Nf-Kappa-B site. Nucleic Acids Research 25, 2424–2429.
GIBBS, R. B. & AGGARWAL, P. (1998) Estrogen and basal forebrain cholinergic neurons: Implications for brain againg and Alzheimer?s Disease-related cognitive decline. Hormones and Behaviour 34, 98–111.
GREEN, P. S., BISHOP, J. & SIMPKINS, J. W. (1997) 17-Alpha-estradiol exerts neuroprotective effects on sk-n-sh cells. Journal of Neuroscience 17, 511–515.
GU, Q., KORACH, K. S. & MOSS, R. L. (1999) Rapid action of 17 beta-estradiol on kainate-induced currents in hippocampal neurons lacking intracellular estrogen receptors. Endocrinology 140, 660–666.
GUSTAFSSON, J. A. (1999) Estrogen receptor ?: A new dimension in estrogen mechanism of action. Journal of Endocrinology 163, 379–383.
HAMPSON, E. (1990) Estrogen-regulated variations in human spatial and articulatory-motor skills. Psychoneuroendocrinology 15, 97–111.
HARDY, J. (1997) Amyloid, the presenilins and alzheimer?s disease. Trends in Neuroscience 20, 154–159.
HECK, S., LEZOUALC'H, F., ENGERT, S. & BEHL, C. (1999) Insulin-like growth factor-1-mediated neuroprotection against oxidative stress is associated with activation of nuclear factor kappaB. Journal of Biological Chemistry 274, 9828–9835.
HENDERSON, V. W. (1997) Estrogen replacement therapy for the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer?s disease. CNS Drugs 8, 343–351.
HOSODA, T., KARIYA, K., KIKUCHI, N., URABE, M. & HONJO, H. (1999) Does estrogen suppress apoptosis in Alzheimer?s disease: Protective effect from the neurodegeneration induced by amyloid beta protein in vitro. In 9th International Menopause Society World Congress on the Menopause.? 13–17.
IMPROTA-BREARS, T., WHORTON, A. R., CODAZZI, F., YORK, J. D., MEYER, T. & MCDONNELL, D. P. (1999) Estrogen-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase requires mobilization of intracellular calcium. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 96, 4686–4691.
KELLY, M. J., LAGRANGE, A. H., WAGNER, E. J. & RONNEKLEIV, O. K. (1999) Rapid effects of estrogen to modulate G protein-coupled receptors via activation of protein kinase A and protein kinase C pathways. Steroids 64, 64–75.
KIMURA, D. (1992) Sex differences in the brain. Scientific American 267, 119–125.
KUIPER, G. G. J. M., SHUGRUE, P. J., PELTKOHUIKKO, M., MERCHENTHALER, I. & GUSTAFSSON, J.-A. (1998) The estrogen receptro ? subtype: A novel mediator of estrogen action in neuroendocrine systems. Frontiers in Neuroe docrinology 19, 253–286.
LEVIN, E. R. (1999) Cellular functions of the plasma membrane estrogen receptor. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism 10, 374–377.
LEZOUALCH, F., SAGARA, Y., HOLSBOER, F. & BEHL, C. (1998) High constitutive nf-kappa-b activity mediates resistance to oxidative stress in neuronal cells. Journal of Neuroscience 18, 3224–3232.
MARKESBERY, W. R. & CARNEY, J. M. (1999) Oxidative alterations in Alzheimer?s disease. Brain Pathology 9, 133–146.
MCEWEN, B. S. & ALVES, S. E. (1999) Estrogen actions in the central nervous system. Endocrine Reviews 20, 279–307.
MENDELSOHN, M. E. & KARAS, R. H. (1999). The protective effects of estrogen on the cardiovascular system. New England Journal of Medicine 340, 1801–1811.
MOOSMANN, B. & BEHL, C. (1999) The antioxidant neuroprotective effects of estrogens and phenolic compounds are independentfromtheir estrogenic properties. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 96, 8867–8872.
MUDD, L. M., TORRES, J., LOPEZ, T. F. & MONTAGUE, J. (1998) Effects of growth factors and estrogen on the development of septal cholinergic neurons from the rat. Brain Research Bulletin 45, 137–142.
OKAMOTO, T., SCHLEGEL, A., SCHERER, P. E. & LISANTI, M. P. (1998) Caveolins, a family of scaffolding proteins for organizing preassembled signaling complexes at the plasma membrane. Journal of Biological Chemistry 273, 5419–5422.
PAGANINI-HILL, A. & HENDERSON, V. W. (1994) Estrogen deficiency and risk of Alzheimer?s disease in women. American Journal of Epidemiology 140, 256–261.
RAMIREZ, V. D. & ZHENG, J. (1996) Membranesex-steroid receptors in the brain. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology 17, 402–439.
RAZANDI, M., PEDRAM, A., GREENE, G. L. & LEVIN, E. R. (1999) Cell membrane and nuclear estrogen receptors (ERs) originate froma single transcript: Studies of ER alpha and ER beta expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Molecular Endocrinology 13, 307–319.
RUPPRECHT, R. & HOLSBOER, F. (1999) Neuroactive steroids: Mechanisms of action and neuropsychopharmacological perspectives. Trends in Neurosciences 22, 410–416.
SANO, M., ERNESTO, C., THOMAS, R. G., KLAUBER, M. R., SCHAFER, K., GRUNDMAN, M., WOODBURY, P., GROWDON, J., COTMAN, D. W., PFEIFFER, E., SCHNEIDER, L. S. & THAL, L. J. (1997) A controlled trial of selegiline, alpha-tocopherol, or both as treatment for Alzheimer?s Disease. New England Journal of Medicine 336, 1216–1222.
SAWADA, H., IBI, M., KIHARA, T., URUSHITANI, M., AKAIKE, A. & SHIMOHAMA, S. (1998) Estradiol protects mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons from oxidative stress-induced neuronal death. Journal of Neuroscience Research 54, 707–719.
SCHLEGEL, A., WANG, C. G., KATZENELLENBOGEN, B. S., PESTELL, R. G. & LISANTI, M. P. (1999) Caveolin-1 potentiates estrogen receptor alpha (ER alpha) signaling-Caveolin-1 drives ligand-independent nuclear translocation and activation of ER alpha. Journal of Biological Chemistry 274, 33551–33556.
SCHNEIDER, L. S., FARLOW, M. R., HENDERSON, V. W. & POGODA, J. M. (1996) Effects of estrogen replacementtherapy on response to tacrine in patients with Alzheimer?s Disease. Neurology 46, 1580–1584.
SELKOE, D. J. (1999) Translating cell biology into therapeutic advances in Alzheimer?s disease. Nature 399 (6738 Suppl S), A23-A31.
SHERWIN, B. B. (1997) Estrogen effects on cognition in menopausal women. Neurology 48 (Suppl 7), S 21-S 26.
SHERWIN, B. B. (1998) Estrogen and cognitive functioning in women. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology & Medicine 217, 17–22.
SHERWIN, B. B. (1999) Can estrogen keep you smart? Evidence from clinical studies. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience 24, 315–321.
SHERWIN, B. B. (1994) Estrogenic effects on memory in women. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 743, 213–231.
SHERWIN, B. B. & TULANDI, T. (1996) ?Add-back? estrogen reverses cognitive deficits induced by gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist in women with leiomyomata uteri. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 81, 2545–2549.
SHUGHRUE, P. J., LANE, M. V. & MERCHENTHALER, I. (1997) Comparative distribution of estrogen receptoralpha and-beta mrna in the rat central nervous system. Journal of Comparative Neurology 388, 507–525.
SHUGHRUE, P. J., SCRIMO, P. J. & MERCHENTHALER, I. (1998) Evidence for the colocalization of estrogen receptor-beta mRNA and estrogen receptor-alpha immunoreactivity in neurons of the rat forebrain. Endocrinology 139, 5267–5270.
SIMPKINS, J. W., SINGH, M. & BISHOP, J. (1994) The potential role for estrogen replacement therapy in the treatment of the cognitive decline and neurodegeneration associated with Alzheimer?s disease. Neurobiology of Aging 15, 195–197.
SINGER, C. A., FIGUEROA-MASOT, X. A., BATCHELOR, R. H. & DORSA, D. M. (1999) The mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway mediates estrogen neuroprotection after glutamate toxicity in primary cortical neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 19, 2455–2463.
SINGH, M., MEYER, E. M., MILLARD, W. J. & SIMPKINS, J. W. (1994) Ovarian steroid deprivation results in a reversible learning impairment and compromised cholinergic function in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Brain Research 644, 305–312.
SINGH, M., SEATLO, G., GUAN, X. P., WARREN, M. & TORAN-ALLERAND, C. D. (1999) Estrogen-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in cerebral cortical explants: Convergence of estrogen and neurotrophin signaling pathways. Journal of Neuroscience 19, 1179–1188.
STEIN, B. & YANG, M. X. (1995) Repression of the interleukin-6 promoter by estrogen receptor is mediated by nf-kappa-b and c/ebp-beta. Molecular & Cellular Biology 15, 4971–4979.
SUDO, S., WEN, T. C., DESAKI, J., MATSUDA, S., TANAKA, J., ARAI, T., MAEDA, N. & SAKANAKA, M. (1997) Beta-estradiol protects hippocampal CA1 neurons against transient forebrain ischemia in gerbil. Neuroscience Research 29, 345–354.
TANG, M. X., JACOBS, D., STERN, Y., MARDER, K., SCHOFIELD, P., GURLAND, B., ANDREWS, H. & MAYEUX, R. (1996) Effect of oestrogen during menopause on risk and age at onset of Alzheimer?s Disease. Lancet 348, 429–432.
TORAN-ALLERAND, C. D. (1996) The estrogen/neurotrophin connection during neural development-is colocalization of estrogen receptors with the neurotrophins and their receptors biologically relevant. Developmental Neuroscience 18, 36–48.
TORAN-ALLERAND, C. D., SINGH, M. & SETALO, G. (1999) Novel mechanisms of estrogen action in the brain: New players in an old story. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology 20, 97–121.
VALVERDE, M. A., ROJAS, P, AMIGO, J., COSMELLI, D., ORIO, P., BAHAMONDE, M. I., MANN, G. E., VERGARA, C. & LATORRE, R. (1999) Acute activation of Maxi-K channels (hSlo) by estradiol binding to the beta subunit. Science 285, 1929–1931.
VEDDER, H., ANTHES, N., STUMM, G., WURZ, C., BEHL, C. & KRIEG, J. C. (1999) Estrogen hormones reduce lipid peroxidation in cells andtissues of the central nervous system. Journal of Neurochemistry 72, 2531–2538.
WATSON, S. J. & AKIL, H. (1999) Gene chips and arrays revealed: Aprimer on their power and their uses. Biological Psychiatry 45, 533–543.
WATTERS, J. J. & DORSA, D. M. (1998) Transcriptional effects of estrogen on neuronal neurotensin gene expression involve camp/protein kinase a-dependent signaling mechanisms. Journal of Neuroscience 18, 6672–6680.
WEIGEL, N. L. (1996) Steroid hormone receptors and their regulation by phosphorylation. Biochemical Journal 319, 657–667.
WETZEL, C. H. R., HERMANN, B., BEHL, C., PESTEL, E., RAMMES, G., ZIEGLGANSBERGER, W., HOLSBOER, F. & RUPPRECHT, R. (1998) Functional antagonism of gonadal steroids at the 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 receptor. Molecular Endocrinology 12, 1441–1451.
WOOLLEY, C. S. (1999) Electrophysiological and cellular effects of estrogen on neuronal function. Critical Reviews in Neurobiology 13, 1–20.
XU, H. X., GOURAS, G. K., GREENFIELD, J. P., VINCENT, B., NASLUND, J., MAZZARELLI, L., FRIED, G., JOVANOVIC, J. N., SEEGER, M., RELKIN, N. R., LIAO, F., CHECLER, F., BUXBAUM, J. D., CHAIT, B. T., THINAKARAN, G., SISODIA, S. S., WANG, R., GREENGARD, P. & GANDY, S. (1998) Estrogen reduces neuronal generation of alzheimer beta-amyloid peptides. Nature Medicine 4, 447–451.
YAFFE, K., SAWAYA, G., LIEBERBURG, I. & GRADY, D. (1998) Estrogen therapy in postmenopausal women: Effects on cognitive function and dementia. Journal of the American Medical Association 279, 688–695.
ZAKON, H. H. (1998) The effects of steroid hormones on electrical activity of excitable cells. Trends in Neurosciences 21, 202–207.
ZHANG, Y. Q., SHI, J., RAJAKUMAR, G., DAY, A. L. & SIMPKINS, J. W. (1998) Effects of gender and estradiol treatment on focal brain ischemia. Brain Research 784, 321–324.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behl, C., Manthey, D. Neuroprotective activities of estrogen: An update. J Neurocytol 29, 351–358 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007109222673
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007109222673