Abstract
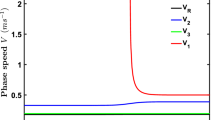
A method for determination of characteristics of quasi-Rayleigh (qR) wave in a transversely isotropic homogeneous half-space with inclined axis of symmetry is outlined. The solution is obtained as a superposition of qP, qSV and qSH waves, and surface wave velocity is determined from the boundary conditions at the free surface and at infinity, as in case of Rayleigh wave in an isotropic half-space. Though the theory is simple enough, a numerical procedure for calculation of surface wave velocity presents some difficulties. The difficulty is caused by necessity to calculate complex roots of a non-linear equation, which in turn contains functions determined as roots of non-linear equations with complex coefficients. Numerical analysis shows that roots of the equation corresponding to the boundary conditions do not exist in the whole domain of azimuths and inclinations of the symmetry axis. The domain of existence of qR wave depends on the ratio of the elastic parameters: for some strongly anisotropic models the wave cannot exist at all. For some angles of inclination qR-wave velocities deviate from those calculated on the basis of the perturbation method valid for weak anisotropy, though they have the same tendency of variation with azimuth. The phase of qR wave varies with depth unlike Rayleigh wave in an isotropic half-space. Unlike Rayleigh wave in an isotropic half-space, qR wave has three components - vertical, radial and transverse. Particle motion in horizontal plane is elliptic. Direction of the major axis of the ellipsis coincides with the direction of propagation only in azimuths 0° (180°) and 90° (270°).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson D.L., 1961. Elastic wave propagation in layered anisotropic media. J. Geophys. Res., 66, 2953–2963.
Crampin S., 1970. The dispersion of surface waves in multilayered anisotropic media. Geophys. J. Roy. astr. Soc., 21, 387–402.
Crampin S., 1975. Distinctive particle motion of surface waves as a diagnostic of anisotropic layering. Geophys. J. Roy. astr. Soc., 40, 177–186.
Crampin S. and Taylor D.B., 1971, The propagation of surface waves in anisotropic media, Geophys. J. Roy. astr. Soc., 25, 71–87.
Farnell G.W., 1970. Properties of elastic surface waves. In: W.P. Mason (Ed.), Physical Acoustics VI, Academic Press, New York, 109–166.
Forsyth D.W., 1975. The early structural evolution and anisotropy of oceanic upper mantle. Geophys. J. Roy. astr. Soc., 43, 103–162.
Laske G. and Masters G., 1998. Surface wave polarization data and global anisotropic structure. Geophys. J. Int., 132, 508–520.
Lothe J. and Barnett D.M., 1976. On the existence of Rayleigh (surface) wave solutions for anisotropic half-spaces with free surface. J. Appl. Phys., 47, 428–433.
Maupin V., 1989. Surface waves in weakly anisotropic structures: on the use of ordinary or quasi-degenerate perturbation methods. Geophys. J. Int., 98, 553–563.
Maupin V., 2001. A multiple-scattering scheme for modelling surface wave propagation in isotropic and anisotropic three-dimensional structures. Geophys. J. Int., 146, 332–348.
McEvilly T.V., 1964. Central U.S. crust-upper mantle structure from Love and Rayleigh wave phase velocity inversion. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am., 54, 1997–2015.
Montagner J-P. and Nataf H.C., 1986. On inversion of the azimuthal anisotropy of surface waves. J. Geophys. Res., 91, 511–520.
Montagner J-P. and Tanimoto T., 1990. Global anisotropy in the upper mantle inferred from the regionalization of phase velocities. J. Geophys. Res., 95, 4797–4819.
Nishimura C.L., and Forsyth D.W., 1989. The anisotropic structure of the upper mantle in the Pacific. Geophys. J. Int., 96, 203–229.
Park J., 1996. Surface waves in layered anisotropic structures. Geophys. J. Int., 126, 173–184.
Petterson O. and Maupin V., 2002. Lithospheric anisotropy on the Kergelen hotspot track inferred from Rayleigh wave polarization anomalies. Geophys. J. Int., 149, 225–246.
Smith M.L. and Dahlen F.A., 1973. The azimuthal dependence of Love and Rayleigh wave propagation in a slightly anisotropic medium. J. Geophys. Res., 78, 3321–3333.
Smith M.L. and Dahlen F.A., 1975. Correction to “The azimuthal dependence of Love and Rayleigh wave propagation in a slightly anisotropic medium”. J. Geophys. Res., 80, 1923.
Suetsugu D. and Nakanishi I., 1987. Regional and azimuthal dependence of phase velocities of mantle Rayleigh waves in the Pacific ocean. Phys. Earth Planet. Int., 47, 230–245.
Tanimoto T. and Anderson D.L., 1985. Lateral heterogeneity and azimuthal anisotropy of the upper mantle: Love and Rayleigh waves 100–250 s. J. Geophys. Res., 90, 1842–1858.
Thomson C.J., 1997. Modelling surface waves in anisotropic structures. 1. Theory. Phys. Earth Planet. Int., 103, 195–206.
Yu Y. and Park J., 1994. Hunting for azimuthal anisotropy beneath the Pacific Ocean region. J. Geophys. Res., 99, 15399–15422.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanovskaya, T., Savina, L. Quasi-Rayleigh Waves in Transversely Isotropic Half-Space with Inclined Axis of Symmetry. Studia Geophysica et Geodaetica 48, 251–264 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SGEG.0000015595.08489.ae
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SGEG.0000015595.08489.ae