Abstract
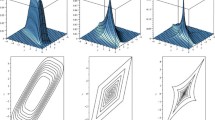
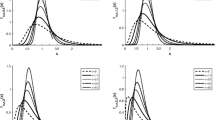
The paper introduces an approach to the ordering of dependence which is based on central regions. A d-variate probability distribution is described by a nested family of sets, called central regions. Those regions are affine equivariant, compact and starshaped and concentrate about a properly defined center. They can be seen as level sets of a depth function. Special cases are Mahalanobis, zonoid, and likelihood regions. A d-variate distribution is called more dependent than another one if the volume of each central region is smaller with the first distribution. This dependence order is characterized by an inequality between determinants of certain parameter matrices if either (i) F and G are arbitrary distributions and the central regions are Mahalanobis or (ii) F and G belong to an elliptical family of distributions and the central regions are arbitrary. If the regions are zonoid regions, the dependence order implies the ordering of lift zonoid volumes. Alternatively, the dependence order is applied to the copulae of the given distributions. Generalized correlation indices are proposed which are increasing with the dependence orders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Block, A. Sampson, and T. Savits, Topics in Statistical Dependence, Institute of Mathematical Statistics Hayward, California, 1990.
M. Dall'Aglio and M. Scarsini, “When Lorenz met Lyapunov,” Statistics and Probability Letters vol. 54 pp. 101—105, 2001.
S. Dharmadhikari and K. Joag-Dev, Unimodality, Convexity, and Applications, Academic Press: Boston, 1988.
R. Dyckerhoff, “Inference based on data depth, Chapter 5,” In Multivariate Dispersion, Central Regions and Depth: The Lift Zonoid Approach, K. Mosler, Springer: New York, 2002.
T. Hettmansperger, J. Möttönen, and H. Oja, “Affine invariant multivariate rank tests for several samples,” Statistica Sinica vol. 8 pp. 785—800, 1998.
H. Joe, Multivariate Models and Dependence Concepts, Chapman and Hall: London, 1997.
G. Koshevoy and K. Mosler, “Multivariate Gini indices,” Journal of Multivariate Analysis vol. 60 pp. 252—276, 1997a.
G. Koshevoy and K. Mosler, “Zonoid trimming for multivariate distributions,” Annals of Statistics vol. 25 pp. 1998—2017, 1997b.
R. Liu, J. M. Parelius, and K. Singh, “Multivariate analysis by data depth: Descriptive statistics, graphics and inference,” Annals of Statistics vol. 27 pp. 783—858, 1999, With discussion.
K. Mosler, Multivariate Dispersion, Central Regions and Depth: The Lift Zonoid Approach, Springer: New York, 2002.
A. Müller and D. Stoyan, Comparison Methods for Stochastic Models and Risks, John Wiley: New York, 2002.
H. Oja, “Affine invariant multivariate sign and rank tests and corresponding estimates,” Scandinavian Journal of Statistics vol. 26 pp. 319—343, 1999.
Y. Zuo and R. Serfling, “General notions of statistical depth function,” Annals of Statistics vol. 28 pp. 461—482, 2000a.
Y. Zuo and R. Serfling, “Nonparametric notions of multivariate ‘scatter measure’ and ‘more scattered’ based on statistical depth functions,” Journal of Multivariate Analysis vol. 75 pp. 62—78, 2000b.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mosler, K. Central Regions and Dependency. Methodology and Computing in Applied Probability 5, 5–21 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024144420002
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024144420002