Abstract
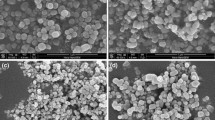
The particle size and morphology of hydrothermally synthesised lead zirconate titanate (PZT) powders can be controlled by concentrations of the mineraliser such as potassium hydroxide (KOH), and the hydrothermal synthesis temperature and time, which all influence the particle nucleation and growth mechanisms. The mineraliser is crucial in facilitating both the in-situ transformation process during the nucleation stage and the nuclei-coagulation process during the subsequent growth stage. Its concentration must be high enough to ensure the formation of only pure perovskite PZT particles but low enough to prevent excessive PZT particle growth. The minimum necessary mineraliser concentration has, however, strong dependence on both the hydrothermal synthesis temperature and chemical environment in hydrothermal solution. Thus, perovskite PZT powders with ca. 200 nm particle size and narrow particle size distribution can be synthesised hydrothermally at 300°C using KOH as a mineraliser with a minimum concentration of 0.4 M.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. F. LANGE, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 72 (1989) 9.
W. J. DAWSON, Amer. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 67 (1988) 1673.
R. E. RIMAN, in"High-performance Ceramics," edited by R. Pugh and L. Bergstrom (Marcel-Dekker, New York, 1993) p. 29.
T. R. N. KUTTY and R. BALACHANDRAN, Mater. Res. Bull. 19 (1984) 1479.
T. ICHIHARA, T. TSURUMI, K. ASAGA, K. H. LEE and M. DAIMON, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. Intel. Ed. 98 (1990) 155.
H. CHENG, J. MA, B. ZHU and Y. Cui, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 76 (1993) 625.
M. M. LENCKA, A. ANDERKO and R. E. RIMAN, ibid. 78 (1995) 2609.
M. TRAIANIDIS, C. COURTIS and A. LERICHE, J. Euro. Ceram. Soc. 20 (2000) 2713.
E. SOVACI, A. DOGAN, J. ANDERSON and J. H. ADAIR, Chem. Eng. Comm. 190 (2003) 843.
K. C. BEAL,"Advances in Ceramics, Ceramic Powder Science" (The American Ceramic Society Inc., 1987) Vol. 21, p. 33.
S. B. CHO, M. OLEDZKA and R. E. RIMAN, J. Cryst. Growth 226 (2001) 313.
Y. OHBA, T. RIKITOKU, T. TSURUMI and M. DAIMON, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 104 (1996) 6.
B. SU, T. W. BUTTON and C. B. PONTON, Rev. High Press. Sci. Tech. 7 (1998) 1348.
C. F. BAES JR. and R. E. MESMER, "The Hydrolysis of Cations" (Krieger Publishing Company, Florida, 1986) p. 147.
G. D. SMITH, C. N. CAUGHLAN and J. A. CAMPBELL, Inorg. Chem. 11 (1972) 2989.
D. HENNINGS, G. ROSENSTEIN and H. SCHREINEMACHER, J. Euro. Ceram. Soc. 8 (1991) 107.
D. V. LUEBKE,US Patent, 3,442,817 (1969).
E. J. MARGOLIS, "Chemical Principles in Calculations of Ionic Equilibria" (Macmillan, New York, 1966).
J. E. FERGUSSON, "The Heavy Elements: Chemistry, Environmental Impact and Health Effects" (Pergamon, Oxford, 1990).
S. S. SENGUPTA, L. MA, D. L. ADLER and D. A. PAYNE, J. Mater. Res. 10 (1995) 1345.
I. LAAZIZ, A. LARBOT, A. JULBE, C. GUIZARD and L. COT, J. Solid State Chem. 98 (1992) 393.
P. BARBOUX, P. GRIESMAR, F. RIBOT and L. MAZEROLLES, ibid. 117 (1995) 343.
R. J. HUNTER, "Zeta Potential in Colloidal Science: Principle and Applications" (Academic Press Ltd., London, 1981) p. 22.
J. N. ISRAELACHVILI, "Intermolecular and Surface Forces" (Academic Press Ltd., London, 1992) p. 248
A. C. PIERRE, Amer. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 70 (1991) 1281.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, B., Button, T.W. & Ponton, C.B. Control of the particle size and morphology of hydrothermally synthesised lead zirconate titanate powders. Journal of Materials Science 39, 6439–6447 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000044881.35754.ea
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000044881.35754.ea