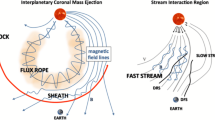
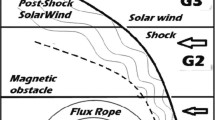
Abstract
Plasma and magnetic field parameter variations across fast forward interplanetary shocks are analyzed during the last solar cycle minimum (1995–1996, 15 shocks), and maximum year 2000 (50 shocks). It was observed that the solar wind velocity and magnetic field strength variation across the shocks were the parameters better correlated with Dst. Superposed epoch analysis centered on the shock showed that, during solar minimum, B z profiles had a southward, long-duration variation superposed with fluctuations, whereas in solar maximum the B z profile presented 2 peaks. The first peak occurred 4 hr after the shock, and seems to be associated with the magnetic field disturbed by the shock in the sheath region. The second peak occurred 19 hr after the shock, and seems to be associated with the ejecta fields. The difference in shape and peak in solar maximum (Dst peak =−50 nT, moderate activity) and minimum (Dst peak =−30 nT, weak activity) in average Dst profiles after shocks are, probably, a consequence of the energy injection in the magnetosphere being driven by different interplanetary southward magnetic structures. A statistical distribution of geomagnetic activity levels following interplanetary shocks was also obtained. It was observed that during solar maximum, 36% of interplanetary shocks were followed by intense (Dst≤−100 nT) and 28% by moderate (−50≤Dst <−100 nT) geomagnetic activity. During solar minimum, 13% and 33% of the shocks were followed by intense and moderate geomagnetic activity, respectively. Thus, during solar maximum a higher relative number of interplanetary shocks might be followed by intense geomagnetic activity than during solar minimum. One can extrapolate, for forecasting goals, that during a whole solar cycle a shock has a probability of around 50–60% to be followed by intense/moderate geomagnetic activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuña, M. H., Ogilvie, K. W., Baker, D. N., Curtis, S. A., Fairfield, D. H., and Mish, W. H.: 1995, Space Sci. Rev. 71, 5.
Berdichevsky, D. B., Szabo, A., Lepping, R. P., Viñas, A. F., and Mariani, F.: 2000, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 27289.
Bothmer, V. and Schwenn, R.: 1995, J. Geomag. Geoelectr. 47, 1127.
Burlaga, L. F.: 1995, Interplanetary Magnetohydrodynamics, Oxford University Press, New York.
Burlaga, L. F., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., and Schwenn, R.: 1981, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 6673.
Cane, H. V., Richardson, I. G., and Wibberenz, G.: 1997, J. Gepophys. Res. 102, 7075.
Cane, H. V., Richardson, I. G, and Cyr, O. C. St.: 2000, Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 3591.
Domingo, V.: 1996, J. Geomag. Geoelectr. 48, 24.
Dryer, M.: 1975, Space Sci. Rev. 17, 277.
Dungey, J. W.: 1961, Phys. Rev. Lett. 6, 47.
Echer, E., Gonzalez, W. D., Vieira, L. E. A., Dal Lago, A., Guarnieri, F. L. Prestes, A., Gonzalez, A. L. C., and Schuch, N. J.: 2003a, Braz. J. Phys. 33, 115.
Echer, E., Gonzalez, W. D., Dal Lago, A., Vieira, L. E. A., Guarnieri, F. L., Clua de Gonzalez, A. L., and Schuch, N. J.: 2003b, Adv. Space Res., submitted.
Echer, E., Gonzalez, W. D., Alves, M. V., Gonzalez, A. L. C., Dal Lago, A., Vieira, L. E. A., Guarnieri, F. L., and Schuch, N. J.: 2003c, Proc. ISCS 2003 Symposium, 'solar Variability as an Input to the Earth's Environment' ESA SP–535, 641.
Gonzalez, W. D. and Tsurutani, B. T.: 1987, Planetary Space Sci. 35, 1101 (GT87).
Gonzalez, W. D., Joselyn, J. A., Kamide, Y., Kroehl, H. W., Rostoker, G., Tsurutani, B. T., and Vasyliunas, V. M.: 1994, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 5771.
Gonzalez, W. D., Clúa de Gonzalez, A. L., Dal Lago, A., Tsurutani, B. T., Arballo, J. K., Lakhina, G. K., Buti, B., Ho, C. M., and Wu, S.-T: 1998, Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 963.
Gonzalez, W. D., Tsurutani, B. T., and Clúa de Gonzalez, A. L.: 1999, Space Sci. Rev. 88, 529.
Gosling, J. T.: 1997, in N. Crooker, J. A. Joselyn and J. Feynman (eds.), Coronal Mass Ejections, AGU Monograph 99, American Geophysical Union, Washington D.C.
Gosling, J. T., Bame, S. J., McComas, D. J., and Phillips, J. L.: 1990, Geophys. Res. Lett. 17, 901.
Gosling, J. T., McComas, D. J., Phillips, J. L., and Bame, S. J.: 1991, J. Geophys. Res. 96, 7831.
Jurac, S., Kasper, J. C., Richardson, J. D., and Lazarus, A. J.: 2002, Geophys. Res. Lett. 29, 10.1029/2001GL014034.
McComas, D. J., Gosling, J. T., Bame, S. J., Smith, E. J., and Cane, H. V.: 1989, J. Geophys. Res. 94, 1465.
Nishida, A.: 1978, Geomagnetic Diagnosis of the Magnetosphere, Physics and Chemistry in Space, V.9, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Schwenn, R.: 1986, Space Sci. Rev. 44, 139.
Schwenn, R.: 2000, Adv. Space Res. 26, 43.
Spiegel, M. R. and Stephens, L. J.: 1998, Schaums Outline of Statistics, McGraw-Hill Inc. USA.
Stone, E. C., Frandsen, A. M., Mewaldt, R. A., Christian, E. R., Margolies, D., Ormes, J. F., and Snow, F.: 1998, Space Sci. Rev. 86, 1.
Sugiura, M.: 1964, Hourly values of equatorial Dst for the IGY, Annual International Geophysical Year, V. 35, p. 9, Pergamon, New York.
Tsurutani, B. T., Gonzalez, W. D., Tang, F., Akasofu, S.-I., and Smith, E. J.: 1988, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 8519.
Tsurutani, B. T., Gonzalez, W. D., Tang, F., and Lee, Y. T.: 1992, Geophys. Res. Lett. 19, 73.
Webb D. F., Cliver, E. W., Crooker, N. U., St. Cyr, O. C., and Thompson, B. J.: 2000, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 7491.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Echer, E., Alves, M. & Gonzalez, W. Geoeffectiveness of interplanetary shocks during solar minimum (1995–1996) and solar maximum (2000). Solar Physics 221, 361–380 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SOLA.0000035045.65224.f3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SOLA.0000035045.65224.f3