Abstract
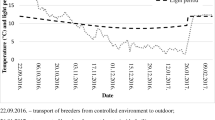
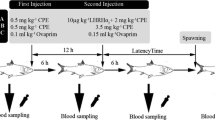
Pikeperch were induced to spawn 3 months prior to the natural spawning period through photothermal and hormonal stimulation. Females (five specimens in each group) were stimulated with injection of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) once (200 IU kg−1), twice (200 IU kg−1, second dose after 48 h–400 IU kg−1) or three times (200 IU kg−1, after 24 h–200 IU kg−1 and after another 24 h–200 IU kg−1). The control group was injected once with 0.9% NaCl. The males were stimulated with a single hormone dose of 200 IU kg−1. Eggs were obtained from all the hormonally treated fish. None of the control group females, which were only stimulated photothermally, ovulated any eggs. The time of ovulation was 66–71 h following the first injection, and the eggs viability until the eyed stage (from 71.5 to 77.5%) did not depend on the number of hormone doses (P > 0.05). The out-of-season spawning method described in this paper could be used to provide pikeperch larvae for intensive culture systems (recirculating water systems) before natural spawning season and to produce larger-sized pikeperch fingerlings for stocking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry, T.P., Malison, J.A., Lapp, A.F. and Procarione, L.S. 1995. Effects of selected hormones and male cohorts on final oocyte maturation, ovulation, and steroid production in walleye (Stizostedion vitreum). Aquaculture 138: 331-347.
Brzuska, E. and Bieniarz, K. 1977. A method of in vivo designating oocytes maturation of carp females with connection of injection with common carp pituitary extract. The Stanis?aw Sakowicz Inland Fisheries Institute, Olsztyn, No. 105, p. 27.
Dabrowski, K., Ciereszko, A., Ramseyer, L., Culver, D. and Kestemont, P. 1994. Effects of hormonal treatment on induced spermation and ovulation in the yellow perch (Perca flavescens). Aquaculture 120: 171-180.
Dabrowski, K., Ciereszko, R.E., Ciereszko, A., Toth, G.P., Christ, S.A., El-Saidy, D. and Ottobre, J.S. 1996. Reproductive physiology of yellow perch (Perca flavescens): environmental and endocrinological cues. Journal of Applied Ichthyology 12: 139-148.
Dabrowski, K., Czesny, S., Kolkovski, S., Lynch Jr., W.E., Bajer, P. and Culver, D.A. 2000. Intensive culture of walleye larvae produced out of season and during regular spawning. North American Journal of Aquaculture 62: 219-224.
Demska-Zakes, K. and Zakes, Z. 2002. Controlled spawning of pikeperch Stizostedion lucioperca (L.), in lake cages. Czech Journal of Animal Sciences 47: 230-238.
Heidinger, R.C., Tetzlaff, B. and Brooks, R.C. 1996. Hormone induced spawning of walleye. In: Summerfelt, R.C. (ed.), Walleye culture manual, NCRAC Culture Series 101, Iowa State University, Ames, pp. 59-62.
Kazuń, K. and Siwicki, A.K. 2001. Propiscin-a new safe anaesthetic for fish. Archives of Polish Fisheries 9: 183-190.
Kestemont, P. and Melard, C. 2000. Aquaculture. In: Craig, J.F. (ed.), Percid Fishes, Systematics, Ecology and Exploitation. Blackwell Science, Oxford, pp. 191-224.
Kolkovski, S. and Dabrowski, K. 1998. Off-season spawning of yellow perch. The Progressive Fish-Culturist 60: 133-136.
Malison, J.A., Procarione, L.S., Kayes, T.B., Hansen, J.F. and Held, J.A. 1998. Induction of out-of-season spawning in walleye (Stizostedion vitreum). Aquaculture 163: 151-161.
Migaud, H., Fontaine, P., Sulistyo, I., Kestemont, P. and Gardeur, J.-N. 2002. Induction of out-of-season spawning in Eurasian perch Perca fluviatilis: effects of rates of cooling and cooling durations on female gametogenesis and spawning. Aquaculture 205: 253-267.
Schlumberger, O. and Proteau, J.P. 1996. Reproduction of pike-perch (Stizostedion lucioperca) in captivity. Journal of Applied Ichthyology 12: 149-152.
Steffens, W., Geldhauser, F., Gerstner, P. and Hilge, V. 1996. German experiences in the propagation and rearing of fingerling pikeperch (Stizostedion lucioperca). Annales Zoologici Fennici 33: 627-634.
Tate, A.E. and Helfrich, L.A. 1998. Off season spawning of sunshine bass (Morone chrysops×M. saxatilis) exposed to 6 and 9 month phase shifted photothermal cycles. Aquaculture 167: 67-83.
Zakes, Z. and Szkudlarek, M. 1998. Breeding of wild European pikeperch Stizostedion lucioperca (L.) in controlled conditions. Czech Journal of Animal Sciences 43: 439.
Zakes, Z., Demska-Zakes, K., Mucha, M. and Jelonek, Z. 2000. Effectiveness of hormonal stimulation in controlled pikeperch spawning in lake cages. In: Wolos, A. (ed.), Some Aspects of Fisheries in 2000, IRS Olsztyn, pp. 65-72 (in Polish).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zakes, Z., Szczepkowski, M. Induction of Out-of-Season Spawning of Pikeperch, Sander Lucioperca (L.). Aquaculture International 12, 11–18 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:AQUI.0000017183.40691.7d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:AQUI.0000017183.40691.7d