Abstract
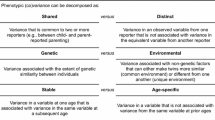
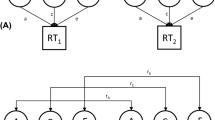
One common assumption in psychology is the impact of parenting and parent-child relationships on the child's adjustment throughout the life span. Studies have indicated that there are genetic influences on memories of parenting, but how these influences are mediated has not typically been investigated. A sample of 150 pairs of monozygotic and 176 pairs of dizygotic Swedish twin women reported on personal characteristics and on remembered relationships with their mother and father using the Parental Bonding Instrument (PBI). Quantitative genetic analyses showed moderate genetic influences for remembered parental warmth, which also was partly explained by genetic influences for optimism, aggression, and humor. The other two PBI scales, authoritarianism and protectiveness, showed only shared and nonshared environmental influences. One interpretation of the findings is that heritable personal characteristics of children elicit parental warmth. However, other explanations such as personality characteristics influencing how experiences with parents are interpreted or circumstances in adult life that affect the recall of experiences could not be ruled out.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumrind, D. (1991). The influence of parenting style on adolescent competence and substance use. Journal of Early Adolescence 11(1):56-95.
Bell, R. Q. (1968). A reinterpretation of the direction of effects in studies of socialization. Psychol. Rev. 75(2):81-95.
Bower, G. H. (1981). Mood and memory. Am Psychol 36(2):129-48.
Bowlby, J. (1988). A secure base: Parent-child attachment and healthy human development. New York: Basicbooks, Inc.
Brändstrom, S., Schlette, P., Przybeck, T. R., Lundberg, M., Forsgren, T., Sigvardsson, S., Nylander, P. O., Nilsson, L. G., Cloninger, R. C., and Adolfsson, R. (1998). Swedish normative data on personality using the Temperament and Character Inventory. Compr. Psychiatry 39(3):122-128.
Cloninger, C. R., Svrakic, D. M., and Przybeck, T. R. (1993). A psychobiological model of temperament and character. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 50(12):975-990.
Crockenberg, S., and Acredelo, C. (1983). Infant temperament ratings: A function of infants, or mothers, or both? Infant Behavior and Development 6:61-72.
Crockenberg, S., and Smith, P. (1982). Antecedents of mother-infant interaction and infant irritability in the first three months of life. Infant Behavior and Development 5:105-119.
Deater-Deckard, K., & O'Connor, T. G. (2000). Parent-child mutuality in early childhood: Two behavioral genetic studies. Dev. Psychol. 36(5):561-570.
Derryberry, D., and Reed, M. A. (1994). Temperament and attention: Orienting toward and away from positive and negative signals. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 66(6):1128-1139.
Dureman, I., Keebon, L., and österberg, E. (1971). Manual till DS Batteriet [Manual of the DS Battery]. Stockholm: Psykologi Förlaget.
Elkins, I. J., McGue, M., and Iacono, W. G. (1997). Genetic and environmental influences on parent-son relationships: Evidence for increasing genetic influence during adolescence. Dev. Psychol. 33(2):351-363.
Ge, A., Conger, R., Cadoret, R., Neiderhiser, J., Yates, W., Troughton, E., and Stewart, M. (1996). The developmental interface between nature and nurture: Mutual influence model of child antisocial behavior and parent behaviors. Dev. Psychol. 32:574-589.
Gray, J. (1981). A critique of Eysenck's theory of personality. In H., Eysenck (ed.), A model for personality (pp. 246-276). New York: Springer.
Gustavsson, J. P. (1997). Stability and validity of self-reported personality traits: Contributions to the evaluation of the Karolinska Scales of Personality. Unpublished PhD dissertation, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
Hur, Y. M., and Bouchard, T. J., Jr. (1995). Genetic influences on perceptions of childhood family environment: a reared apart twin study. Child Dev. 66(2):330-345.
Isley, S. L., O'Neil, R., Clatfelter, D., and Parke, R. D. (1999). Parent and child expressed affect and children's social competence: modeling direct and indirect pathways. Dev. Psychol. 35(2):547-560.
Kendler, K. S. (1996). Parenting: a genetic-epidemiologic perspective. Am. J. Psychiatry 153(1):11-20.
Kendler, K. S., Myers, J., and Prescott, C. A. (2000). Parenting and adult mood, anxiety and substance use disorders in female twins: An epidemiological, multi-informant, retrospective study. Psychol. Med. 30(2):281-294.
Larsen, R., and Ketelaar, T. (1989). Extraversion, neuroticism and susceptibility to positive and negative mood induction procedures. Personality and Individual Differences 10:1221-1228.
Larsen, R. J., and Ketelaar, T. (1991). Personality and susceptibility to positive and negative emotional states. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 61(1):132-140.
Leve, L. D., Winebarger, A. A., Fagot, B. I., Reid, J. B., and Goldsmith, H. H. (1998). Environmental and genetic variance in children's observed and reported maladaptive behavior. Child Dev. 69(5):1286-1298.
Martin, M., Ward, J., and Clark, D. (1983). Neuroticism and the recall of positive and negative personality information. Behavioural Research and Therapy 21:495-503.
Messer, B., and Harter, S. (1986). Manual for the adult self-perception profile. Denver CO: University of Denver.
Neale, M. C. (1999). Mx: Statistical Modeling: User's guide (5th ed.), Department of Human Genetics, Medical College of Virginia, Richmond, VA.
Neale, M. C., and Cardon, L. R. (1992). Methodology for genetic studies of twins and families. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publisher.
Neale, M. C., Walter, E., Heath, A. C., Kessler, R. C., Pérusse, D., Eaves, L. J., and Kendler, K. S. (1994). Depression and parental bonding: Cause, consequence, or genetic covariance? Genetic Epidemiology 11:503-522.
O'Connor, T. G., Hetherington, E. M., Reiss, D., and Plomin, R. (1995a). A twin-sibling study of observed parent-adolescent interactions. Child Dev. 66(3):812-829.
O'Connor, T. G., Hetherington, E. M., Reiss, D., and Plomin, R. (1995b). A twin-sibling study of observed parent-adolescent interactions. Child Dev. 66(3):812-829.
Parker, G. (1979a). Parental deprivation and depression in a nonclinical group. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 13(1):51-56.
Parker, G. (1979b). Reported parental characteristics in relation to trait depression and anxiety levels in a non-clinical group. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 13(3):260-264.
Parker, G. (1986). Validating an experiential measure of parental style: The use of a twin sample. Acta. Psychiatr. Scand. 73(1):22-27.
Parker, G., and Gladstone, G. (1996). Parental characteristics as influences on adjustment in adulthood. In G. Pierce, B. Sarason, and I. Sarason, (eds.), Handbook of social support and the family (pp. 195-218). London: Plenum.
Parker, G., and Hadzi-Pavlovic, D. (1992). Parental representations of melancholic and non-melancholic depressives: Examining for specificity to depressive type and for evidence of additive effects. Psychol. Med. 22(3):657-665.
Parker, G., Hadzi-Pavlovic, D., Greenwald, S., and Weissman, M. (1995). Low parental care as a risk factor to lifetime depression in a community sample. J. Affect. Disord. 33(3):173-180.
Parker, G., Tupling, H., and Brown, L. (1979c). A parental bonding instrument. British Journal of Medical Psychology 52:1-10.
Parrott, W. G., and Sabini, J. (1990). Mood and memory under natural conditions: Evidence for mood incongruent recall. Journal of Personality & Social Psychology 59(2):321-336.
Pike, A., and Plomin, R. (1997). A behavioural genetic perspective on close relationships. International Journal of Behavioral Development 21(4):647-667.
Plantes, M. M., Prusoff, B. A., Brennan, J., and Parker, G. (1988). Parental representations of depressed outpatients from a U.S.A. sample. J. Affect. Disord. 15(2):149-55.
Plomin, R. (1994). Genetics and experience: The interplay between nature and nurture Vol. 6) Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Plomin, R., DeFries, J. C., and Loehlin, J. C. (1977). Genotypeenvironment interaction and correlation in the analysis of human behavior. Psychological Bulletin 84(2):309-322.
Plomin, R., McClearn, G. E., Pedersen, N. L., Nesselroade, J. R., and Bergeman, C. S. (1988). Genetic influence on childhood family environment perceived retrospectively from the last half of the life span. Developmental Psychology 24:738-745.
Plomin, R., Reiss, D., Hetherington, E., and Howe, G. (1994). Nature and nurture: Genetic contributions to measures of the family environment. Developmental Psychology 30:32-43.
Reiss, D., Neiderhiser, J., Hetherington, E., and Plomin, R. (2000). The relationship code. Deciphering genetic and social influences on adolescent development. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Reiss, D., Pedersen, N., Cederblad, M., Lichtenstein, P., Elthammer, O., Neiderhiser, J., and Hansson, K. (2001a). Genetic probes of three theories of maternal adjustment II: Genetic and environmental influences. Family Process 40:261-272.
Reiss, D., Pedersen, N., Cederblad, M., Lichtenstein, P., Elthammer, O., Neiderhiser, J., and Hansson, K. (2001b). Genetic probes of three theories of maternal adjustment I: Recent evidence and a model. Family Process 40:247-259.
Rusting, C., and Larsen, R. (1998). Personality and cognitive processing of affective information. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 24:200-213.
Scarr, S. (1992). Developmental theories for the 1990s: Development and individual differences. Child Development 63:1-19.
Simpson, J., Rholes, W., and Nelligan, J. (1992). Support seeking and support giving within couples in an anxiety provoking situation: the role of attachment styles. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 62(3):443-446.
van de Boom, D. (1991). The influence of infant irritability on the development of the mother-infant relationship in the first six months of life. In J. Nugent, B., Lester, and B. TB (eds.), The cultural context of infancy Vol. 2), (pp. 63-89). Norwood, NJ: Ablex.
van den Boom, D. C. (1994). The influence of temperament and mothering on attachment and exploration: an experimental manipulation of sensitive responsiveness among lower-class mothers with irritable infants. Child. Dev. 65(5):1457-1477.
Wade, T. D., and Kendler, K. S. (2000). The genetic epidemiology of parental discipline. Psychol. Med. 30(6):1303-1313.
Wiklund, I., Gorkin, L., Pawitan, E., Schron, E., Schoenberger, J., Jared, L., and Schumaker, S. (1992). Methods for assessing quality of life in the Cardiac Arrythmia Suppression Trial (CAST). Quality of Life Research 1:187-201.
Zelenski, J. M., and Larsen, R. J. (1999). Susceptibility to affect: A comparison of three personality taxonomies. J. Pers. 67(5):761-791.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lichtenstein, P., Ganiban, J., Neiderhiser, J.M. et al. Remembered Parental Bonding in Adult Twins: Genetic and Environmental Influences. Behav Genet 33, 397–408 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025317409086
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025317409086