Abstract
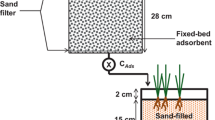
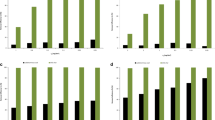
The removal and recovery of heavy metals from a coal pilerunoff water using a mixture of multiple metal-tolerantbacterial strains of ATCC 55673, and ATCC 55674 and a Pseudomonas sp. was investigated. The analysis of elementalcomposition of metal precipitates recovered from the bacterialbiomass by transmission electron microscopy and energy dispersiveX-ray analysis revealed the presence of metals originally presentin the wastewater. In addition, analysis of metals in culturesupernatant and bacterial biomass by inductively coupled plasmaemission spectroscopy (ICP-ES) indicated a removal range of 82-100% and a recovery of 15-58% of metals from the wastewater and bacterial biomass, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrechtsen, H. and Christensen, T.: 1994, 'Evidence for microbial iron reduction in a landfill leacheate-polluted aquifer', Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60, 3920-3925.
Allens, S., Allen, J. and Lucas, S.: 1996a, 'Concentration of contaminants in surface water samples collected in West Central Indiana impacted by acidic mine drainage', Environ. Geology. 27, 34-37.
Allen, J., Lucas, S. and Allen, S.: 1996b, 'Formation of hydroxy radical in illminated surface waters contaminated with acidic mine drainage', Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15. 107-113.
Baillet, F., Margnin, J., Cheruy, A. and Ozil, P.: 1998, 'Chromium precipitation by acidophilic bacterium Thiobacillus ferroxidans', Biotechn. Lett. 20, 95-99.
Brower, J., Ryan, R. and Paziraandeh, M.: 1997, 'Comparison of ion exchange resins and biosorbents for the removal of heavy metals from plating factory wastewater', Environ. Sci Technol. 31, 2910-2914.
Dressler, C., Kues, U., Nies, D. and Friedrich, B.: 1991, 'Determinants encoding resistance to several heavy metals in newly isolated copper-resistant bacteria', Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57, 3079-3085.
Ehrlich, H. L.: 1997, 'Microbes and metals', Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 48, 687-692.
Foos, A.: 1996, 'Geochemical modeling of coal mine drainage, Summit County, Ohio', Environ. Geol. 31, 205-210.
Faison, B., Cancel, C., Lewis, S. and Alders, H.: 1990, 'Binding of dissolved strontium by Micrococcus luteus', J. Appl. Environ. 56, 3649-3656.
Hu, M., Norman, J. and Faison, B.: 1996, 'Biosorption of uranium by Pseudomonas aeroginosa strain CSU: Characterization and comparison studies', Biotechnol. Bioeng. 51, 237-247.
Ibeanusi, V. and Wilde, E.: 1998, 'Bioremediation of coal pile run off waters using an integrated microbial ecosystem', Biotechnol. Lett. 11, 1077-1079.
Latinwo, L., Donald, C., Ikediobi, C. and Simon, S.: 1998, 'Effects of intracellular glutathione on sensitivity of Escherichia coli to mercury and arsenite', Biolog. Biophys. Res. Commun. 242, 67-70.
Levy, D., Cutis, W. and Rock, P.: 1997, 'The aqueous geochemistry of the abandoned spenceville copper pit, Nevada County, California', J. Environ. Quality. 26, 233-243.
Lovell, H.: 1983, 'Coal mine drainage in the United States-an overview', Wat. Sci Tech. 15, 1-25.
Lyew, D. and Sheppard, J.: 1997, 'Effects of physical parameters of a gravel bed on the activity of sulphate-reducing bacteria in the presence of acid mine drainage', J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 70, 223-230.
Masscheleyn, P., Delaune, R. and Patrick W.: 1991, 'Effects of redox potential and pH on arsenic speciation and solubility in a contaminated soil', Environ. Sci. Technol. 25, 1414-1419.
Streekrishnan, T. and Tyagi, R.: 1994, 'Heavy metal leaching sewage sludges: A techno-economic evaluation of the process options', Environ. Technol. 15, 531-543.
Strasser, H., Brunner, H. and Schinner, F.: 1995, 'Leaching of iron and toxic heavy metals from anaerobically-digested sewage sludge', J. Indust. Microbiol. 14, 281-287.
United States Environmental Protection Agency: 1991. 'Recovery of Metals from Sludge', EPA/600/82-91/041. Washington D.C.
Vinyard, G.: 1996, 'A chemical and biological assessment of water quality impacts from acid mine drainage in first order mountain stream and comparison of two bioassay techniques'. Environ. Technol. 17, 273-281.
Watson, J., Scott, C. and Faison, B.: 1990, 'Evaluation of a Cell-Biopolymer Sorbent for Uptake of Strontium from Dilute Solutions', in Emerging Technologies in Hazardous waste Management, pp. 172-184.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibeanusi, V.M., Phinney, D. & Thompson, M. Removal and Recovery of Metals From a Coal Pile Runoff. Environ Monit Assess 84, 35–44 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022822710687
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022822710687