Abstract
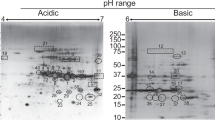
The new antigen Bm95 from the cattle tick Boophilus microplus was recently isolated, cloned and expressed in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. The recombinant protein has shown to induce protection in cattle against infestations of B. microplus under controlled and production conditions. In this paper we report the production and large-scale purification of the Bm95 protein, following a simple and cost-effective process. The antigen was obtained highly aggregated, forming particles ranging from 26 to 30 nm and with purity higher than 80%. The process yield was 0.55 g of pure Bm95 protein per liter of culture. The 98% of the primary structure of the recombinant protein was verified by mass spectrometry. Three amino acid changes in comparison with the sequence deduced from cDNA were detected by LC-MS/MS. The antigen was also obtained N-glycosylated, as previously reported for heterologous protein expression in P. pastoris.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aswad D.W. 1984. Stoichiometric methylation of porcine adrenocorticotropin by protein carboxyl methyltransferase requires deamidation of asparagine 25. Evidence for methylation at the alphacarboxyl group of atypical L-isoaspartyl residues. J. Biol. Chem. 259: 10714–10721.
Betancourt L.H., Takao T., González L.J., Reyes O., Besada V., Padrón G. and Shimonishi Y. 1999. The metastable decomposition of a peptide containing oxidized methionine(s) in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 13: 1075–1076.
Boué O., Sánchez K., Tamayo G., Hernández L., Reytor E. and Enríquez A. 1997. Single-step purification of recombinant Bm86 protein produced in Pichia pastoris by salting-out and by acid precipitation of contaminants. Biotechnol. Techniq. 13: 561–565.
Boué O., Garcia J.L., Villar M., Alazo K., Perez A., Ramos E., Morales C., Morera O.L., Redondo M., Montero C. and Rodríguez M. 2000. Antiviral and antiluteolytic activity of recombinant bovine IFNomega1 obtained from Pichia pastoris. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 20: 677–683.
Canales M., Enrique A., Ramos E., Cabrera D., Dandie H., Soto A., Falcon V., Rodríguez M. and de la Fuente J. 1997. Large-scale production in Pichia pastoris of the recombinant vaccine GavacTM against cattle tick. Vaccine 15: 414–422.
Canales M., Buxadó J.A., Heynngnezz L. and Enríquez A. 1998. Mechanical disruption of Pichia pastoris yeast to recover the recombinant glycoprotein Bm86. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 23: 58–63.
Charbonneau H. 1989. A Practical Guide to Protein and Peptide Purification for Microsequencing. Matsudaira P.T. (ed). Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 15–30.
Clarke S. 1987. Propensity for spontaneous succinimide formation from aspartyl and asparaginyl residues in cellular proteins. Int. J. Peptide Protein Res. 30: 808–821.
Cobon G., Hungerford J., Woodrow M., Smith D. and Willadsen P. 1995. Vaccination against B. microplus: the Australian field experience. In: de la Fuente (ed) Recombinant Vaccines for the Control of Cattle Tick. La Habana, Elfos Scientiae, pp. 163–176.
de la Fuente J., Rodríguez M., Redondo M., Montero C., García-García J.C., Méndez L., Serrano E., Valdés M., Enrique A., Canales M., Ramos E., Boue O. Machado H., Lleonart R., de Armas C.A., Rey S., Rodríguez J.L., Artiles M. and Garcia L. 1998. Field studies and cost-effectiveness analysis of vaccination with GavacTM against the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Vaccine 16: 365–374.
García-García J.C., Montero C., Rodríguez M., Soto A., Redondo M., Valdés M., Méndez L. and de la Fuente J. 1998. Effect of particulation on the immunogenic and protective properties of the recombinant Bm86 antigen expressed in Pichia pastoris. Vaccine 16: 374–380.
García-García J.C., Montero C., Redondo M., Vargas M., Canales M., Boué O., Rodríguez M., Joglar M., Machado H., Gonzélez I.L., Valdés M., Méndez L. and de la Fuente J. 2000. Control of ticks resistant to the immunization with Bm86 in cattle vaccinated with the recombinant antigen Bm95 isolated from the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus. Vaccine 18: 2275–2287.
Kemp D.H., Pearson R.D., Gough J.M. and Willadsen P. 1989. Vaccination against Boophilus microplus: localization of antigens on tick gut cells and their interaction with the host immune system. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 7: 43–58.
Laemmli U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Lagerwerf F.M., van-de-Weert M., Heerma W. and Haverkamp J. 1996. Identification of oxidized methionine in peptides. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 10: 1905–1910.
Lowry D.H., Rosembrough N.J., Farr A.L. and Randal Y.R.J. 1951. Protein measurements with the folin-phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193: 265–269.
Montesino R., Cremata J.A., Rodríguez M., Besada V., Falcon V. and de la Fuente J. 1996. Biochemical characterization of the recombinant Boophilus microplus Bm86 antigen expressed by transformed Pichia pastoris cells. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 23: 23–28.
Montesino R., Quintero O., García R. and Cremata J.A. 1998a. Glycosylation profiling of heterologous protein expressed in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. In: Cregg James and Higgins David (ed) Methods in Molecular Biology. Pichia protocols. Vol. 103. Chapter 8, Humana Press, pp. 95–105.
Montesino R., García R., Quintero O. and Cremata J.A. 1998b. Variation in N-linked oligosaccharide structures on heterologous proteins secreted by the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Protein Expres. Purif. 14: 197–207.
Murray Jr. E.D. and Clarke S. 1984. Synthetic peptide substrates for the erythrocyte protein carboxyl methyltransferase. Detection of a new site of methylation at isomerized L-aspartyl residues. J. Biol. Chem. 259: 10722–10732.
Nuñez J.C., Pugliese M.E., Shaw R.D. 1972. Boophilus microplus Can. Pruebas de susceptibilidad in vitro con veinte cepas argentinas. Medicina Veterinaria 53: 3–7.
Rand K.N., Sirikantha A., Spring K., Tellan R., Willadsen P. and Cobon G.S. 1989. Cloning and expression of a protective antigen from the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 9657–9661.
Redondo M., Fragoso H., Ortiz M., Montero C., Lona J., Medellin J.A., Fria R., Hernandez V., Franco R., Machado H., Rodriguez M. and de la Fuente J. 1999. Integrated control of acaricide-resistant Boophilus microplus populations on grazing cattle in Mexico using vaccination with GavacTM and amidine treatments. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 23: 841–849.
Rodríguez M., Rubiera R., Penichet M., Montesino R., Cremata J., Falcón V., Sánchez G., Bringas R., Cordovés C., Valdés M., Lleonart R., Herrera L. and de la Fuente J. 1994. High level expression of the Boophilus microplus Bm86 antigen in the yeast Pichia pastoris forming highly immunogenic particles for cattle. J. Biotech. 33: 135–146.
Triguero A., Blanco R., Machado H., Rodríguez M. and de la Fuente J. 1999. Development of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay to measure Bm86 antigen of Boophilus microplus (cattle tick) and to detect anti-Bm86 antibodies in serum samples. Biotech. Techniq. 13: 119–125.
Turnbull I.F., Smith D.R.J., Sharp P.J., Cobon G.S. and Hynes M.J. 1990. Expression and secretion in Aspergillus nidulans and Aspergillus niger of a cell surface glycoprotein from the cattle tick Boophilus microplus, by using the fungal amds promoter system. Appl. Environ. Microbial. 56: 2847–2852.
Willadsen P., McKenna R.V. and Riding G.A. 1988. Isolation from the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus, of antigenic material capable of eliciting a protective immunological response in the bovine host. Int. J. Parasitol. 18: 183–189.
Willadsen P., Riding G.A., McKenna R.V., Kemp D.-H., Tellam R.L., Nielsen J.N., Lahstein J., Cobon G.S. and Gough J.M. 1989. Immunological control of a parasitic arthropod. Identification of a protective antigen from Boophilus microplus. J. Immunol. 143: 1346–1351.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boué, O., Farnós, O., González, A. et al. Production and biochemical characterization of the recombinant Boophilus microplus Bm95 antigen from Pichia pastoris . Exp Appl Acarol 32, 119–128 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:APPA.0000018199.87122.e4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:APPA.0000018199.87122.e4