Abstract
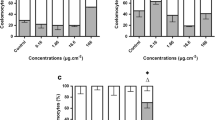
The toxic effects of nickel on survival, growth, and reproduction of Eisenia veneta were investigated following 4 weeks of exposure to a nickel-chloride spiked loamy sand soil. The ability of a simple earthworm biomarker, the lysosomal membrane stability of coelomocytes, to reflect nickel exposure was also studied. Nickel caused a significant toxic effect on E.veneta at soil concentrations above 85 mg Ni/kg. Reproduction (cocoon production) was the most sensitive parameter being reduced at soil concentrations above 85 mg Ni/kg (EC10 = 85 mg Ni/kg). Survival of adults was only reduced at concentrations above 245 mg Ni/kg, while adult and cocoon wet weight were not affected by soil nickel concentrations up to 700 mg Ni/kg. The lysosomal membrane stability, measured as neutral-red retention time, was reduced at soil nickel concentrations similar to those that reduced reproduction, and demonstrated a dose-response relationship. The neutral-red retention time showed large individual variation for the earthworms within each exposure concentration. It was concluded that the lysosomal membrane stability, measured as neutral red retention time, has a potential role in risk assessment, but care should be taken conducting this test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bengtsson, G. and Tranvik, L. (1989) Critical metal concentrations for forest soil invertebrates. Water Air Soil Pollut. 47, 381–417.
Forbes, T.L. and Forbes, V.L. (1993) A critique of the use of distribution-based extrapolation models in ecotoxicology. Funct. Ecol. 7, 249–254.
Furst, A., Chien Y. and Chien P.K. (1993) Worms as a substitute for rodents in toxicology: acute toxicity of three nickel compounds. Toxicol. Meth. 3, 19–23.
Harreus, D., Köhler, H.-R. and Weeks, J.M. (1997) Combined noninvasive cell isolation and neutral-red retention assay for measuring the effect of copper on the lumbricid Aporrectodea rosea (Savigny). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 59, 44–49.
Hartenstein, R., Neuhauser, E.F. and Narahara, A. (1981) Effects of heavy metal and other elemental additives to activated sludge on growth of Eisenia foetida. J. Environ. Qual. 10, 372–376.
Hoekstra, J. A. and van Ewijk, P.H. (1993) Alternatives for the No-Observed-Effect level. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12, 187–194.
Hopkin, S.P. (1993) Ecological implication of '95% protection levels' for metals in soil. Oikos 66, 137–141.
Ma W.C. (1983) Biomonitoring of soil pollution: ecotoxicological studies of the effect of soil-borne heavy metals on lumbricid earthworms. In Annual Report 1982, pp. 83–97. Research Institute for Nature Management, The Netherlands.
Malecki, M.R., Neuhauser, E.F. and Loehr, R.C. (1982) The effect of metals on the growth and reproduction of Eisenia foetida (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae). Pedobiologia 24, 129–137.
Moore, M.N. (1990) Lysosomal reaction to environmental stress and pollution. In Estarine Ecotoxicology, P.L. Chambers and C.M. Chambers, eds, pp. 81–87, JAPAGA, UK.
Morgan, A.J., Morgan, J.E., Turner, M., Winters, C. and Yarwood, A. (1993) Metal relationships of earthworms. In Ecotoxicology of Metals in Invertebrates. R. Dallinger and P.S. Rainbow, eds, pp. 333–358, Chelsea, UK: Lewis Publishers.
Neuhauser, E.F., Malecki, M.R. and Loehr, R.C. (1983) Methods using earthworms for the evaluation of potentially toxic materials in soils. In Proceedings of the Second Symposium on Hazardous and Industrial Solid Waste Testing. ASTM STP, R.A. Conway, ed. pp. 313–203, Gulledge WP, USA.
Neuhauser, E.F., Malecki, M.R. and Loehr, R.C. (1984) Growth and reproduction of the earthworm Eisenia fetida after exposure to sublethal concentrations of metals. Pedobiologia 27, 89–97.
Neuhauser, E.F., Loehr, R.C., Milligan, D.L. and Malecki, M.R. (1985) Toxicity of metals to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Biol. Fert. Soil. 1, 149–152.
Neuhauser, E.F., Loehr, R.C. and Malecki, M.R. (1986) Contact and artificial soil tests using earthworms to evaluate the impact of waste in soil. In Proceedings of the Fourth Symposium on Hazardous and Industrial Solid Waste Testing, ASTM STP. 886, J.K. Petros, W.J., Lacy, and R.A. Conway, eds. pp. 192–203, Gulledge WP, USA.
Nordberg-King, T.J. (1993) A Linear Interpolation Method for Sublethal Toxicity: The inhibition concentration (Icp) Approach (Version 2.0). and Dunnett Program (Version 1.5), NETAC Technical Report 03–93, Duluth, MN: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Pedersen, M.B. and Bjerre, A. (1991) The relationship between mass of newly hatched individuals and cocoon mass in lumbricid earthworms. Pedobiologia 35, 35–39.
Rozen, A. (1996) Do earthworms (Dendrobaena octaedra) originating from polluted forests vary in body mass and cocoon production? In Proceedings of the International Colloquium on Soil Zoology, J.P. Curry, T. Bolger, B. Kaye and Purvis G., eds. p. 262.
Scott-Fordsmand, J.J. (1997) Toxicity of nickel to soil organisms in Denmark. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 148, 1–34.
Scott-Fordsmand, J.J., Krogh, P.H., and Weeks, J.M. (1997) Sublethal toxicity of copper to a soil-dwelling springtail, Folsomia fimetaria (Collembola: Isotomidae). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 16, 2538–2542.
Spurgeon, D.J., Hopkin, S.P. and Jones, D.T. (1994) Effects of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc on growth, reproduction and survival of the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny): Assessing the environmental impact of point-source metal contamination in terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 84, 123–130.
Spurgeon, D.J. and Hopkin, S.P. (1995) Extrapolation of the laboratory based OECD earthworm test to metal-contaminated field sites. Ecotoxicology 4, 190–205.
Spurgeon, D.J. and Hopkin, S.P. (1996a) Effect of variation in organic matter content and pH of soil on the availability and toxicity of zinc to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Pedobiologia 40, 80–96.
Spurgeon, D.J. and Hopkin, S.P. (1996b) Effects of metal-contaminated soils on the growth, sexual development, and early cocoon production of the earthworm Eisenia fetida, with particular reference to zinc. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 35, 86–95.
Svendsen, C. and Weeks, J.M. (1997a) Relevance and applicability of a simple earthworm biomarker of copper exposure. I: Links to ecological effects in a laboratory study with Eisenia andrei. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 36, 72–79.
Svendsen, C. and Weeks, J.M. (1997b) Relevance and applicability of a simple earthworm biomarker of copper exposure. II: Validation and applicability under field conditions in a mesocosm experiment with Lumbricus rubellus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 36, 72–79.
Svendsen, C., Meharg, A.A., Freestone, P. and Weeks, J.M. (1996) Use of an earthworm lysosomal biomarker for the ecological assessment of pollution from an industrial plastics fire. Appl. Soil Ecol. 3, 99–107.
Van Gestel, C.A.M., van Dis, W.A., Van Breemen, E.M. and Sparenburg, P.M. (1989) Development of a standardized reproduction toxicity test with the earthworm species Eisenia fetida using copper, pentachlorophenol and 2,4-dichloroaniline. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 18, 305–312.
Van Gestel, C.A.M., van Dis, W.A., Dirren-Van Breemen, E.M., Sparenburg, P.M. and Baerselman, R. (1991) Influence of cadmium, copper and pentachlorophenol on growth and sexual development of Eisenia andrei (Oligochaeta: Annelida). Biol. Fert. Soils 12, 117–121.
Van Gestel, C.A.M., van Dis, W.A., Dirren-Van Breemen, E.M. and Baerselman, R. (1993) Accumulation and elimination of cadmium, copper, chromium and zinc and effects on growth and reproduction in Eisenia andrei (Oligochaeta: Annelida). Sci. Tot. Environ. Suppl., (Part 1), 585–597.
Weeks, J.M. and Svendsen, C. (1996) Neutral-red retention by lysosomes from earthworm (Lumbricus rubellus) coelomocytes: A simple biomarker for exposure of soil invertebrates. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15, 1801–1805.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scott-Fordsmand, J.J., Weeks, J.M. & Hopkin, S.P. Toxicity of Nickel to the Earthworm and the Applicability of the Neutral Red Retention Assay. Ecotoxicology 7, 291–295 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008824531114
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008824531114