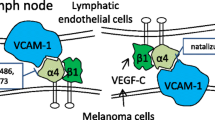
Abstract
There are fundamental issues regarding the role of integrins in human disease which remain to be elucidated. Human cutaneous melanoma is an attractive model for studying integrin involvement in tumor progression because it generally follows a sequential series of definable stages. Furthermore, the most specific marker for the transition of cells from the more benign, non-metastatic radial growth phase stage to the more malignant, metastatically competent vertical growth phase stage is associated with the onset of αvβ3 integrin expression and function. This same pattern, however, does not hold true for human ocular/uveal melanomas which do not progress through these stages, but preferentially metastasize to the liver by dissemination of the cells via a direct hematogenous pathway. It is also unclear whether the αvβ3 integrin is functionally involved in uveal melanoma metastasis or not. Our results show that perturbation of the αvβ3 integrin on moderately invasive A375M human cutaneous melanoma cells with either specific antibodies or ligands results in an increase in the cells' ability to invade in vitro coincident with an increase in the cells' expression and extracellular levels of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2, gelatinase A). The highly invasive C8161 human cutaneous melanoma cells express little-to-no αvβ3 integrin, but are more invasive and express higher levels of MMPs after perturbation of their α5β1 integrin. This augmented invasiveness could subsequently be abrogated with a function-blocking anti-MMP-2 antibody. Primary uveal melanoma cells and cells derived from uveal metastases appear to grow in either a spindle or epithelioid morphology. The less invasive uveal melanoma cells are spindle shaped and express higher levels of the αvβ3 integrin, while the more invasive cell lines are epithelioid shaped and express reduced levels of the αvβ3 integrin. The apparent conflict between these results and the current model for cutaneous melanoma progression may be addressed as follows: The expression and function of the αvβ3 integrin plays an important role(s) during the transition of cells from the radial growth phase stage to the vertical growth phase stage. However, further progression leading to metastases may require changes in the cells' integrins that would facilitate their ability to leave the primary tumor, and aid in their ability to invade and ultimately form metastases. It is also conceivable that the αvβ3 integrin is reexpressed during various stages of metastatic dissemination, and, in particular, during tumor reestablishment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hynes RO: Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 69: 11-25, 1992
Gille J, Swerlick RA: Integrins: role in cell adhesion and communication. Ann New York Acad Sci 797: 93-107, 1996
Ruoslahti E, Pierschbacher MD: New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science 238: 491-497, 1987
Loftus JC, Smith JW, Ginsberg MH: Integrin-mediated cell adhesion: the extracellular face. J Biol Chem 269: 25235-25238, 1994
Hynes RO: Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell 48: 459-552, 1987
Fornaro M, Languino LR: Alternatively spliced variants: a new view of the integrin cytoplasmic domain. Matrix Biology 16: 185-193, 1997
Humphries MJ: Integrin activation: the link between ligand binding and signal transduction. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8: 632-640, 1996
Gailit J, Ruoslahti E: Regulation of the fibronectin receptor affinity by divalent cations. J Biol Chem 263: 12927-12933. 1988
Kirchhofer D, Gailit J, Ruoslahti E, Grzesiak J, Pierschbacher MD: Cation-dependent changes in the binding specificity of the platelet receptor GPIIb/IIIa. J Biol Chem 265: 18525-18530, 1990
Schwartz MA, Schaller MD, Ginsberg MH: Integrins: emerging paradigms of signal transduction. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 11: 549-599, 1995
Kornberg LJ, Earp HS, Turner CE, Prockop C, Juliano RL: Signal transduction by integrins: increased protein tyrosine phosphorylation caused by clustering of β 1 integrins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 8392-8395, 1991
Guan JL, Shalloway D: Regulation of focal adhesion-associated protein tyrosine kinase by both cellular adhesion and oncogenic transformation. Nature 358: 690-692, 1992
Symington BE: Fibronectin receptor modulates cyclin dependent kinase activity. J Biol Chem 267: 25744-25747, 1993
Vuori K, Ruoslathi E: Activation of protein kinase C precedes α 5 β 1 integrin-mediated cell spreading on fibronectin. J Cell Biol 268: 21495-21462, 1993
Morino N, Mimura T, Hamasaki K, Tobe K, Ueki K, Kikuchi K, Takehara K, Kadowaki T, Yazaki Y, Nojima Y: Matrix/integrin interaction activates the mitogen-activated protein kinases, p44erk-1 and p42erk-2. J Biol Chem 270: 269-273, 1995
Schlaepfer DD, Hanks SK, Hunter T, Van der Geer P: Integrin mediated signal transduction linked to Ras pathway by Grb2 binding to focal adhesion kinase. Nature 372: 786-790, 1994
Chen Q, Kinch MS, Lin TH, Burridge K, Juliano RL: Integrin mediated cell adhesion activates mitogen activated protein kinases. J Biol Chem 269: 26602-26605, 1994
Chen H-C, Guan J-L: Association of focal adhesion kinase with its potential substrate phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 10148-10152, 1994
Guinebault C, Payrastre B, Racaud-Sultan C, Mazarguil H, Breton M, Maunco G, Plantavid M, Chap H: Integrindependent translocation of phosphinositide 3-kinase to the cytoskeleton of thrombin-activated platelets involves specific interaction of p85a with actin filaments and focal adhesion kinase. J Cell Biol 129: 831-842, 1995
Kapron-Bras C, Fitz-Gibbon L, Jeevaratnam P, Wilkins J, Dedhar S: Integrin clustering stimulates p21 ras activation. J Biol Chem 268: 20701-20704, 1993
Yebra M, Filardo E, Bayna E, Kawahara J, Cheresh D: Induction of carcinoma cell migration on vitronectin by NF-κB dependent gene expression. Mol Biol Cell 6: 841-850, 1995
Scatena M, Almeida M, Chaisson ML, Fausto N, Nicosia RF, Giachelli CM: NFκB mediates α v β 3 integrininduced endothelial cell survival. J Cell Biol 141: 1083-1093, 1998
Yamada KM, Miyamoto S: Integrin transmembrane signaling and cytoskeletal control. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7: 681-689, 1995
Parsons JT: Integrin-mediated signalling: regulation by protein tyrosine kinases and small GTP-binding proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8: 146-152, 1996
Lafrenie RM, Yamada KM: Integrins and matrix molecules in salivary gland cell adhesion, signaling, and gene expression. Ann New York Acad Sci 842: 42-48, 1998
Varner AJ, Cheresh DA: Integrins and cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8: 724-730, 1996
Giancotti FG: Integrin signaling: specificity and control of cell survival and cell cycle progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9: 691-700, 1997
Rosmarin AG, Luo M, Caprio DG, Shang J, Simkevich CP: Sp1 cooperates with the ets transcription factor, GABP, to activate the CD18 (beta2 leukocyte integrin) promotor. J Biol Chem 273: 13097-13103, 1998
Thomas GJ, Jones J, Speight PM: Integrins and oral cancer. Oral Oncology 33: 381-388, 1997
Ruoslahti E, Reed J: Anchorage independence, integrins and apoptosis. Cell 77: 477-478, 1994
Meredith JE Jr, Schwartz M: Integrins, adhesion and apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 7: 146-150, 1997
Frisch SM, Ruoslahti E: Integrins and anoikis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9: 701-706, 1997
Brooks PC, Montgomery MP, Rosenfeld M, Reisfeld RA, Hu T, Klier G, Cheresh DA: Integrin α v β 3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell 79: 1157-1164, 1994
Joseph-Silverstein J, Silverstein RL: Cell adhesion molecules: an overview. Cancer Invest 16: 176-182, 1998
Holzmann B, Gosslar U, Bittner M: alpha 4 integrins and tumor metastasis. Curr Topics Microbiol Immunol 231: 125-141, 1998
Nip J, Brodt P: The role of the integrin vitronectin receptor, alpha v beta 3 in melanoma metastasis. Cancer Metastas Rev 14: 241-252, 1995
Akiyama SK, Olden K, Yamada KM: Fibronectin and integrins in invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastas Rev 14: 173-189, 1995
Li X, Graner MW, Williams EL, Roote CE, Bunch TA, Zusman S: Requirements for the cytoplasmic domain of the alphaPS1, alphaPS2 and betaPS integrin subunits during Drosophila development. Development 125: 701-711, 1998
Van der Flier A, Gaspar AC, Thorsteinsdottir S., Baudoin C, Groeneveld E, Mummery CL, Sonnenberg A: Spacial and temporal expression of the beta1D integrin during mouse development. Developmental Dynamics 210: 472-486, 1997
Sueoka K, Shiokawa S, Miyazaki T, Kuji N, Tanaka M, Yoshimura Y: Integrins and reproductive physiology: expression and modulation in fertilization, embryogenesis, and implantation. Fertility Sterility 67: 799-811, 1997
Faull RJ, Ginsberg MH: Inside-out signaling through integrins. J Am Soc Nephrol 7: 1091-1097, 1996
Van Waes C: Cell adhesion and regulatory molecules involved in tumor formation, hemostasis, and wound healing. Head Neck 17: 140-147, 1995
Brooks PC, Clark RAF, Cheresh DA: Requirement of vascular integrin α v β 3 for angiogenesis. Science 264: 569-571, 1994
Sepp NT, Li L-J, Lee KH, Brown EJ, Caughman SWW, Lawley TJ, Swerlick RA: Basic fibroblast growth factor increases expression of the α v β 3 complex on human microvessel endothelial cells. J Invest Dermatol 103: 295-299, 1994
Enenstein J, Waleh NS, Kramer RH: Basic FGF and TGFβ differentially modulate integrin expression of human microvascular endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res 203: 499-503, 1992
Friedlander M, Brooks PC, Shaffer RW, Kincaid CM, Varner JA, Cheresh DA: Definition of two angiogenic pathways by distinct α v integrins. Science 27: 1500-1502, 1995
Brooks P, Stromblad S, Klemke R, Visscher D, Starkar F, Cheresh D: Antiintegrin α v β 3 blocks breast cancer growth and angiogenesis in human skin. J Clin Invest 96: 1815-1822, 1995
Drake CJ, Cheresh DA, Little CD: An antagonist of integrin α v β 3 prevents maturation of blood vessels during embryonic neovascularization. J Cell Sci 108: 2655-2661, 1995
Gavrilovskaya IN, Shepley M, Shaw R, Ginsberg MH, Mackow ER: Beta(3) integrins mediate the cellular entry of hantaviruses that cause respiratory failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 7074-7079, 1998
Coburn J, Magoun L, Bodary SC, Leong LM: Integrins alpha(v)beta(3) and apha(5)beta(1) mediate attachment of lyme disease spriochetes to human cells. Infection Immunity 66: 1946-1952, 1998
Blystone SD, Lindberg FP, Williams MP, McHugh KP, Brown EJ: Inducible tyrosine phosphorylation of the beta3 integrin requires the alpha v integrin cytoplasmic tail. J Biol Chem 271: 31458-31462, 1996
Wei Y, Lukashev M, Simon DI, Bodary SC, Rosenberg S., Doyle MV, Chapman HA: Regulation of integrin function by the urokinase receptor. Science 273: 1551-1555, 1996
Chapman HA: Plasminogen activators, integrins, and coordinated regulation of cell adhesion and migration. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9: 714-724, 1997
Schwartz MA: Integrins, oncogenes, and anchorage independence. J Cell Biol 139: 575-578, 1997
Bauer JS, Schreiner CL, Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E, Juliano RL: Motility of fibronectin receptor-deficient cells on fibronectin and vitronectin: collaborative interactions among integrins. J Cell Biol 116: 477-487, 1992
Simon KO, Nutt EM, Abraham DG, Rodan GA, Duong LT: The α v β 3 integrin regulates α 5 β 1-mediated cell migration toward fibronectin. J Biol Chem 272: 29380-29389, 1997
Chung J, Gao AF, Frazier WA: Thrombospondin acts via integrin-associated protein to activate the platelet integrin α IIb β 3. J Biol Chem 123: 485-496, 1993
Berditchevski F, Zutter MM, Hemler ME: Characterization of novel complexes on the cell surface between integrins and proteins with 4 transmembrane domains (TM4 proteins). Mol Biol Cell 7: 193-207, 1996
Hemler ME: Integrin associated proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 10: 578-585, 1998
Yauch RL, Berditchevski F, Harler MB, Reichner J, Hemler ME: Highly stoichiometric, stable and specific association of integrin α 3 β 1 with CD151 provides a major link to phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase, and may regulate cell migration. Mol Biol Cell 9: 2751-2765, 1998
Blystone SD, Graham FP, Lindberg FP, Brown EJ: Integrin α v β 3 differentially regulates adhesive and phagocytic functions of the fibronectin receptor α v β 1. J Cell Biol 127: 1129-1137, 1994
Blystone SD, Lindberg FP, LaFlamme SE, Brown EJ: Integrin β 3 cytoplasmic tail is necessary and sufficient for regulation of α 5 β 1 phagocytosis by α v β 3 and integrin associated protein. J Cell Biol 130: 745-754, 1995
Porter JC, Hogg N: Integrin cross talk: activation of lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 on human T cells alters α 4 β 1. J Cell Biol 138: 1437-1447, 1997
Blystone SD, Slater SE, Williams MP, Crow MT, Brown EJ: Molecular mechanism of integrin crosstalk: α v β 3 suppression of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulates α 5 β 1 function. J Cell Biol 145: 889-897, 1999
Schwartz MA, Both G, Lechene C: Effect of cell spreading on cytoplasmic pH in normal and transformed fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 4525-4529, 1989
Schwartz MA, Gragoe EJ Jr, Lechene CP: pH regulation in spread and round cells. J Biol Chem 265: 1327-1332, 1990
Schwartz MA: Spreading of human endothelial cells on fibronectin or vitronectin triggers elevation of intracellular free calcium. J Cell Biol 120: 1003-1010, 1992
McNamee HP, Ingber DE, Schwartz MA: Adhesion to fibronectin stimulates inositol lipid synthesis and enhances PDGF-induced inositol lipid breakdown. J Cell Biol 121: 673-678, 1993
Guadagno TM, Ohtsubo M, Roberts JM, Assoian RK: A link between cyclin A expression and adhesion-dependent cell cycle proliferation. Science 262: 1572-1575, 1993
Vuori K, Ruoslahti E: Association of insulin receptor substrate-1 with integrins. Science 226: 1576-1578, 1994
Kheradmand F, Werner E, Tremble P, Symons M, Werb Z: Role of Rac1 and oxygen radicals in collagenase-1 expression induced by cell shape change. Science 280: 898-902, 1998
Brooks PC, Stromblad S, Sanders LC, von Schalscha TL, Aimes RT, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Quigley JP, Cheresh DA: Localization of matrix metalloproteinase MMP-2 to the surface of invasive cells by interactions with integrin alpha v beta 3. Cell 85: 683-693, 1996
Schneller M, Vuori K, Ruoslahti E: α v β 3 integrin associates with activated insulin and PDGF β receptors and potentiates the biological activity of PDGF. EMBO J 16: 5600-5607, 1997
Woodard AS, Garcia-Cardena G, Leong M, Madri JA, Sessa WC, Languino LR: The synergistic activity of α v β 3 integrin and PDGF receptor increases cell migration. J Cell Science 111: 469-478, 1998
Wayner EA, Orlando RA, Cheresh DA: Integrins α v β 3 and α v β 5 contribute to cell attachment to vitronectin but differently distribute on the cell surface. J Cell Biol 113: 919-929, 1991
Filardo EJ, Brooks PC, Deming SL, Damsky C, Cheresh DA: Requirement of the NPXY motif in the integrin β 3 subunit cytoplasmic tail for melanoma cell migration in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Biol 130: 441-450, 1995
Seftor REB, Seftor EA, Gehlsen KR, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Brown PD, Ruoslahti E, Hendrix MJC. Role of the α v β 3 integrin in human melanoma cell invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 1557-1561, 1992
Ruiter DJ, Van Muijen GMP: Markers of melanocytic tumour progression. J Path 186: 340-342, 1998
Clark WH Jr, Elder DE, Guerry D, Epstein MN, Greene MH, Van Horn M: A study of tumor progression: the precursor lesions of superficial spreading and nodular melanoma. Hum Pathol 15: 1147-1165, 1984
Clark WH Jr: Tumor progression and the nature of cancer. Br J Cancer 64: 631-644, 1991
Hsu M-Y, Shi D-T, Meier FE, Van Belle P, Hsu J-Y, Elder DE, Buck CA, Herlyn M: Adenoviral gene transfer of β 3 integrin subunit induces conversion from radial to vertical growth phase in primary human melanoma. Am J Pathol 153: 1435-1442, 1998
Seftor REB: Commentary: Role of the β 3 integrin subunit in human primary melanoma progression: multifunctional activities associated with α v β 3 integrin expression. Am J Path 153: 1347-1351, 1998
Albelda SM, Mette SA, Elder DE, Stewart R, Damajanovich L, Herlyn M, Buck CA: Integrin distribution in malignant melanoma: association of the β 3 subunit with tumor progression. Cancer Res 50: 6757-6764, 1990
Danen EH, Ten Berge PJ, Van Muijen GN, Van't Hof-Grootenboer AE, Brocker EB, Ruiter DJ: Emergence of α 5 β 1 fibronectin-and α v β 3 vitronectin-receptor expression in melanocytic tumor progression. Histopathology 24: 249-256, 1994
Danen EH, Jansen KF, Van Kraatis AA, Cornelissen IM, Ruiter DJ, Van Muijen GN: α v-integrins in human melanoma: gain of α v β 3 and losss of α v β 5 are related to tumor progression in situ but not to metastatic capacity of cell lines in nude mice [published erratum appears in Int J Cancer 62: 365, 1995]. Int J Cancer 61: 491-496, 1995
Natali PG, Nicotra MR, Di Filippo F, Bigotti A: Expression of fibronectin, fibronectin isoforms and integrin receptors in melanocytic lesions. Br J Cancer 71: 1243-1247, 1995
Ten Berge PJM, Danen EHJ, Van Muijen GNP, Jager MJ, Ruiter DJ: Integrin expression in uveal melanoma differs from cutaneous melanoma. Inv Ophthal Vis Science 34: 3635-3640, 1993
Marshal JF, Rutherford DC, Happerfield L, Hanby A, McCartney ACE, Newton-Bishop J and Hart IR: Comparative analysis of integrins in vitro and in vivo in uveal and cutaneous melanomas. Br J Cancer 77: 522-529, 1998
Hendrix MJC, Seftor EA, Seftor REB, Gardner LM, Boldt HC, Meyer M, Pe'er J, Folberg R: Biological determinants of uveal melanoma metastatic phenotype: role of intermediate filaments as predictive markers. Lab Inv 78: 153-163, 1998
Hendrix MJC, Seftor EA, Seftor REB, Krischmann DA, Gardner LM, Boldt HC, Meyer M, Pe'er J, Folberg R: Regulation of uveal melanoma interconverted phenotype by hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/sc). Am J Path 152: 855-863, 1988
Liotta LA, Rao CN, Wewer UM: Biochemical interactions of tumor cells with the basement membrane. Annu Rev Biochem 55: 1037-1057, 1986
Hendrix MJC, Seftor EA, Seftor REB, Fidler IJ: A simple quantitative assay for studying the invasive potential of high and low human metastatic variants. Cancer Lett 38: 137-147, 1987
Hayman EG, Pierschbacher MD, Suzuki S, Ruoslahti E: Vitronectin — a major cell attachment-promoting protein in fetal bovine serum. Exp Cell Res 160: 245-258, 1985
Werb Z, Tremble PM, Behrendtsen O, Crowley E, Damsky CH: Signal transduction through the fibronectin receptor induces collagenase and stromelysin gene expression. J Cell Biol 109: 877-889, 1989
Albini A, Melchiori A, Santi L, Liotta LA, Brown PD, Stetler-Stevenson WG: Tumor cell invasion inhibited by TIMP-2. J Natl Cancer Inst 83: 775-779, 1991
Matrisian LM: Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in matrix remodeling. Trends Genetics 6: 121-125, 1990
Stetler-Stevenson WG: Type IV collagenases in tumor invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastas Rev 9: 289-303, 1990
Brown PD, Levy AT, Marguiles IMK, Liotta LA, Stetler-Stevenson WG: Independent expression and cellular processing of Mr72, 000 type IV collagenase and interstitial collagenase in human tumorigenic cell lines. Cancer Res 50: 6184-6191, 1990
Liotta LA, Thorgeirsson UP, Garbisa S: Role of collagenase in tumor cell invasion. Cancer Metastas Rev 1: 277-288, 1982
Liotta LA, Wewer UM, Rao CN, Schiffmann E, Stracke M, Guiguis R, Thorgeirsson U, Muschel R, Sobel M: Biochemical mechanisms of tumor invasion and metastasis. Prog Clin Biol Res 256: 3-16, 1988
Mignatti P, Robbins E, Rifkin DB: Tumor invasion through the human amnion membrane: requirement for a proteinase cascade. Cell 47: 487-498, 1986
Hoyhta M, Hujanen E, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T, Thorgeirsson UP, Liotta LA, Tryggvason K: Modulation of type IV collagenase activity and invasive behaviour of metastatic human melanoma (A2058) cells in vitro by monoclonal antibodies to type IV collagenase. Int J Cancer 46: 282-286, 1990
Seftor REB, Seftor EA, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Hendrix MJC: The 72 kDa type IV collagenase is modulated via differential expression of α v β 3 and α 5 β 1 integrins during human melanoma cell invasion. Cancer Res 53: 3411-3415, 1993
Hendrix MJC, Seftor EA, Chu Y-W, Seftor REB, Nagle RB, McDaniel KM, Leong SPL, Yohem KH, Leibovitz AM, Meyskens FL Jr, Conaway DH, Welch DR, Liotta LA, Stetler-Stevenson WG: Coexpression of vimentin and keratins by human melanoma tumor cells: correlation with invasive and metastatic potential. J Natl Cancer Inst 84: 165-174, 1992
Natali PG, Hamby CV, Felding-Habermann B, Liang B, Nicotra MR, Di Filippo F, Giannarelli D, Temponi M, Ferrone S: Clinical significance of the α v β 3 integrin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in cutaneous malignant melanoma lesions. Cancer Res 57: 1554-1560, 1997
Eliceiri BP, Klemke R, Stroblad S, Cheresh DA: Integrin alphavbeta3 requirement for sustained mitogen-activated protein kinase activity during angiogenesis. J Cell Biol 140: 1255-1263, 1998
Ruoslahti E: Integrins as signaling molecules and targets for tumor therapy. Kidney International 51: 1413-1417, 1997
Yun Z, Menter DG, Nicolson GL: Involvement of the integrin alpha(v) beta3 in cell adhesion, motility, and liver metastasis of murine RAW117 large cell lymphoma. Cancer Res 56: 3103-3111, 1996
Arap W, Pasqualini R, Ruoslahti E: Cancer treatment by targeted drug delivery to tumor vasculature in a mouse model. Science 279: 377-380, 1998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seftor, R.E., Seftor, E.A. & Hendrix, M.J. Molecular Role(s) for Integrins in Human Melanoma Invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev 18, 359–375 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006317125454
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006317125454