Abstract
1. Inorganic tin and organotin compounds, occurring in aquatic ecosystems, are toxic and can cause behavioral abnormalities in living organisms. To determine the possible neuronal basis of these actions, the effects of both forms of Sn were studied on identified neurones of the mollusk, Lymnaea stagnalis L.
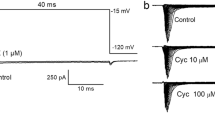
2. SnCl2 caused a dose-dependent decrease in the acetylcholine (Ach)-induced inward current. The effective threshold concentration, measured by a two microelectrode voltage clamp technique, was 0.1 μM, and the maximal effect occurred at 5 μM SnCl2. The depression of the inward current was greater after a 10 min preapplication (20%) than after 3 min treatment (7%).
3. The next series of experiments compared the actions of inorganic or organic tin compounds. In whole cell clamp experiments both (CH3)2SnCl2 and (CH3)3SnCl, like inorganic Sn, decreased the amplitude of Ach-induced current. Increasing the duration of the preapplication time resulted in an increase in the effect, but the action was not reversible. SnCl2 treatment caused a concentration-dependent alteration (initial potentiation followed by depression) of the amplitude of I Na(V) over the whole voltage range and slightly shifted the I–V curves to the left. In contrast, trimethyl tin decreased the amplitude of I Na(V) only at high concentration (100 μM). The activation time course of I Na was increased (τ = 0.43 ms in control and 0.55 ms in Sn), but Sn did not alter the inactivation parameters (τ = 3.43 and 3.41 ms).
4. These results support earlier findings that agonist- and voltage-activated channels are direct targets of toxic metals. We conclude that tin in both inorganic and organic forms acts at neuronal membranes to modulate synaptic transmission through direct actions on agonist-activated ion channels, and suggest that these actions may be the basis of the altered behavior of animals in tin-polluted environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Arakawa, O., Nakahiro, M., and Narahashi, T. (1991). Mercury modulation of GABA-activated chloride channels and non-specific cation channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. Brain. Res. 551:58–63.
Atchinson, W. D., and Narahashi T. (1984). Mechanism of action of lead on neuromuscular junction. Neurotoxicology 5:276–282.
Atchinson, W. D., Clark, A. W., and Narahashi, T. (1984). Presynaptic effects of methylmercury at the mammalian neuromuscular junction. In Narahashi, T. (ed.), Cellular and Molecular Toxicology, Raven Press, New York pp. 23–43.
Beaumont, A. R., and Budd, M. D. (1984). High mortality of the larvae of the common mussel at low concentrations of tributyltin. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 15:402–405.
Biondi, C., Fabbri, E., Ferretti, M. E., Sonetti, D., and Bolognani Fantin, A. M. (1989). Effects of lead exposure on cAMP and correlated enzymes in Viviparus ater (Mollusca, Gastropoda) nervous system. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 94C:327–333.
Bryan, G. W., and Gibbs, P. E. (1991). Impact of low concentrations of tributyltin (TBT) on marine organisms: A review. In Newman, M. C., and McIntosh, A. W. (eds.), Metal Ecotoxicology. Concepts and Application, Lewis Publishers, Chelsea, MI, pp. 323–361.
Bulten, E. J., and Meinema, H. A. (1991). Tin. In Merian, E. (ed.), Metals and Their Compounds in the Environment, VCH, Weinheim, FRG, pp. 1243–1259.
Büsselberg, D., Michael, D., and Platt B. (1994b). Pb2+ reduces voltage-and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-activated calcium channel currents. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 14:711–722.
Büsselberg, D., Pekel, M., Michael, D., and Platt, B. (1994a). Mercury (Hg2+) and zinc (Zn2+): Two divalent cations with different actions on voltage-activated calcium channel currents. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 14:675–687.
Büsselberg, D., Platt, B., Michael, D., and Carpenter, D. O. (1994c). Mammalian voltage-activated calcium channel currents are blocked by Pb2+, Zn2+ and Al3+. J. Neurophysiol. 71:1491–1497.
Carpenter, D. O. (1994). The public health significance of metal neurotoxicity. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 14:591–597.
Evans, M. L., Büsselberg, D., and Carpenter, D. O. (1991). Pb2+ blocks calcium currents of cultured dorsal root ganglion cells. Neurosci. Lett. 129:103–106.
Farkas, A., and Salánki, J. (2000). Effect of organic and inorganic micropollutants on the filtration ability of the freshwater mussel. Anodonta cygnaea L. Hidr. Közl. in press.
Forshaw, P. J. (1977). The inhibitory effect of cadmium on neuromuscular transmission in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 42:371–377.
Foucin, J. F., and Gruner, J. E. (1979). Tin neurotoxicity. In Vinken, P. J., and Bruyn, G. W. (eds.), Handbook of Clinical Neurology, North Holland, Amsterdam pp. 279–290.
Györi, J., Fejtl, M., Carpenter, D. O., and Salánki, J. (1994). Effect of HgCl2 on acetylcholine, carbachol and glutamate currents of Aplysia neurons. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 14:653–664.
Györi, J., Kiss, T., Shcherbatko, A. D., Belan, P. V., Tepikin, A. V., Osipenko, O. N., and Salánki, J. (1991). Effect of Ag+ on membrane permeability of perfused Helix pomatia neurones. J. Physiol. (London) 442:1–13.
Hattori, T., and Maehashi, H. (1989). Stannous chloride-induced increase in calcium entry into motor nerve terminals of the frog. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 166:527–530.
Hattori, T., and Maehashi, H. (1991). Activation of N-type calcium channels by stannous chloride at frog motor nerve terminals. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 74:125–128.
Johansen, K., and Mohlenberg, F. (1987). Impairment of egg production in Acartia tonsa exposed to tributyltin oxide. Ophelia 27:137–141.
Khakh, B. S., and Lester, H. A. (1999). Dynamic selectivity filters in ion channels. Neuron 23:653–658.
Kostenko, M. A., Geletyuk, V. I., and Veprintsev, B. N. (1974). Completely isolated neurons in the mollusc, Lymnaea stagnalis. A new objective for nerve cell biology investigation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 49A:89–100.
Matthiessen, P., and Thain, J. E. (1989). A method for studying the impact of polluted marine sediment on intertidal colonising organism; Tests with diesel-based drilling mud and tributyltin antifouling paint. Hydrobiologia 188/189:477–485.
Müller, T. H., Swandula, D., and Lux, H. D. (1989). Activation of three types of membrane currents by various divalent cations of identified molluscan pacemaker neurones. J. Gen. Physiol. 94:997–1014.
Miyamoto, M. D. (1983). Hg2+ causes neurotoxicity at an intracellular site following entry through Na and Ca channels. Brain Res. 267:375–379.
Narahashi, T., Ma, J. Y., Arakawa, O., Reuveny, E., and Nakahro, M. (1994). GABA receptor-channel complex as a target site of mercury, copper, zink and lanthanides. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 14:599–621.
Rainbow, P. S., and Dallinger, R. (1993). Metal uptake, regulation, and excretion in freshwater invertebrates. In: Dallinger, R., and Rainbow, P. S. (eds.), Ecotoxicology of Metals in Invertebrates, Lewis Publishers, Boca Rata, FL, pp. 120–131.
Rubakhin, S. S., Györi, J., Carpenter, D. O., Salánki, J. (1995). HgCl2 potentiates GABA activated currents in Lymnaea stagnalis L. neurones. Acta Biol. Hung. 46:431–444.
Salánki, J., Györi, J., and Carpenter, D. O. (1994). Action of lead on glutamate-activated chloride currents in Helix pomatia L. neurones. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 14:755–768.
Salánki, J., Györi, J., Platokhin, A., S.-Rózsa, K. (1998). Neurotoxicity of environmental pollutants: effects of tin (Sn2+) on Ach induced currents in snail neurones. Russ. J. Physiol. (Moscow) 84:1061–173.
Salánki, J., Osipenko, O. N., Kiss, T., and Györi, J. (1991). Effect of Cu2+ and Pb2+ on membrane excitability of snail neurones. In Kits, K. S., Boer, H. H., and Joosse, J. (eds.), Molluscan Neurobiology, North-Holland, Amsterdam-Oxford-New York, pp. 214–220.
Savolainen H., Valkonen, S. (1986). Dose-dependent brain tin concentration in rats given stannous chloride in drinking water. Toxicol. Lett. 30:35–39.
S-Rózsa, K., and Salánki, J. (1991). Ion channels of nerve membrane as targets for environmental pollutants. In Jeffrey, D., and Madden, B. (eds.), Bioindicators and Environmental Management, Academic Press, London, pp. 389–399.
Szücs A., Angiello, C., Salánki J., and Carpenter, D. O. (1997). Effects of inorganic mercury and methylmercury on the ionic currents of cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 17:273–288.
Weinreich, D., and Wonderlin, W. F. (1987). Copper activates a unique inward current in molluscan neurons. J. Physiol. (London) 394:429–443.
Winlow, W., and Benjamin, P. R. (1976). Neuronal mapping of the brain of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis (L.). In Salánki, J. (ed.), Neurobiology of Invertebrates, Akade´miai Kiadó, Budapest, pp. 41–59.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Györi, J., Platoshyn, O., Carpenter, D.O. et al. Effect of Inorganic and Organic Tin Compounds on ACh- and Voltage-Activated Na Currents. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20, 591–604 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007016012520
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007016012520