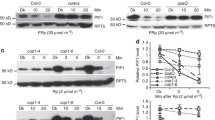
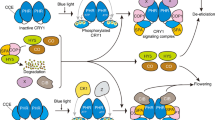
Abstract
Arabidopsis seedling development follows contrasting patterns depending on ambient light conditions, photomorphogenesis in the light and skotomorphogenesis or etiolation in darkness. COP1 is a limiting or regulatory component in mediating repression of photomorphogenesis in the absence of light. COP1 acts within the nucleus in the dark, directly interacts and regulates specific transcription factors that are required for promoting photomorphogenesis. Light abrogates COP1 action and results in progressive nuclear depletion of COP1 with increasing light stimuli. COP1 contains multiple structural modules, which are responsible for interacting with distinct cellular factors and play specific functional roles. We review the most recent progress in understanding the COP1 action and propose specific models based on the recent studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang, L.H. and Deng, X.W. 1994. Regulatory hierarchy of photomorphogenic loci: allele-specific and light-dependent interaction between the HY5 and COP1 loci. Plant Cell 6(5): 613–628.
Ang, L.H., Chattopadhyay, S., Wei, N., Oyama, T., Okada, K., Batschauer, A. and Deng, X.W. 1998. Molecular interaction between COP1 and HY5 defines a regulatory switch for light control of Arabidopsis development. Mol. Cell 1: 213–222.
Chamovitz, D.A., Wei, N., Osterlund, M.T., von Arnim, A., Staub, J.M., Matsui, M. and Deng, X.W. 1996. The COP9 complex, a novel multisubunit nuclear regulator involved in light control of a plant developmental switch. Cell 86: 115–121.
Chory, J.1997Light modulation of vegetative development.Plant Cell9:1225–1234
Chory, J., Peto, C.A., Feinbaum, R., Pratt, L. and Ausubel, F. 1989. Arabidopsis thaliana mutant that develops as a light-grown plant in the absence of light.Cell58: 991–999.
Deng, X.-W., Caspar, T. and Quail, P.H.1991.cop1: a regulatory locus involved in light-controlled development and gene expression in Arabidopsis.Genes Dev.5:1172–1182
Deng, X.W., Matsui, M., Wei, N., Wagner, D., Chu, A.M., Feldmann, K.A. and Quail, P.H. 1992. COP1, an Arabidopsis regulatory gene, encodes a protein with both a zinc-binding motif and a G beta homologous domain.Cell71(5):791–801.
Kendrick, R.E. and Kronenberg, G.H.M (Eds). 1994. Photomorphogenesis in Plants, 2nd ed., Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands.
Kwok, S.F., Solano, R., Tsuge, T., Chamovitz, D.A., Ecker, J.R., Matsui, M. and Deng, X.W. 1998. Arabidopsis homologs of a c-Jun coactivator are present both in monomeric form and in the COP9 complex, and their abundance is differentially affected by the pleiotropic cop/det/fus mutations. Plant Cell 10(11): 1779–1790.
Maniatis, T. 1999. A ubiquitin ligase complex essential for the NF-kappaB, Wnt/Wingless, and Hedgehog signaling pathways.Genes Dev. 13: 505–510.
McNellis, T.W. and Deng, X.W. 1995. Light control of seedling morphogenetic pattern. Plant Cell 7: 1749–1761.
McNellis, T.W., von Arnim, A.G. and Deng, X.W. 1994a. Evidence for Arabidopsis COP1 as an autonomous light-inactivatable repressor of photomorphogenic develoment. Plant Cell 6: 1391–1400.
McNellis, T.W., von Arnim, A.G., Araki, T., Komeda, Y., Misera, S. and Deng, X.-W. 1994b. Genetic and molecular analysis of an allelic series of cop1 mutants suggests functional roles for the multiple protein domains. Plant Cell 6: 487–500.
McNellis, T.W., Torii, K. and Deng, X.W. 1996. Expression of an N terminal fragment of COP1 confers dominant-negative suppression of seedling photomorphogenic development in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 8: 1491–1503.
Matsui, M., Stoop, C.D., von Arnim, A., Wei, N. and Deng, X.W.
1995. Arabidopsis COP1 protein specifically interacts in vitro with a cytoskeleton-associated protein, CIP1. Proc. Natl. Acad.Sci. USA 92: 4239–4243.
Osterlund, M.T., Ang, L.H. and Deng, X.W. 1999. The molecular and cellular basis of COP1 as a repressor of photomorphogenic development in Arabidopsis. Trends Cell Biol. 9: 113–118.
Peters, J.M. 1998. SCF and APC: the Yin and Yang of cell cycle regulated proteolysis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 10: 759–768.
Seeger, M., Kraft, R., Ferrell, K., Bech, O.D., Dumdey, R., Schade, R., Gordon, C., Naumann, M. and Dubiel, W. 1998. A novel protein complex involved in signal transduction possessing similarities to 26S proteasome subunits. FASEB J. 12: 469–478.
Serino, G., Tsuge, T., Kwok, S.F., Matsui, M., Wei, W. and Deng, X.W. 1999. Arabidopsis cop8 and fus4 mutations define the same locus that encodes subunit 4 of the COP9 signalosome. Plant Cell, in press.
Skowyra, D., Koepp, D.M., Kamura, T., Conrad, M.N., Conaway, R.C., Conaway, J.W., Elledge, S.J. and Harper, J.W. 1999. Reconstitution of G1 cyclin ubiquitination with complexes containing SCFGrr1 and Rbx1 [see comments]. Science 284: 662–665.
Stacey, M.G., Hicks, S.N. and von Arnim, A. 1999. Discrete domains mediate the light-responsive nuclear and cytoplasmic localization of Arabidopsis COP1. Plant Cell 11: 349–364.
Stacey, M.G. and von Arnim, A. 1999. A novel motif mediates the targeting of the Arabidopsis COP1 protein to subnuclear foci. J.Biol. Chem., in press.
Torii, K.U., McNellis, T.W. and Deng, X.W. 1998. Functional dissection of Arabidopsis COP1 reveals specific roles of its three structural modules in light control of seedling development.EMBO J. 17: 5577–5587.
Torii, K.U., Stoop-Myer, C.D., Okamoto, H., Coleman, J.E., Matsui, M. and Deng, X.W. 1999. The RING-finger motif of photomorphogenic repressor COP1 specifically interacts with the RING-H2 motif of a novel Arabidopsis protein. J. Biol. Chem.274: 27674–27681.
von Arnim, A. and Deng, X.W. 1994. Light inactivation of Arabidopsis photomorphogenic repressor COP1 involves a cellspecific regulation of its nucleocytoplasmic partitioning. Cell 79: 1035–1045.
von Arnim, A. and Deng, X.W. 1996. A role for transcriptional repression during light control of plant development. Bioessays 18(11): 905–910.
von Arnim, A.G., Mark T. Osterlund, Kwok, S.F. and Deng, X.W. 1997. Genetic and developmental control of nuclear accumulation of COP1, a repressor of photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 114: 779–788.
Wang, H., Kang, D.M., Deng, X.W. and Wei, N. 1999. Evidence for functional conservation of a mammalian homologue of the light-responsive plant protein COP1. Curr. Biol. 9: 711–714.
Wei, N. and Deng, X.W. 1996. The role of the COP/DET/FUS genes in light control of arabidopsis seedling development. Plant Physiol. 112(3): 871–878.
Wei, N. and Deng, X.W. 1999. Making sense of the COP9 signalosome. A regulatory protein complex conserved from Arabidopsis to human. Trends Genet. 15: 98–103.
Wei, N., Tsuge, T., Serino, G., Dohmae, N., Takio, K., Matsui, M. and Deng, X.W. 1998. The COP9 complex is conserved between plants and mammals and is related to the 26S proteasome regulatory complex. Curr. Biol. 8(16): 919–922.
Yamamoto, Y.Y., Matsui, M., Ang, L.H. and Deng, X.W. 1998. Role of a COP1 interactive protein in mediating light-regulated gene expression in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10: 1083–1094.
Zachariae, W., Shevchenko, A., Andrews, P.D., Ciosk, R., Galova, M., Stark, M.J., Mann, M. and Nasmyth, K. 1998. Mass spectrometric analysis of the anaphase-promoting complex from yeast: identification of a subunit related to cullins. Science 279: 1216–1219.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holm, M., Deng, X.W. Structural organization and interactions of COP1, a light-regulated developmental switch. Plant Mol Biol 41, 151–158 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006324115086
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006324115086